
- 342 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
About this book
Towards Smart World: Homes to Cities Using Internet of Things provides an overview of basic concepts from the rising of machines and communication to IoT for making cities smart, real-time applications domains, related technologies, and their possible solutions for handling relevant challenges. This book highlights the utilization of IoT for making cities smart and its underlying technologies in real-time application areas such as emergency departments, intelligent traffic systems, indoor and outdoor securities, automotive industries, environmental monitoring, business entrepreneurship, facial recognition, and motion-based object detection.
Features
The book covers the challenging issues related to sensors, detection, and tracking of moving objects, and solutions to handle relevant challenges.
- It contains the most recent research analysis in the domain of communications, signal processing, and computing sciences for facilitating smart homes, buildings, environmental conditions, and cities.
- It presents the readers with practical approaches and future direction for using IoT in smart cities and discusses how it deals with human dynamics, the ecosystem, and social objects and their relation.
- It describes the latest technological advances in IoT and visual surveillance with their implementations.
This book is an ideal resource for IT professionals, researchers, undergraduate or postgraduate students, practitioners, and technology developers who are interested in gaining deeper knowledge and implementing IoT for smart cities, real-time applications areas, and technologies, and a possible set of solutions to handle relevant challenges.
Dr. Lavanya Sharma is an Assistant Professor in the Amity Institute of Information Technology at Amity University UP, Noida, India. She has been a recipient of several prestigious awards during her academic career. She is an active nationally recognized researcher who has published numerous papers in her field.
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
Part 1
1
The Rise of Internet of Things and Smart Cities
Noida, India
- 1.1The Emergence of the Smart City from the Traditional City
- 1.2Features of a Smart City and Its Components
- 1.2.1Smart Transportation
- 1.2.2Smart Energy Empowerment
- 1.2.3Smart Data
- 1.2.4Smart Networks and Connecting Devices
- 1.2.5Smart Quality of Life
- 1.3Smart City Architecture
- 1.3.1Goals, People, and the Ecosystem
- 1.3.2Soft Infrastructure
- 1.3.3Hard Infrastructure
- 1.4Smart City Tools and Technologies
- 1.4.1IoT and Big Data
- 1.4.2IOT and Computer Vision
- 1.4.3IoT and Remote Sensing
- 1.4.4IoT and Artificial Intelligence
- 1.4.5IoT and Machine Learning
- 1.4.6IoT and Fog Computing
- 1.5Conclusion
- References
1.1 The Emergence of the Smart City from the Traditional City
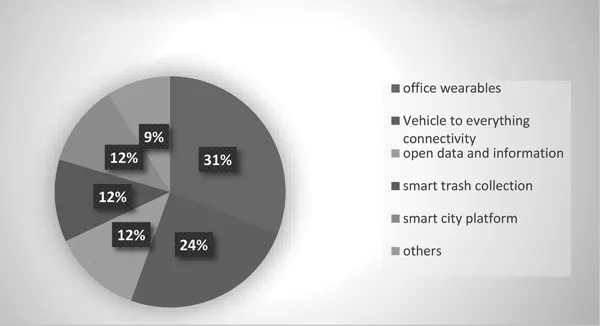
Global growth rate for smart cities (2017–2020) [5, 6].
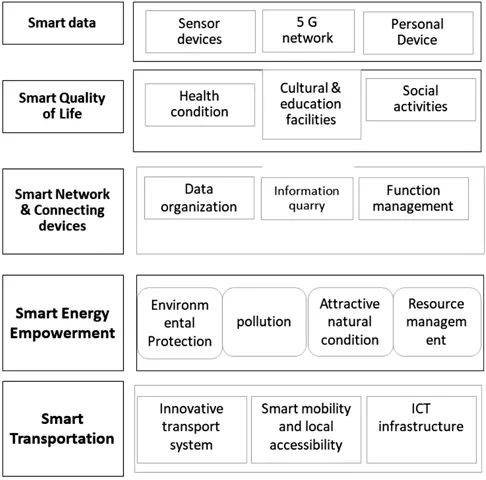
Features of a smart city and its components.
1.2 Features of a Smart City and Its Components
1.2.1 Smart Transportation
- Developing cities lag behind due to inadequate capacity to mobilize the large amount of funds that will be required to initiate the transport development projects.
- The rapid increase in population is one of the biggest challenging issues that has to be taken on a priority basis.
- Unlawful occupancy of automobiles on footpaths and bicycle traffic lanes is another important challenging issue.
1.2.2 Smart Energy Empowerment
1.2.3 Smart Data
Table of contents
- Cover
- Half Title
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Dedication
- Contents
- Preface
- Acknowledgments
- Editor Bio
- Contributors
- Part 1
- Part 2
- Part 3
- Part 4
- Index