
Machine Learning Using TensorFlow Cookbook
Over 60 recipes on machine learning using deep learning solutions from Kaggle Masters and Google Developer Experts
- 416 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Machine Learning Using TensorFlow Cookbook
Over 60 recipes on machine learning using deep learning solutions from Kaggle Masters and Google Developer Experts
About this book
Comprehensive recipes to give you valuable insights on Transformers, Reinforcement Learning, and more
Key Features
- Deep Learning solutions from Kaggle Masters and Google Developer Experts
- Get to grips with the fundamentals including variables, matrices, and data sources
- Learn advanced techniques to make your algorithms faster and more accurate
Book Description
The independent recipes in Machine Learning Using TensorFlow Cookbook will teach you how to perform complex data computations and gain valuable insights into your data. Dive into recipes on training models, model evaluation, sentiment analysis, regression analysis, artificial neural networks, and deep learning - each using Google's machine learning library, TensorFlow.
This cookbook covers the fundamentals of the TensorFlow library, including variables, matrices, and various data sources. You'll discover real-world implementations of Keras and TensorFlow and learn how to use estimators to train linear models and boosted trees, both for classification and regression.
Explore the practical applications of a variety of deep learning architectures, such as recurrent neural networks and Transformers, and see how they can be used to solve computer vision and natural language processing (NLP) problems.
With the help of this book, you will be proficient in using TensorFlow, understand deep learning from the basics, and be able to implement machine learning algorithms in real-world scenarios.
What you will learn
- Take TensorFlow into production
- Implement and fine-tune Transformer models for various NLP tasks
- Apply reinforcement learning algorithms using the TF-Agents framework
- Understand linear regression techniques and use Estimators to train linear models
- Execute neural networks and improve predictions on tabular data
- Master convolutional neural networks and recurrent neural networks through practical recipes
Who this book is for
If you are a data scientist or a machine learning engineer, and you want to skip detailed theoretical explanations in favor of building production-ready machine learning models using TensorFlow, this book is for you.
Basic familiarity with Python, linear algebra, statistics, and machine learning is necessary to make the most out of this book.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
6
Neural Networks
- The seminal paper describing backpropagation is Efficient Back Prop by Yann LeCun et al. The PDF is located here: http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/publis/pdf/lecun-98b.pdf.
- CS231, Convolutional Neural Networks for Visual Recognition, by Stanford University. Class resources are available here: http://cs231n.stanford.edu/.
- CS224d, Deep Learning for Natural Language Processing, by Stanford University. Class resources are available here: http://cs224d.stanford.edu/.
- Deep Learning, a book by the MIT Press. Goodfellow, et al. 2016. The book is located here: http://www.deeplearningbook.org.
- The online book Neural Networks and Deep Learning by Michael Nielsen, which is located here: http://neuralnetworksanddeeplearning.com/.
- For a more pragmatic approach and introduction to neural networks, Andrej Karpathy has written a great summary with JavaScript examples called A Hacker's Guide to Neural Networks. The write-up is located here: http://karpathy.github.io/neuralnets/.
- Another site that summarizes deep learning well is called Deep Learning for Beginners by Ian Goodfellow, Yoshua Bengio, and Aaron Courville. The web page can be found here: http://randomekek.github.io/deep/deeplearning.html.
- Implementing operational gates
- Working with gates and activation functions
- Implementing a one-layer neural network
- Implementing different layers
- Using a multilayer neural network
- Improving the predictions of linear models
- Learning to play Tic-Tac-Toe
Implementing operational gates
Getting ready
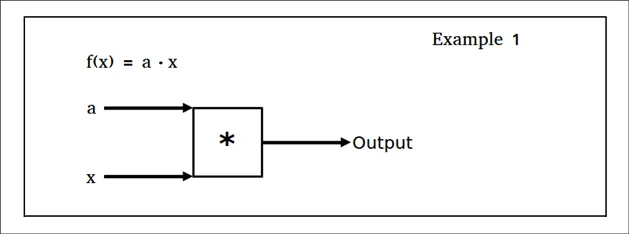
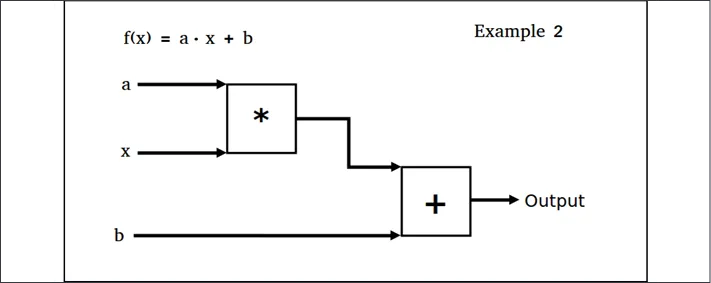
How to do it...
Table of contents
- Preface
- Getting Started with TensorFlow 2.x
- The TensorFlow Way
- Keras
- Linear Regression
- Boosted Trees
- Neural Networks
- Predicting with Tabular Data
- Convolutional Neural Networks
- Recurrent Neural Networks
- Transformers
- Reinforcement Learning with TensorFlow and TF-Agents
- Taking TensorFlow to Production
- Other Books You May Enjoy
- Index
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app