
- 352 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
Introduction to the Bible
About this book
This book includes the true meaning of Inspiration, guidelines to understanding the Bible and the Chuch's role as the Bible's official interpreter. Also gives an introduction to each of the Bible's 72 books, with well-chosen Scriptural passages from most of the books that render a representative example of what they are like and about. First published in 1932, it is nevertheless not dated; the information contained here remains as valid as the traditional Catholic teaching it presents.
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription.
At the moment all of our mobile-responsive ePub books are available to download via the app. Most of our PDFs are also available to download and we're working on making the final remaining ones downloadable now. Learn more here.
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 1000+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn more here.
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more here.
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS or Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Yes, you can access Introduction to the Bible by Rev. Fr. John Laux, M.A. in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Theology & Religion & Christian Denominations. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.
Information
Topic
Theology & ReligionSubtopic
Christian DenominationsPART II
THE BOOKS OF THE OLD TESTAMENT
CHAPTER I
CHRONOLOGICAL TABLE OF THE BOOKS OF THE OLD TESTAMENT

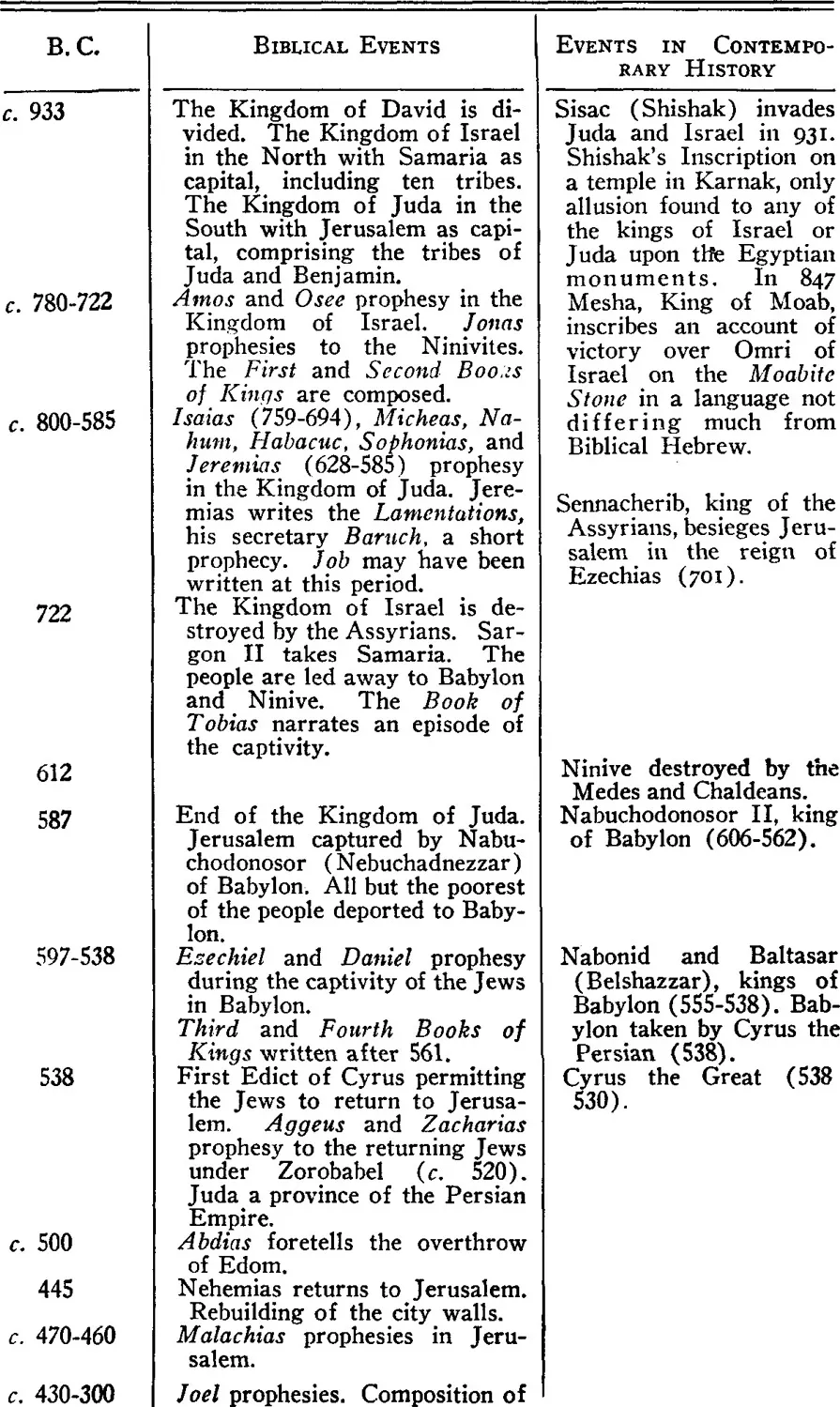
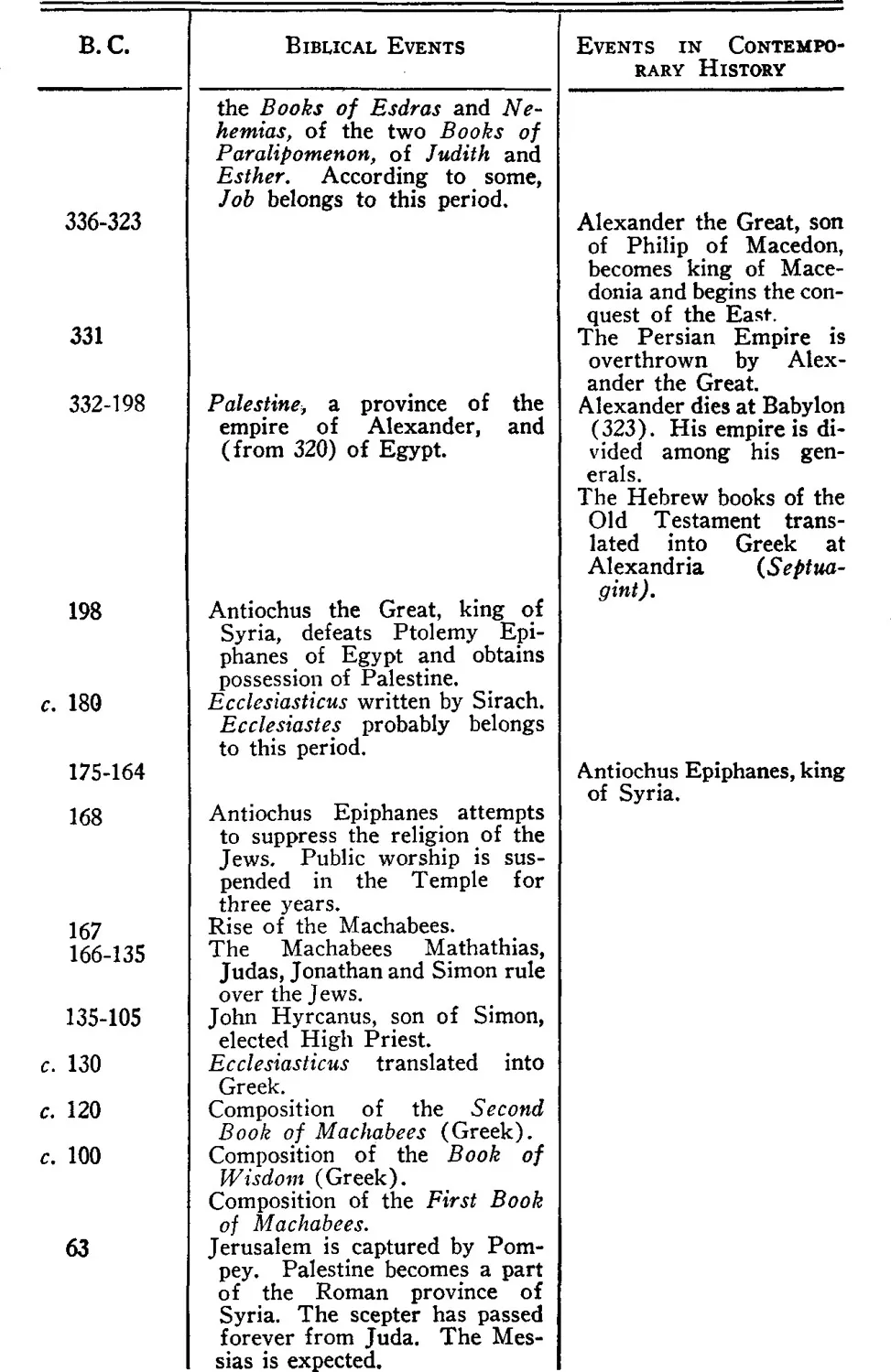
CHAPTER II
THE HISTORICAL CREDIBILITY AND INTEGRITY OF THE OLD TESTAMENT
1. The infallible teaching authority of the Church, "the pillar and ground of truth," guarantees the truthfulness and integrity of the Scriptures; guarantees, in other words, that the writers of the Bible books deserve our confidence, and that the text of their writings is at least substantially the same as it left their hands.
2. But the credibility and integrity of the Scriptures can also be proved scientifically, and successfully defended against the attacks of unbelievers.
The credibility and integrity of the books of the Old Testament rest on the testimony of the Sacred Writings themselves, as well as on the testimony of Jewish and Christian tradition.
a) From the Bible itself we learn the following facts about the various books of which it is composed:
Moses wrote the "words of the law and delivered it to the Levites to be put in the side of the Ark of the Covenant" (Deut. 31, 9-13; 24-26). Josue made additions to the "volume of the law of the Lord" (Jos. 24, 26). Samuel "wrote the law of the kingdom in a book, and laid it up before the Lord" (1 Kings 10, 25). The Prophets, e.g., Isaias, Jeremias, Ezechiel, wrote down prophecies and accounts of historical events and entrusted them to their disciples (Is. 8, 16; Ecclus. 49, 10; Dan. 9, 2; 2 Par. 26, 22). A collection of the writings of the Minor Prophets existed about 200 B.C. (Ecclus. 49, 12). The Psalms of David were used in public worship about 700 B.C. (2 Par. 29, 30). About 450 B.C. Esdras collected the Mosaic Law and read it to the people (2 Esd. 8). A little later, Nehemias collected the books of the Kings, of David, and of the Prophets into a library (2 Mach. 2, 13). During the last four centuries before Christ the deutero-canonical books were written and acknowledged as inspired by the Jews, and the whole Hebrew Bible was translated into Greek.
b) From all this it is clear that the Jewish authorities collected the Sacred Books, and hence regarded them as genuine. The Catholic Church received the Old Testament Books through Christ and His Apostles in the Greek Translation. The Church from the very beginning accepted the deutero-canonical books—though there were some Fathers who hesitated—as inspired. They were quoted by the earliest Fathers, and the Christians borrowed scenes from them (e.g., Daniel in the Lions' Den, the Story of Susanna) for the decoration of the catacombs. The Eastern Schismatic Church, as well as all the heretical sects that separated from the Church in the early centuries, agrees with the Catholic Church in regard to the inspiration of the books of the Old Testament.
"The Old Testament Scriptures," says a modern Biblical scholar, "are in no way a national self-glorification of the Jewish people. They faithfully report its defects and show no mercy to its aberrations. The Jews to this day keep the prophetic books of the Old Testament, although they are a witness against themselves. The Old Testament story, while setting forth the glorious mission of the chosen people of God and His extraordinary providence in its behalf, makes no secret of its changeable character, its unfaithfulness to God, its worldly spirit and cruel vindictiveness. The Jews have, then, no reason for retaining their Bible except the firm conviction of its authenticity and truthfulness" (Brüll-Messmer).
c) The integrity of the text of the Old Testament is proved by the fact that the Bible has always been jealously guarded by the Jews, who in their reverence for it have even counted the letters in each book. Furthermore, the oldest extant Hebrew Manuscript of the Old Testament (10th century A.D.) agrees substantially with the oldest extant Greek, Syriac, Samaritan, and other translations of the Old Testament, some of which were made a thousand years earlier.
d) For the truthfulness of the Old Testament we also have the testimony of Christ and His Apostles (Cf. John 5, 39; 5, 45-46; 19, 36; Luke 24, 44; 2 Tim. 3, 16; 2 Pet. 1, 21). Whoever accepts the New Testament must also accept the Old Testament on which it is based.
e) The history of the Old Testament is closely interwoven with the history of most of the great nations of ancient times. Still, no well-ascertained fact of profane history contradicts the sacred narrative. A few examples will show how, on the contrary, modern research has led to astonishing confirmations of many points in the sacred books:—
Isaias (20, 1) mentions an Assyrian king Sargon. Since no profane historian of antiquity knew of such a king, many modern critics relegated him to the realm of fable. Then in the latter half of the 19th century excavations at Ninive brought to light not only numerous inscriptions referring to him, but even his portrait.
In 3 Kings 14, 25 ff., an Egyptian King Sesac (Sheshonk) is mentioned as having invaded Palestine and plundered Jerusalem under Roboam, the successor of Solomon. His name was also unknown to profane history. In recent times, however, an inscription was found in Karnak in Egypt which confirmed almost word for word the Biblical account.
Babylonian inscriptions have proved the correctness of the account in 4 Kings 18, 14 ff., of Sennacherib's expedition to Jerusalem, and of his assassination on his return to Assyria.
According to ancient historians, Nabonidus was the last king of Babylon, whereas the Bible confers this honor on Baltassar (Belshazzar). The critics consequently declared the whole story related in Dan. 5 a myth. Then two documents, written on cylinders of clay, were found in the ruins of Babylon, in which Nabonidus speaks of his first-born son "Balsarussur"; in another document reference is made to the reign of Balsarussur. Daniel's story was no myth, after all, but sober history.
The striking similarities between certain Old Testament narratives and a number of Babylonian stories—the Creation, the Fall, the Deluge, etc., have given rise to long and bitter controversies. Special emphasis is laid by the opponents of Revelation and Inspiration on the many resemblances between the Code of Hammurabi, a contemporary of Abraham, and the Mosaic Law. These facts would militate against the authority of the Bible only if we had to hold that the entire text of the Bible was revealed or dictated by God. But Revelation is not the same as Inspiration. We know from the Bible itself that the sacred writers made use of both oral and written sources. By His special guidance God enabled them to use these sources without error. Hence if the sacred writers did draw on the Babylonian writings for their knowledge, God enlightened them to select only what was true. As a matter of fact the Babylonian narratives are full of foolish and immoral polytheistic fables, whereas the Bible is strictly monotheistic and inculcates doctrines of the highest ethical value. However, it is more probable that the Babylonian as well as the Biblical accounts are derived from a common source, viz., primitive tradition—preserved intact in the Bible, and debased and distorted in the Babylonian documents.
Though the religion of the Old Testament is purely monotheistic, still the conception of God, especially of His holiness and justice, His goodness and mercy, developed from age to age, had reached its culmination in the Psalms and the Prophets. God's revelation of Himself was gradual, and was completed only in the New Testament. Hence the superiority of the New Testament over the Old Testament.
CHAPTER III
...Table of contents
- Cover Page
- Copyright Page
- PREFACE
- PREFACE TO TEACHER
- CONTENTS
- PART IGeneral Introduction to the Bible
- PART IIThe Books of the Old Testament
- PART IIIThe New Testament
- APPENDIX: CHRONOLOGICAL TABLE OF THE BOOKS OF THE NEW TESTAMENT