
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in 2D/3D Medical Image Processing
- 196 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in 2D/3D Medical Image Processing
About this book
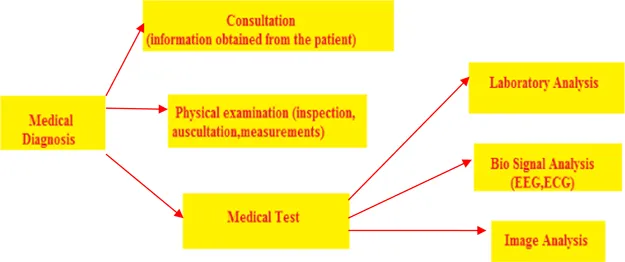
Digital images have several benefits, such as faster and inexpensive processing cost, easy storage and communication, immediate quality assessment, multiple copying while preserving quality, swift and economical reproduction, and adaptable manipulation. Digital medical images play a vital role in everyday life. Medical imaging is the process of producing visible images of inner structures of the body for scientific and medical study and treatment as well as a view of the function of interior tissues. This process pursues disorder identification and management.
Medical imaging in 2D and 3D includes many techniques and operations such as image gaining, storage, presentation, and communication. The 2D and 3D images can be processed in multiple dimensions. Depending on the requirement of a specific problem, one must identify various features of 2D or 3D images while applying suitable algorithms. These image processing techniques began in the 1960s and were used in such fields as space, clinical purposes, the arts, and television image improvement. In the 1970s, with the development of computer systems, the cost of image processing was reduced and processes became faster. In the 2000s, image processing became quicker, inexpensive, and simpler. In the 2020s, image processing has become a more accurate, more efficient, and self-learning technology.
This book highlights the framework of the robust and novel methods for medical image processing techniques in 2D and 3D. The chapters explore existing and emerging image challenges and opportunities in the medical field using various medical image processing techniques. The book discusses real-time applications for artificial intelligence and machine learning in medical image processing. The authors also discuss implementation strategies and future research directions for the design and application requirements of these systems.
This book will benefit researchers in the medical image processing field as well as those looking to promote the mutual understanding of researchers within different disciplines that incorporate AI and machine learning.
FEATURES
- Highlights the framework of robust and novel methods for medical image processing techniques
- Discusses implementation strategies and future research directions for the design and application requirements of medical imaging
- Examines real-time application needs
- Explores existing and emerging image challenges and opportunities in the medical field
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
| 1 | An Introduction to Medical Image Analysis in 3D |
CONTENTS
1.1 Introduction
1.2 Comparison Between 2D and 3D Techniques in Medical Imaging
1.3 Importance of 3D Medical Image
1.4 Medical Imaging Types and Modalities
Table of contents
- Cover
- Half Title
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Contents
- Preface
- Introduction
- Editors
- Contributors
- Chapter 1 An Introduction to Medical Image Analysis in 3D
- Chapter 2 Automated Epilepsy Seizure Detection from EEG Signals Using Deep CNN Model
- Chapter 3 Medical Image De-Noising Using Combined Bayes Shrink and Total Variation Techniques
- Chapter 4 Detection of Nodule and Lung Segmentation Using Local Gabor XOR Pattern in CT Images
- Chapter 5 Medical Image Fusion Using Adaptive Neuro Fuzzy Inference System
- Chapter 6 Medical Imaging in Healthcare Applications
- Chapter 7 Classification of Diabetic Retinopathy by Applying an Ensemble of Architectures
- Chapter 8 Compression of Clinical Images Using Different Wavelet Function
- Chapter 9 PSO-Based Optimized Machine Learning Algorithms for the Prediction of Alzheimer’s Disease
- Chapter 10 Parkinson’s Disease Detection Using Voice Measurements
- Chapter 11 Speech Impairment Using Hybrid Model of Machine Learning
- Chapter 12 Advanced Ensemble Machine Learning Model for Balanced BioAssays
- Chapter 13 Lung Segmentation and Nodule Detection in 3D Medical Images Using Convolution Neural Network
- Index
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app