
- 353 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
About this book
The book presents basic and advanced concepts of circularly polarized antennas, including design procedure and recent applications. Cross dipole antennas, microstrip antennas, helical antennas, quadrifilar helix antennas, frequency independent antennas, horn antennas, omnidirectional circularly polarized antennas and radial line arry antennas are discussed. With abundant examples, the book is an essential reference for researchers and engineers.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
Chapter 1 Parameters of antennae
An antenna is an energy convertor in the radio equipment that converts bound circuit fields into propagating electromagnetic waves from the transmitter or converts propagating electromagnetic waves into bound circuit fields to the receiver. With the development of wireless technology, antennae find wider use. The performances of many wireless systems are mainly limited by antennae. The antenna requirements of a system are dependent on antenna parameters in practical engineering. This chapter mainly deals with the antenna parameters used in practical engineering.
1.1 Radiation power density and radiation intensity
1.1.1 Radiation power density
Spherical waves radiated by antennas will propagate in the radial direction for a coordinate system centered on the antenna [1]–[3]. These waves can be approximated at large distances by plane waves in a small area at the antenna directional angle.
Both the direction of propagation and the power density of the electromagnetic wave can be described by the Poynting vector. It is the vector cross product of the electric and magnetic fields and is denoted by S and expressed as follows:
(1.1)
where E is the electric field vector measured in units of volt per meter (V/m). H is the magnetic field vector measured in units of ampere per meter (A/m). is the complex conjugate of the magnetic field vector. The direction of the Poynting vector is orthogonal to both electric and magnetic fields. The directions of E, H and S define a right-handed coordinate system. We can determine the intensity and direction of the energy flow at any point in the space if we know E and H by using eq. (1.1).
The average power density, W, could be expressed as follows:
(1.2)
where η is the intrinsic impedance of the medium (η = 376.73 Ω in free space).
Power density can be expressed as a spherical energy flow. The total power P of the antenna radiation can be obtained by taking the closed-surface integration of the power density on the enclosed surface of the antenna.
(1.3)
where is the differentiation of the solid angle, shown in Fig. 1.1.
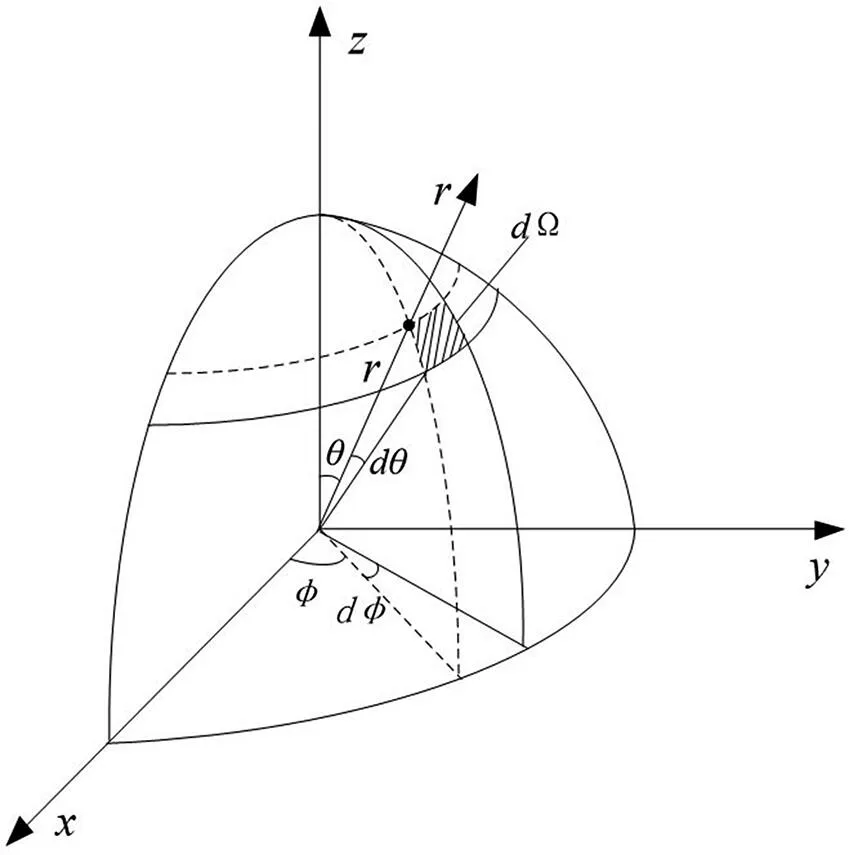
Fig. 1.1: The dΩ shown in polar coo...
Table of contents
- Title Page
- Copyright
- Contents
- Introduction
- Chapter 1 Parameters of antennae
- Chapter 2 Polarization theory
- Chapter 3 Crossed dipole circularly polarized antenna
- Chapter 4 Circularly polarized microstrip antenna
- Chapter 5 Helix antenna
- Chapter 6 Quadrifilar helix antennas
- Chapter 7 Circularly polarized frequency-independent antenna
- Chapter 8 Circularly polarized horn antennas
- Chapter 9 Omnidirectional circularly polarized antenna
- Chapter 10 Circularly polarized radial line array antenna
- Index
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription
No, books cannot be downloaded as external files, such as PDFs, for use outside of Perlego. However, you can download books within the Perlego app for offline reading on mobile or tablet. Learn how to download books offline
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 990+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn about our mission
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more about Read Aloud
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS and Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Yes, you can access Circularly Polarized Antenna Technology by in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Technology & Engineering & Science General. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.