![]()
Chapter 1
Introduction
1.1 Why a new textbook?
A traditional power system dynamics and control book covers synchronous generator models (steady-state and dynamics), generator voltage control, power system frequency control, and power system transient stability. A typical textbook is Bergen and Vittal’s book Power Systems Analysis (Chapters 6, 7, 8, 11, and 14). With today’s smart grid industry, the following aspects need to be added in teaching and in textbooks.
1. How to carry out demonstration for power system dynamics and control.
To address this task, dynamic simulation of ordinary differential equation-based models and further programming implementation in software environment such as MATLAB® or Python should be covered. This part is usually not found in a traditional textbook. Rather, students have to go to another course or read another book on computing to learn how to conduct validation and demonstration. In this text, tutorial examples on programming and dynamic simulation will be provided and students can quickly manage to conduct validation through coding or MATLAB/Simulink.
2. How to carry out control design.
Classic control methods such as the root locus method are repeatedly used in Bergen and Vittal (2009). In the 1980s, MATLAB and its control toolbox were not yet popular. Therefore, Bergen and Vittal (2009) did not present examples related to MATLAB codes. This textbook will provide MATLAB examples for control design problems.
3. How to better explain rotating machines.
Generator model derivation is the most sophisticated part in Bergen and Vittal (2009). In Bergen and Vittal (2009), Park’s transformation was employed to derive generator models. The alternative to Park’s transformation is space vector and complex vector transformation, a concept used much more often in machines and power electronics after the 1980s. The space vector concept makes Park’s transformation straightforward. In this textbook, the author will explain synchronous generator dynamics, the most formidable dynamics in power systems, using the space vector concept.
4. How are microgrids controlled?
In the traditional power system dynamics and control books, the focus is on synchronous generators. With the current industry where renewable energy, power electronics converters and microgrids arise, the related system-level dynamics and control should be covered. For example, when frequency control is discussed, it is very natural to extend the applications from large-scale power systems to microgrids where droop control is also used. Coverage on microgrid control is a highlight of this textbook.
In short, the aim of this textbook is to provide more insights using programming examples, state-of-the-art control design tools, and advanced control concepts to explain traditional power system dynamics and control. In addition, microgrid control will be covered as extended applications.
While reading this textbook, readers will get the chance of training in programming and control design. They will gain knowledge on dynamics and control in both synchronous generator-based power systems and power electronic converter enabled microgrids.
1.2 Structure of this book
The book is organized in eight chapters. The book has two main parts: control (frequency and voltage control) and dynamics (large-signal stability and small-signal stability). Before control problems are introduced, the validation tool: dynamic simulation, is examined in Chapter 2. Along with dynamic simulation, linear system analysis tools such as Bode plots, are also introduced.
There are four chapters related to control: Chapters 3-6. Frequency control and power sharing of synchronous generators are examined in Chapter 3. Electromechanical dynamics of a synchronous generator is considered while electromagnetic dynamics are not considered in Chapter 3. This treatment makes analysis concise with only critical dynamics included. After frequency control, voltage control is to be examined. To better explain voltage control, a detailed examination of a synchronous generator’s model with electromagnetic dynamics is required. Therefore, Chapter 4 focuses on the derivation of synchronous generator models using the space vector concept. Both steady-state and dynamic models are presented in Chapter 4. Chapter 5 presents voltage control of synchronous generator.
Chapter 6 covers converter control and power sharing among converters in a microgrid. The materials presented in Chapter 6 have never been found in any textbook on power system control and dynamics. Chapter 6 first presents a single voltage source converter’s control. Depending on its operation mode, a converter can either work in PQ control mode for grid-connected operation or in VF control mode for autonomous operation. With the fundamental control covered, droop control for power sharing among converters is then presented. This chapter gives many examples on control design and simulation-based validation.
Part II of the book focuses on dynamics. Two chapters are included. Chapter 7 focuses on large-signal stability. An example is transient stability of a synchronous generator. Chapter 8 focuses on small-signal stability. Three engineering problems are used as examples in this chapter: small-signal model derivation of a single-machine infinite-bus (SMIB) system for stability analysis, inter-area oscillation explanation using networked control theory, and torsional interactions in a synchronous generator. For each problem, linear system models are derived and linear system analyses are conducted.
This book provides many examples and tutorials to facilitate learning. Through the study of this book, readers can master the skill of linear system analysis and simulation-based validation. What’s more, this book builds a bridge between traditional synchronous generator-based large-scale power system control and converter-based microgrid control.
![]() Part I: Control
Part I: Control![]()
Chapter 2
Dynamic Simulation
2.1 Introduction
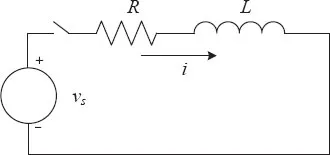
In this chapter, we will describe how to build validation testbeds for control and dynamic analysis using dynamic simulation or time-domain simulation. Take a simple RL circuit example shown in Figure 2.1. We would like to know the current i(t). The voltage source vs = VDC is assumed as known, e.g., 5 V. Initially, the circuit is open. Assume that at t0, the switch turns on. We first establish an ordinary differential equation (ODE) to describe the circuit model.
Figure 2.1: An RL circuit.
For a simple system described by (2.1), we can find a closed-form expression for i(t) using the ODE solving techniques from calculus.
The solution i(t) of (2.1) consists ...