
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Fundamentals of physics
About this book
This book aims to provide solid bases for the study of physics for the university and it is divided into four parts, each dedicated to a fundamental branch of physics: quantum mechanics, theoretical physics, particle physics and condensed matter physics. In the first part we start with the concept of wave function, until the Heisenberg uncertainty principle. In the second part, after recalling the basic concepts of relativity, we treat the elementary particles and the hadrons, arriving to the notions of scattering and cross section. The third part is dedicated to the theoretical physics, where we analyze the field theory and the concepts of Lagrangian and Hamiltonian, introducing the quantum electrodynamics (QED), passing through the Klein-Gordon, Dirac and Maxwell fields. In the last part of the book we expose the basics of the condensed matter physics, including diffusion and Brownian motion, Drude and Sommerfeld models, the calculation of specific heat and the principal mechanical properties of solids, with references to lattice defects and semiconductors.
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
Part I
Quantum Mechanics
Introduction
The wave function
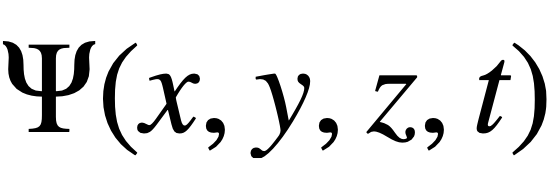
Table of contents
- Contents
- Introduction
- Part I
- Quantum Mechanics
- Introduction
- The wave function
- The Schrödinger equation
- Wave packets
- Normalization
- Fourier transform
- Expectation value
- Operators
- Commutation relations
- Uncertainty principle
- Eigenvalue equations
- Part II
- Particle Physics
- Introduction
- Natural units
- Bases of relativity
- Particles
- Energy loss
- Quantum numbers and symmetries
- Scattering and decays
- Part III
- Theoretical Physics
- Introduction
- Lagrangian and Hamiltonian
- Symmetries and gauge invariance
- Campo di Klein-Gordon
- The electromagnetic field
- The Dirac field
- Quantum electrodynamics
- Part IV
- Condensed Matter Physics
- Introduction
- Brownian motion and diffusion
- Drude model
- Sommerfeld model
- Mechanical properties of solids
- Lattice defects
- Semiconductors