
Introduction to Industrial Internet of Things and Industry 4.0
- 370 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Introduction to Industrial Internet of Things and Industry 4.0
About this book
Industrial IoT (IIoT) and Industry 4.0 are newly developing and fast emerging domains of interest among students, researchers, and professionals in academia and industry. Due to the popular demand of this topic, Introduction to Industrial Internet of Things and Industry 4.0 is written to serve a diverse readership from the domains of computer science and engineering, mechanical engineering, information technology, industrial engineering, electronics engineering, and other related branches of engineering. Based on the lead author's massive open online courses (MOOCs), this book can be used as a textbook on the emerging paradigm of Industry 4.0 and IIoT, as well as a reference for professionals working in sectors of IIoT.
The book covers the significant aspects of IIoT in detail, including sensors, actuators, data transmission, and data acquisition, which form the core of IIoT. Topics and concepts are presented in a comprehensive manner, so that readers can develop expertise and knowledge. The book helps beginners to gain a basic idea of Industry 4.0 and IIoT as the first section is an overview of IoT applications, infrastructure-based protocols, cloud computing, and fog computing. The second section is designed to impart a basic knowledge of Industry 4.0 and IIoT as well as of the different phases of development in industry. Delving into more advanced areas, other sections in the book cover:
- The business models and reference architecture of IIoT
- The technological aspects of Industry 4.0 and IIoT
- Predictive and prescriptive analytics applied in IIoT-based implementations
- Applications and case studies of IIoT
- Key enabling technologies of IIoT
To aid students and professional master IIoT and Industry 4.0, the book includes conceptual questions, exercises, and learning objectives.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
1
Overview of Internet of Things
- This chapter covers the basics of the Internet of Things (IoT), architecture, and its protocols.
- New readers will be able to have an understanding of the basic protocols of IoT, which will help them to grasp the concepts of the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT).
- Additionally, the readers will get a flavor of cloud computing, fog computing, and big data technology.
- For seasoned learners, this chapter will ease the revision of their exixting knowledge.
- The reasons for the shift of technology from the traditional methods to cloud, mobile cloud, and fog computing are outlined.
- The concept of providing physical sensor nodes as service on-demand is also outlined in this chapter.
1.2 Introduction
1.3 IoT Architecture
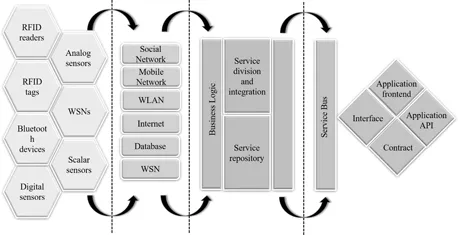
- Sensing layer: The sensing layer consists of IoT devices that are equipped with sensor nodes, Bluetooth devices, scalar sensors, analog sensors, digital sensors, and RFID tags as outlined in Fig. 1.2. The sensor nodes sense, process the sensed information, transmit the real-time information, and communicate among themselves. Moreover, these sensor nodes consume low power and require low data-rate connectivity. They form a Wireless Sensor Network (WSN) among themselves. Based on the application type, these sensor nodes are grouped. Each of the IoT devices has a Universal Unique Identifier (UUID).
- Networking layer: The networking layer helps the IoT devices to share information with other devices. Additionally, this layer handles the colossal amount of data generated by these IoT devices. Certain QoS requirements should be fulfilled to retain communication among these heterogeneous devices. Concerning Fig. 1.2, the networking layer consists of Social Networks, Mobile Networks, WLAN, Internet, Databases, and WSNs. Therefore, the design issues to be kept under primary considerations are latency, scalability, bandwidth requirements, energy efficiency, security, and privacy.
- Service layer: The service layer consistently integrates the services and applications in IoT. This layer executes the overall workflow process, which includes information exchanges, communication, storage, and data management. Additionally, various forms of predictive analytics are performed in this service layer. Further, this layer also maintains trust and utilizes the information extended by the other services.
- Interface layer: The heterogeneous IoT devices do not always follow the same IoT protocol. Due to the presence of various types of IoT devices, problems in interaction exist among these devices. In addition to this, with the rapid increase in IoT devices, it becomes quite difficult to connect, communicate, and operate these devices dynamically. Therefore, an interface layer is essential, which can systematically streamline the management and interconnection among things. For example, a call center operator who can communicate only in English and Chinese receives a call in Spanish. If the received call is not interpreted dynamically, the operator will fail to make sense of the ensuing communication. Therefore, there must be a common language for communication between them.
1.4 Application-based IoT Protocols
- Rapid growth in the number and heterogeneous IoT devices.
- Management of the IoT devices.
- Standardization of protocols within the network.
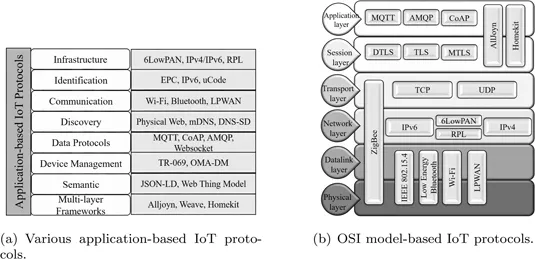
1.4.1 Infrastructure-based protocols
- 6LowPAN: This is a low-power Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6)-based technology for packet delivery in Wireless Personal Area Networks. 6LowPAN allows low-power devices with limited processing power to be connected over The Int...
Table of contents
- Cover
- Half Title
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Dedication
- Contents
- Foreword
- Author Biographies
- Preface
- Endorsements
- 1 Overview of Internet of Things
- 2 Overview of Industry 4.0 and Industrial Internet of Things
- 3 Industry 4.0: Basics
- 4 Industrial Internet of Things: Basics
- 5 Business Models and Reference Architecture of IIoT
- 6 Key Technologies: Off-site Technologies
- 7 Key Technologies: On-site Technologies
- 8 Sensors
- 9 Actuators
- 10 Industrial Data Transmission
- 11 Industrial Data Acquisition
- 12 Introduction to IIoT Analytics
- 13 Machine Learning and Data Science in Industries
- 14 Healthcare Applications in Industries
- 15 Inventory Management and Quality Control
- 16 Plant Safety and Security
- 17 Case Studies
- 18 Test Your Understanding
- References
- Index
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app