
eBook - ePub
Big Data Hadoop Interview Guide
Get answers to the most frequently asked questions in a Hadoop interview (English Edition)
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
Big Data Hadoop Interview Guide
Get answers to the most frequently asked questions in a Hadoop interview (English Edition)
About this book
A power-packed guide with solutions to crack a Big data Hadoop Interview Key Features
- Get familiar with Big data concepts
- Understand the working of Hadoop and its ecosystem.
- Understand the working of HBase, Pig, Hive, Flume, Sqoop and Spark
- Understand the capabilities of Big data including Hadoop and HDFS
- Up and running with how to perform speedy data processing using Apache Spark
-
Description
This book prepares you for Big data interviews w.r.t. Hadoop system and its ecosystems such as HBase, Pig, Hive, Flume, Sqoop, and Spark. Over the last few years, there is a rise in demand for Big Data Scientists/Analysts throughout the globe. Data Analysis and Interpretation have become very important lately The book covers many interview questions and the best possible ways to answer them. Along with the answers, you will come across real-world examples that will help you understand the concepts of Big Data. The book is divided into various sections to make it easy for you to remember and associate it with the questions asked. What you will learn
- Apache Pig interview questions and answers
- HBase and Hive interview questions and answers
- Apache Sqoop interview questions and answers
- Apache Flume interview questions and answers
- Apache Spark interview questions and answers
-
Who this book is for
This book is for anyone interested in big data. It is also useful for all jobseekers and freshers who wants to drive their career in the field of Big Data and Data Processing. Table of Contents
1. Big data, Hadoop and HDFS interview questions
2. Apache PIG interview questions
3. Hive interview questions
4. Hbase interview questions
5. Apache Sqoop interview questions
6. Apache Flume interview questions
7. Apache Spark interview questions About the Authors
Vishwanathan Narayanan is an extreme programmer in various technologies, including Java, Python, and R, and he has around 18 years of experience in the field of information technology and data science. Exposure to real-world data science and advanced analytics using big data technologies gives him a great advantage, which he tries to impart through his books. A passionate teacher, he likes writing books as a hobby.
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription.
At the moment all of our mobile-responsive ePub books are available to download via the app. Most of our PDFs are also available to download and we're working on making the final remaining ones downloadable now. Learn more here.
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 1000+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn more here.
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more here.
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS or Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Yes, you can access Big Data Hadoop Interview Guide by Vishwanathan Narayanan in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Computer Science & Data Processing. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.
Information
SECTION 1
Big Data, Hadoop, and HDFS
Learning objectives
In this session, we will cover:
- Conceptual questions related to big data
- Basic to advanced level questions on Hadoop, HDFS, and Map reduce algorithms
Let’s start!
- What is the big data paradigm? How is it different from the earlier paradigm? Ans. As the name suggests, Big data deals with a large amount of data that cannot be handled by a conventional paradigm. Big data provides an efficient way of storing and processing structured and unstructured data. The difference from the earlier ones is shown by the following properties:
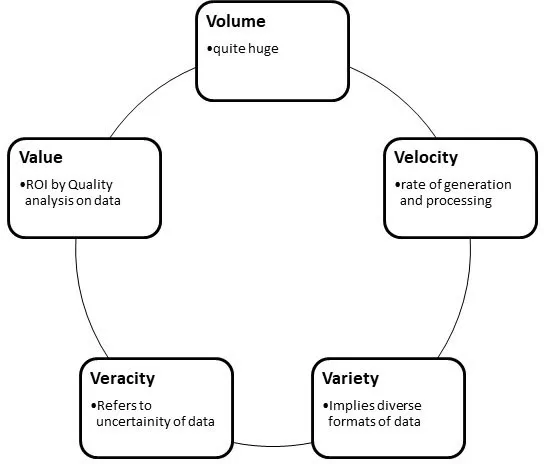 Figure 1.1: 5 V’s of big data
Figure 1.1: 5 V’s of big data - Does it imply that the use of RDBMS will go away with the advent of Big data? Justify. Ans. The answer is no. The use case of RDMS, which is a relational database, and the use case of big data are different. Basically, RDBMS is preferred for transaction-based processing, which is also known as OLTP, while big data is preferred for analytical processing.
- Can you compare big data and RDBMS? Ans. Here’s the comparison:Big dataRDBMSDeals with a very high volume of data in PetabytesDeals with the volume of data which is less than Big data in TerabytesRead many times but write onceRead and write multiple timesData can be structured or unstructuredData is structuredSince the nature of data changes, the schema is more dynamicSince the nature of data is fixed, the schema is staticIntegrity is low as compared to RDBMSIntegrity is high since it follows RDBMSScaling is linear in natureScaling is non-linear in natureTable 1.1: Difference between Big data and RDBMS
- What is the difference between structured and unstructured data? Ans. Here’s the difference between structured and unstructured data:StructuredUnstructuredThe major data format is text, which can be string or numeric. The date is also supported.The data format can be anything from text to images, audios to videos.The data model is fixed before inserting the data.The data model cannot be fixed since the nature of data can change. Consider a tweet message that could be text followed by images and audio.Data is stored in the form of a table, making it easy to search.Data is not stored in the form of a table.Not easy to scale.Very easy to scale.Version is maintained as a column in the table.Versioning is at an entire level.Transaction management and concurrency are easy to support.Transaction management and concurrency are difficult to support.Table 1.2: Difference between structured vs. unstructured data
- What is semi-structured data? Ans. Semi structure data falls between structured and unstructured data, and XML and JSON are the best examples.Sample XML example:
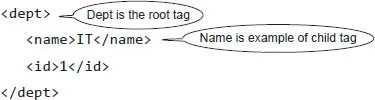 Sample JSON:
Sample JSON: Here, we can clearly see that the schema is part of the data itself and is less rigid, so we can easily add new data into it. Since the schema is part of data, it is called self-describing.Query processing on semi-structured data is a bit slow as compared to RDBMS.
Here, we can clearly see that the schema is part of the data itself and is less rigid, so we can easily add new data into it. Since the schema is part of data, it is called self-describing.Query processing on semi-structured data is a bit slow as compared to RDBMS. - What is the relation between Hadoop and Big data? Ans. Hadoop is a framework that implements Big data features. It allows storing data that can be huge and allows processing it over commodity type servers as compared to costly, heavy servers.
- What is the cluster with respect to Hadoop? Ans. Clusters, in general terms, are collections of various computers that are connected to each other for processing. With respect to Hadoop, clusters are on commodity servers over which data is stored, and the processing algorithms of Hadoop work on it.
- What is the commodity server? Ans. They are also known as off-shell servers that are low-cost servers and easily available, and they can also be easily replaced. One of the advantages of Hadoop is that it can be easily deployed on commodity servers, and there is no demand for high-performing or expensive servers.
- What is MapReduce algorithm? Ans. MapReduce algorithm can be called a programming pattern or design pattern that is widely adopted in processing very big datasets. It works on clusters and parallelly. This algorithm performs two major operations, namely,
Map, which makes the input data into key-value pairs and Reduce, which combines the data output from Map into a smaller set of output.For example: Consider a population dataset consisting of various details of the population from various areas. Let's say we need to find the count of total males and females. This can be achieved using the map and reduce algorithm (Pending). - Describe the advantages of the Map reduce algorithm? Ans.The following are the advantages of Map reduce algorithm:
- Scalability: Scalability can be easily achieved by increasing the number of commodity servers.
- Parallel processing: The nature of map reduce algorithm is to divide and conquer, so it supports parallel operations, improving speed.
- Availability: Since the data is stored in more than one node, it enhances availability.
The following image illustrates this: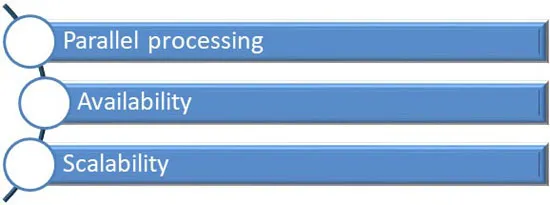 Figure 1.2: Advantages of MapReduce
Figure 1.2: Advantages of MapReduce - What forms the core components of Hadoop? Ans. Hadoop can be divided into two major components: storage, which is generally implemented using nodes of HDFS, and the processing unit, which is implemented using YARN.
- What is HDFS? Ans. Hadoop Distributed File System is also known as HDFS and represents the storage portion of Hadoop.
- What are the components of HDFS? Ans. Two nodes are the important components of HDFS.Name node:
- Also called master node
- Stores information of all other nodes
- Data is stored in the form of blocks on slave nodes, and the metadata information is stored in the Name node
Data node:- Also called slave node
- Responsible for storing blocks of data
- Coordinates with the master node
- What is the concept of t...
Table of contents
- Cover Page
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Dedication Page
- About the Author
- About the Reviewer
- Acknowledgement
- Preface
- Errata
- Table of Contents
- 1. Big Data, Hadoop, and HDFS
- 2. Apache PIG
- 3. Hive Interview Questions
- 4. Hbase
- 5. Apache Sqoop
- 6. Apache Flume
- 7. Apache Spark