
- 406 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Stimuli-Responsive Nanomedicine
About this book
The response to environmental and internal stimuli is one of the basic characteristics of living organisms. Inspired by this natural strategy and fast-developing nanotechnology and materials science, stimuli-responsive nanomedicine has emerged as an active and important field of nanomedicine.
This book offers a fundamental and comprehensive overview of stimuli-responsive nanomedicine and compiles and details the recent cutting-edge findings and most impressive achievements in biomedical applications, from a pharmaceutical science perspective, making it the first book of its kind in this field. By providing readers a broad and in-depth coverage of endogenous and exogenous stimuli as well as their applicable nanomedicines, this book is valuable for students, researchers, and educators in biomedical sciences or anyone interested in this burgeoning field.
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
Chapter 1
Overview of Stimuli-Responsive Nanomedicine
[email protected]
1.1 Introduction
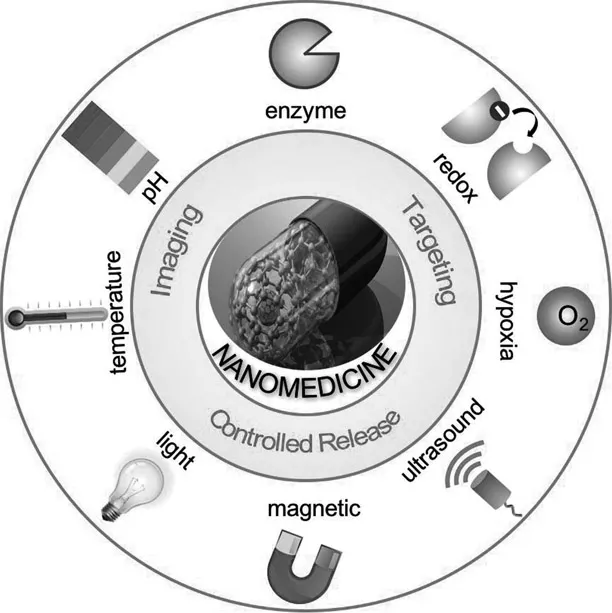
1.2 Typical Stimuli and Stimuli-Responsive Nanomedicines
1.2.1 Internal Stimuli and Stimuli-Responsive Nanomedicines
| Acting stimuli | Characteristics of stimuli | Responsive nanomaterials | Cargoes | Applications | Refs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | Gastric pH: 1.0-3.5; Small-intestinal pH: 7.5-8.0; Large-intestinal pH: 5.5-7.0. | Polysaccharide nanoparticles | Insulin | Oral delivery of insulin | [27] |
| | |||||
| Inflamed tissues (infarcted myocardium): pH6-7 | Hydrogel: p(NIPAAm-co-PAA-co-BA) | bFGF | Injection to the infarct zone | [28] | |
| | |||||
| Tumor extracellular pH: 6.5-7.2 | iNPG-pDOX | DOX | [29] | ||
| Liposomes: DSPE-KLA-DMA | PTX | Cancer chemotherapy | [30] | ||
| | |||||
| Enzyme | Upregulated tumoral MMPs | Liposomes: PEG-peptide-DOPE | Rh-PE | [31] | |
| Silica nanoparticles: MSN-SS-CD-peptide-PASP | DOX | Tumor-targeted drug delivery | [32] | ||
| | |||||
| Elevated proteolytic enzymes in inflamed tissues | Hydrogel: TGMS-TAC | Tacrolimus | Local injection of immunosuppressants | [33] | |
| | |||||
| Redox | In the tumor: | ||||
| Intracellular redox: 10 mM; | HA-ss-DOCA | PTX | Tumor targeting | [34] | |
| Extracellular redox: 2-10 μM | PAMAM-S-S-NAC | NAC | [35] | ||
| High ROS | PATK polyplexes | Plasmid DNA | [36] | ||
| | |||||
| Hypoxia | Low blood oxygen level in ischemic tissues | Water-soluble lipopolymer | pEpo-SV-VEGF plasmid | Ischemic myocardium targeting | [37] |
| | |||||
| Hypoxia in the solid tumor | Azobenzene nanoparticles | GFP siRNA | Tumor-targeted gene and drug delivery | [38] | |
| 2-nitroimidazole derivative | DOX | [22] | |||
1.2.1.1 pH-responsive nanomedicines
Table of contents
- Cover
- Half Title
- Series Page
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Contents
- Preface
- 1. Overview of Stimuli-Responsive Nanomedicine
- 2. pH-Responsive Nanomedicine for Image-Guided Drug Delivery
- 3. Enzyme-Responsive Nanomedicine
- 4. Redox-Responsive Nanomedicine
- 5. Hypoxia-Responsive Nanomedicines
- 6. Thermosensitive Nanomedicine
- 7. Magnetically Responsive Nanomedicine
- 8. Ultrasound-Responsive Nanomedicine
- 9. Light-Triggered Drug and Gene Delivery
- 10. Stimuli-Responsive Liposomes for Cancer
- 11. Stimuli-Responsive Nanomedicine for Treating Non-Cancer Diseases
- Index