
Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) Attacks
Classification, Attacks, Challenges and Countermeasures
- 124 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) Attacks
Classification, Attacks, Challenges and Countermeasures
About this book
The complexity and severity of the Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks are increasing day-by-day. The Internet has a highly inconsistent structure in terms of resource distribution. Numerous technical solutions are available, but those involving economic aspects have not been given much consideration. The book, DDoS Attacks – Classification, Attacks, Challenges, and Countermeasures, provides an overview of both types of defensive solutions proposed so far, exploring different dimensions that would mitigate the DDoS effectively and show the implications associated with them.
Features:
- Covers topics that describe taxonomies of the DDoS attacks in detail, recent trends and classification of defensive mechanisms on the basis of deployment location, the types of defensive action, and the solutions offering economic incentives.
- Introduces chapters discussing the various types of DDoS attack associated with different layers of security, an attacker's motivations, and the importance of incentives and liabilities in any defensive solution.
- Illustrates the role of fair resource-allocation schemes, separate payment mechanisms for attackers and legitimate users, negotiation models on cost and types of resources, and risk assessments and transfer mechanisms.
DDoS Attacks – Classification, Attacks, Challenges, and Countermeasures is designed for the readers who have an interest in the cybersecurity domain, including students and researchers who are exploring different dimensions associated with the DDoS attack, developers and security professionals who are focusing on developing defensive schemes and applications for detecting or mitigating the DDoS attacks, and faculty members across different universities.
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
Fundamentals of DDoS Attack: Evolution and Challenges1
1.1 DDoS ATTACK: FUNDAMENTALS
1.1.1 Statistics and Recent Trends
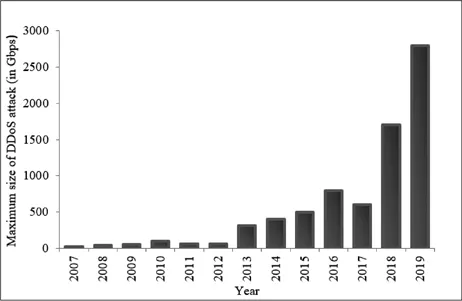
Table of contents
- Cover
- Half Title
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Dedication
- Contents
- Preface
- Acknowledgements
- About the Authors
- 1 Fundamentals of DDoS Attack: Evolution and Challenges
- 2 Role of Incentives, Liabilities, and Cyber Insurance
- 3 Taxonomy of DDoS Defence Mechanisms
- 4 Taxonomy of Economical Solutions
- 5 DDoS Attacks on Various Platforms
- 6 Emerging Solutions for DDoS Attack: Based on SDN and Blockchain Technologies
- Index