
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
About this book
Learn a Programmer-Friendly language Key Features
- Strengthens the foundations, as a detailed explanation of programming language concepts are given in a simple manner
- Lists down all the important points that you need to know related to various topics in an organized manner
- Prepares you for coding related interview and theoretical questions
- Provides an in-depth explanation of complex topics and Questions
- It focuses on how to think logically to solve a problem
- Follows a systematic approach that will help you to prepare for an interview in a short duration of time
- Exercises are exceptionally useful to complete the reader's understanding of a topic
-
Description
Book will come as a relief to the students wishing to go through a comprehensive work explaining the programming concepts of Python. Examples are given with proper description, offering a variety of practical examples and conceptual problems along with their systematically worked out solutions. It also covers all the concepts which are helpful for the students and beginners to learn the basics of Python programming. What will you learn
This book is written, taking into consideration the skills required at the beginner level for understanding Python Programming Concepts. The book covers the practical examples of Python in an easy way so that students can able to understand efficiently. Who this book is for
Book promises to be a perfect starting point for beginners and an asset for those having insight towards programming. Table of Contents
1. Introduction
2. Conditions and Loops
3. Arrays and Functions
4. Lists, Tuples, Iterators and GeneratorsDictionaries and Modules
5. File Handling and Databases
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
CHAPTER 1
Introduction
Introduction
Python is an interpreted and object-oriented high-level programming language. It is designed by Guido Van Rossum and released in 1991. The latest version of Python is Python 3.7.3.
It is a scripting language like PHP, Perl, and Ruby. Python can also be translated into binary code like Java and is used in Math’s and Machine Learning.
Python Installation
Python can be installed in two ways:
- Download Python from its official website and manually install it. The programs can be compiled on the command prompt.
- Install Python by using Anaconda software, for this:
- First download the Anaconda Software (comes with Python Software along with built in libraries of Python).
- This software consists of two popular Integrated Development Environments (IDE) which are Jupyter notebook and Spyder shown in figure 1.1 and figure 1.2.
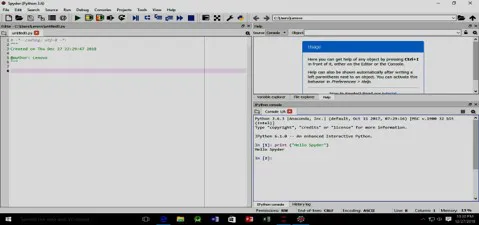
Figure 1.1: Spyder Environment Window
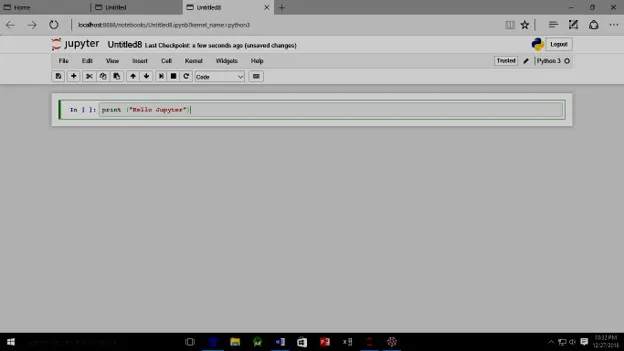
Figure 1.2: Jupyter Environment Window
Where Python can be explored?
Python can be explored to:
- create web applications
- connect to database systems
- handle big data
- machine learning algorithms
- develop predictive trends
- develop web applications with the help of Flask and Django modules
Python has a preinstalled library for machine learning, bigdata, artificial intelligence, natural language processing, and so on.
Note: Extension of Python is “.py”. Python uses indentation as its method of grouping statements. Therefore, in Python while writing programs, always take care of Indentation. If indentation error is there in conditions or loops, the error will prompt “unexpected indent”.
Steps to run the python programs on command line
Python program can be executed on the command line or through Python Shell as shown in figure 1.3(a) and figure 1.3(b). Python uses indentation to indicate a block of code.
- Create a simple program in a notepad as given below and save it in C:\ drive in the directory named “python” and file name is “begin.py”.
print (“Hello World”) - The python print statement is often used to output variables.
- Now, open the command terminal and change the current working directory to your directory where the above program is saved as shown in figure 1.3(a).
Example 1.1: Write a Program to print Hello World
print(“Hello World”) print(“Python is opensource”)The output of the Example 1.1 is shown in figure 1.3(a).
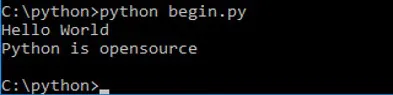
Figure 1.3(a): Window displaying python program output
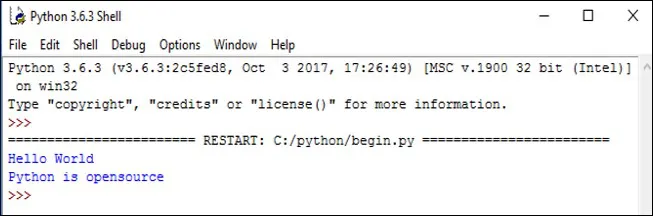
Figure 1.3(b): Output in Python Shell
Variable Declaration
Python has no command for declaring a variable. In Python, variables need not to be declared with any type and one can even change the type of variable after they have been set.
Note: The variable names are case-sensitive.
Get User Input in Python from Command Line
Example 1.2: To get the user input from the command line
name= input(“Enter yourname”)print(“Hello” + format(name))time=input(“Enterthe appointment time”)print(time)Note: Here input is used as a keyword. The format () function used in the program is a built-in function which returns the formatted representation of the given value i.e. it returns a formatted string.
The output of the Example 1.2 is shown in figure 1.4.
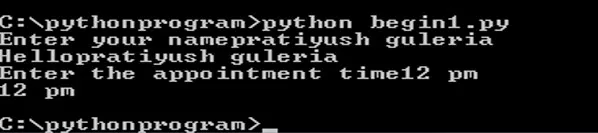
Figure 1.4: User input from the command line
Example 1.3: To add two numbers
a = input(“Enterthe first number”)print (“The value of a is” +format(a))b = input(“Enter the second number”)print(“The value of b is” + format(b))c = a + bprint (“The sum is:”+format(c))The output of the Example 1.3 is shown in figure 1.5.
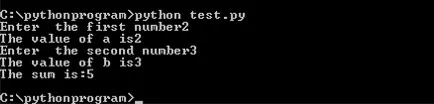
Figure 1.5: Addition of two numbers
Program 1.1: Write a program to swap two values
x=5y=10temp=xx=yy=tempprint (‘The value of x after swapping:{}’.format(x))print(‘The value of y after swapping:{}’.format(y))The output of the above Program 1.1 is shown in figure 1.6.

Figure 1.6: Swap two values
Operators in Python
Example 1.4: To perform arithmetic operations in Python
Save the file as: o1.py
In this example, a an...
Table of contents
- Cover Page
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- About the Author
- Acknowledgement
- Preface
- Errata
- Table of Contents
- 1. Introduction
- 2. Conditions and Loops
- 3. Arrays and Functions
- 4. Lists, Tuples, Iterators and Generators
- 5. Dictionaries and Modules
- 6. File Handling and Databases
- 7. Object-Oriented Programming
- 8. Regular Expressions, Date, and Time
- 9. Exception Handling
- Practice Exercise
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription
No, books cannot be downloaded as external files, such as PDFs, for use outside of Perlego. However, you can download books within the Perlego app for offline reading on mobile or tablet. Learn how to download books offline
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 990+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn about our mission
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more about Read Aloud
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS and Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Yes, you can access Basics of Python Programming by Dr. Pratiyush Guleria in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Computer Science & Programming in Python. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.