
Blockchain for Business
How it Works and Creates Value
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Blockchain for Business
How it Works and Creates Value
About this book
The book focuses on the power of business blockchain. It gives an overview of blockchain in traditional business, marketing, accounting and business intelligence. The book provides a detailed working knowedge of blockchain, user cases of blockchain in business, cryptocurrency and Initial Coin Offering(ICO) along with the risks associated with them. The book also covers the detailed study of decentralization, mining, consensus, smart contracts, concepts and working of distributed ledgers and hyper ledgers as well as many other important concepts. It also details the security and privacy aspects of blockchain.
The book is beneficial for readers who are preparing for their business careers, those who are working with small scale businesses and startups, and helpful for business executives, managers, entrepreneurs, bankers, government officials and legal professionals who are looking to blockchain for secure financial transactions. The book will also be beneficial for researchers and students who want to study the latest developments of blockchain.
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
1
Introduction to Blockchain
1.1 Introduction
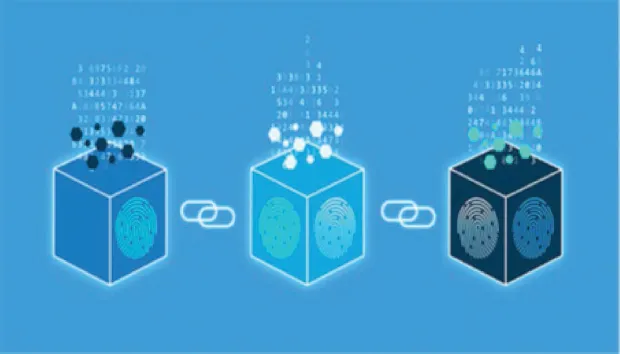
- Immutable—Making the ledge secures with the digital signature or hash function.
- POW—Proof of work, which is a protocol which has the main goal to deterring the cyber attacks.
- Hash—It is unique value being assigned by the set of rules/algorithms/functions or the combination of all to make the ledger unique and separated from other blocks.
- Digital Signature—It is another means of securing measure of the ledge, so that the data must be verified and treated as authentic.
- Mining—Mining in general an activity to collect the useful out of whole.
Table of contents
- Cover
- Table of Contents
- Title page
- Copyright
- Preface
- 1 Introduction to Blockchain
- 2 The Scope for Blockchain Ecosystem
- 3 Business Use Cases of Blockchain Technology
- 4 Ethereum
- 5 E-Wallet
- 6 Blockchain and Governance: Theory, Applications and Challenges
- 7 Blockchain-Based Identity Management
- 8 Blockchain & IoT: A Paradigm Shift for Supply Chain Management
- 9 Blockchain-Enabled Supply Chain Management System
- 10 Security Concerns of Blockchain
- 11 Acceptance and Adoption of Blockchain Technology: An Examination of the Security & Privacy Challenges
- 12 Deficiencies in Blockchain Technology and Potential Augmentation in Cyber Security
- 13 Internet of Things and Blockchain
- 14 Blockchain Applications
- 15 Advance Concepts of Blockchain
- Index
- End User License Agreement