![]()
1
Introduction to Apparel Industry
The textile and fashion industry is a major contributor to several national economies, including both small- and large-scale processes globally. With concern to the employment as well as production, the textile sector is one of the prime industries in the world (Abernathy 2004). The garment sector is a labour-oriented one and provides enormous job opportunities at the entry level for unskilled labour in developed as well as developing nations. Further, it is a sector where comparatively modern technologies could be implemented even in poor countries at moderately low investment costs (Ashdown 1998).
The textile and clothing sector also has the high potential market segment for value added products where design and research and development (R&D) are key competitive factors. The luxury fashion industry utilises higher labour in design and marketing segments. The same applies to market sectors like sportswear where both design and material technology are vital (Ashdown 1998).
1.1 Structure of Textiles and Clothing Industry
The clothing industry is a labour-oriented, low wage industry but a vibrant, innovative sector, depending on the type of market segments upon which the industry focuses. The high-end fashion sector is considered modern technology, with comparatively well-paid workers and designers and a high degree of flexibility (Bailetti and Litva 1995).
The core operations of industries servicing this market sector are mostly situated in developed nations and often in certain geographical locations within these nations. The other kind of major market sector is bulk production of standard products like t-shirts, uniforms, underwear, etc. Manufacturers for this type of standard product market sector are mostly seen in developing countries (Abernathy 2004). For lower- to medium-priced products in the market, the responsibility of the retailer has become more and more important in the organisation of the supply chain. The retail market sector has turned out to be more intense, leaving more market power to multinational retailers (Ashdown 1998).
Textiles are responsible for the key raw material input to the garment industry, developing vertical supply chain relationships between the two containing sales and distribution functions (Bailetti and Litva 1995). The textile and clothing sectors involve
• Acquiring and processing raw materials, that is, the preparation and production of textile fibres.
• Manufacturing of textile yarns and fabrics.
• Dyeing and finishing of textile materials, which provide visual, physical and aesthetic properties that consumers demand, such as bleaching, printing, dyeing and coating.
• Conversion of textiles into garments that can be either fashion or functional garments.
1.1.1 Clothing
The fundamental manufacturing process of the apparel industry has not undergone much change over the past century, and is considered by the progressive bundle system. Work or operation is planned in a manner that each operator is specialised in one or a few operations (Ashdown 1998). The fabric is first cut into various garment panels and then grouped by components of the garment, tied into bundles and sent to an assembling (sewing) section for making a garment. An operator receives a bundle of cut garment panels and executes his or her single operation and keeps the bundle in a buffer. A buffer of about one day’s work is common at each operation. It takes about 40 operations to finish a pair of pants, which entails about 40 days of in-process inventory. Though numerous advances in the industrial engineering segment for systematising the operations and reducing the production time of each individual operation have taken place over a period of time, the basic method has remained the same (Ashdown 1998; Abernathy 2004).
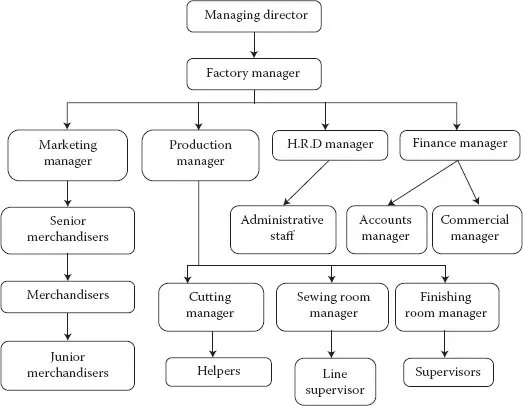
The new technologies, systems and innovations in the clothing sector have improved efficiency at each production stage and enhanced the harmonisation between stages and provided a more seamless interface between them (Bheda et al. 2003). The major breakthrough innovation was the use of computers in clothing manufacturing in areas like pattern making, marker planning and computerised automatic cutting machine. This machine has made it possible to cut increasingly thick layers of cloth accurately (Tyler 1992; Chuter 1995; Fairhurst 2008). These advancements are mainly associated with the preassembly phase of production, where technological developments have been more important than at the assembly stage. The organisation structure of a medium-sized garment industry is shown in Figure 1.1.
FIGURE 1.1
Organisation of an apparel industry.
1.1.2 Textiles
The textile business generally needs more investment compared to the garment sector and it is an extremely automated area. It comprises yarn manufacturing, fabric manufacturing and dyeing and finishing, and these three functions could be carried out in integrated plants. On the other hand, the textile sector suffers from the higher lead time as well as high investment cost, which results in relatively large minimum orders (Chuter 1995).
1.2 Various Departments in the Garment Industry
The various departments or sections in an apparel industry are given below.
1. Merchandising
2. Sampling department
3. Fabric sourcing
4. Purchasing department
5. Fabric inspection department
6. Accessory stores department
7. Planning department
8. Laboratory department
9. Machine maintenance
10. CAD section
11. Cutting section
12. Production department
13. Industrial engineering section (IE)
14. Embroidery department
15. Fabric washing section
16. Quality assurance department
17. Finishing department
1.2.1 Merchandising
It is a vital process that involves planning, developing, executing and dispatching the order (product) to the buyer. The merchandising process comprises guiding and supervising for the successful processing of an order. The types of merchandising done in a garment unit are marketing merchandising and product merchandising (Tyler 1992; Banumathi and Nasira 2012). The main objective of marketing merchandising is development of product, costing and ordering, and it has direct contact with the buyer. Product merchandising is carried out in the respective apparel unit and involves all the responsibilities starting from sourcing to finishing (Chuter 1995).
1.2.2 Sampling Department
The sampling department coordinates with the merchandising and production department. It is carried out to foresee finished product appearance and fit when produced in bulk and to confirm whether there are any inconsistencies in the pattern according to the buyer’s specification (Banumathi and Nasira 2012). It also aids to determine the fabric consumption along with that of thread and other accessories used.
1.2.3 Fabric Sourcing
Fabric sourcing is mainly engaged in deciding where and how the fabrics have to be procured. It works in conjunction with the merchandising department ...