
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
About this book
Discover a comprehensive overview of efficient synthetic routes to an important compound class in organic and pharmaceutical chemistry
Methodologies in Amine Synthesis: Challenges and Applications delivers powerful and state-of-the-art methods for the efficient preparation of amines. The text summarizes recent advances in the electrophilic amination reaction, hydroamination, C-H amination and newly developed photocatalytic approaches. The distinguished editor has included resources that discuss organocatalytic and enzymatic routes to the generation of amines under mild and environmentally friendly conditions.
The book also highlights the relevance of the amino function in bioactive molecules, drugs, and smart materials, as well as the palladium-catalyzed aromatic amination reaction. It presents efficient and practical synthetic methods, highlights the opportunities and challenges associated with each, and discusses their possible applications in pharmaceutical chemistry and materials science.
Edited by the expert who wrote Modern Amination Methods and Amino Group Chemistry, the book includes a breadth and depth of material essential to the practice of academic and industrial chemists working in organic synthesis and catalysis. Readers will also benefit from the inclusion of:
- A thorough introduction to new openings and perspectives in the electrophilic amination
- Discussions of asymmetric catalysed hydroaminomethylation and amino organocatalysis
- A treatment of the synthetic application of transaminase or MAO biocatalysis to the synthesis of amines
- An exploration of recent developments in C-H amination, as well as photocatalytic approaches to the synthesis of amines
- An examination of primary amines from renewable bio-based resources
Perfect for organic, natural product, catalytic, medicinal, and polymer chemists, Methodologies in Amine Synthesis: Challenges and Applications will also earn a place in the libraries of materials scientists and chemists working with organometallics who desire a one-stop reference edited by a well-known expert in the field.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
1
Substitution‐type Electrophilic Amination Using Hydroxylamine‐Derived Reagents
1.1 Introduction
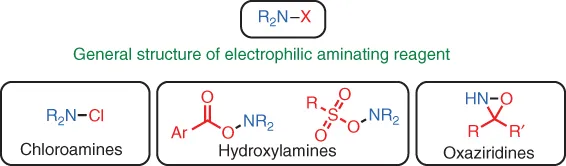
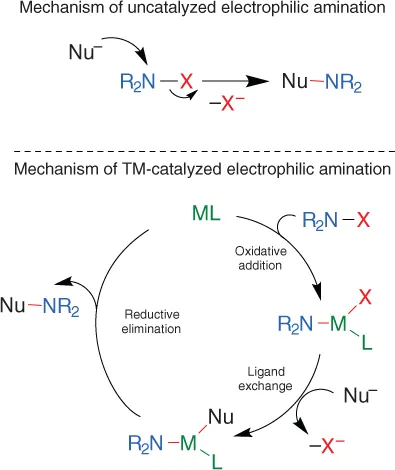
1.2 Cu‐Catalyzed Reactions
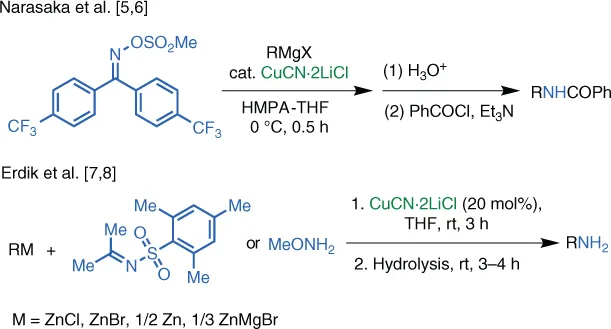
Table of contents
- Cover
- Table of Contents
- Title Page
- Copyright
- Preface
- 1 Substitution‐type Electrophilic Amination Using Hydroxylamine‐Derived Reagents
- 2 Remote Functionalizations Using Nitrogen Radicals in H‐Atom Transfer (HAT) Reactions
- 3 Radical‐Based C—N Bond Formation in Photo/Electrochemistry
- 4 Propargylamines: Recent Advances in Asymmetric Synthesis and Use as Chemical Tools in Organic Chemistry
- 5 Transition‐Metal‐Catalyzed Chiral Amines Synthesis
- 6 Industrial Relevance of Asymmetric Organocatalysis in the Preparation of Chiral Amine Derivatives
- 7 Biocatalytic Synthesis of Chiral Amines Using Oxidoreductases
- 8 Engineering Functional Nanomaterials Through the Amino Group
- 9 Recent Advances in the Synthesis of Nitrogen Compounds from Biomass Derivatives
- 10 Recent Advances in the Synthesis of Arylamines in the Light of Application in Pharmaceutical and Chemical Industry
- Index
- End User License Agreement
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app