
Artificial Intelligence and Global Society
Impact and Practices
- 261 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Artificial Intelligence and Global Society
Impact and Practices
About this book
In the constant battle between human intelligence and machine intelligence, machines are close to surpassing human intelligence. The unrestrained use of digital technologies in automating processes is one of the prime advantages of the third industrial revolution. As a result, all developed and developing nations have started to digitalize mundane tasks. Thus, digital technologies for information and communication technologies (ICT) have achieved high market space in terms of infrastructure building, employment generation, education sector reforms, funds mobilization, electronic governance, hardware manufacturing, software development, etc. Hence, it is evident that every segment of society has been penetrated by ICT or digitalization. This book attempts to spotlight areas where AI is thriving.
FEATURES
- Impact of digitalization and AI on governance
- Novel AI practices being followed across the global community in security, healthcare, crime prevention and detection, education, agriculture, sensor networks, etc.
- Innovative techniques that can be adopted to ensure better quality and better delivery of services to the society
- Avenues for further research by the research community and student fraternity
This book is a guide for university students (especially those from technical backgrounds), industries, NGOs, and policy makers.
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
1
CONTENTS
1.1 Revolution
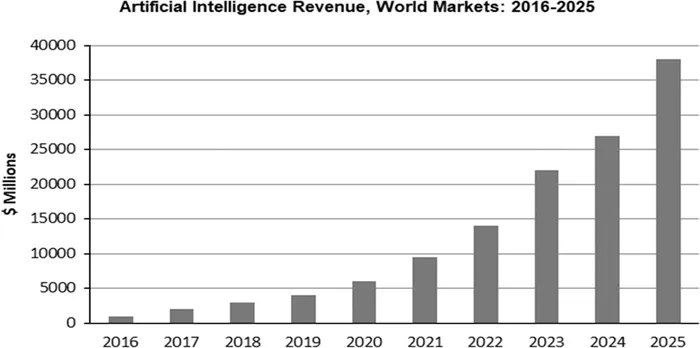
AI revenue in the world market.
1.2 Applications
1.2.1 Gaming
1.2.2 Technology
1.2.3 Computer Vision
Table of contents
- Cover
- Half Title
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Contents
- Preface
- Editors
- Contributors
- 1 Artificial Intelligence: Revolution, Definitions, Ethics, and Foundation
- 2 Impact of Digitization of Governance on Society
- 3 The Impact of AI on World Economy
- 4 Human Behavior Prediction and Artificial Intelligence
- 5 Emotion Recognition for Human Machine Interaction
- 6 Text, Visual and Multimedia Sentiment-Analysis, and Sentiment-Prediction
- 7 Transfer Learning with Convolution Neural Networks Models: An Evolutional Comparison
- 8 Multicriteria Decision Making Using Interval Valued Neutrosophic Soft Set
- 9 Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare
- 10 Computer-Aided Cataract Detection Using MLP and SVM
- 11 Artificial Intelligence Wave: Reshaping Indian Healthcare Sector
- 12 Adoption of Artificial Intelligence in Industrial Sectors and Its Impact
- 13 Model for Agriculture Using Big Data for Crop Disease Classification and Recommendation
- 14 Machine Intelligence versus Terrorism
- 15 IoTCrypt – An Intelligent System for Securing IoT Devices Using Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
- 16 Intelligent Systems: Enhanced Security Using Deep Learning Technology
- 17 Method for Generating Text by Eye Blink and Eye-Gaze Pattern for Locked-In Syndrome Patients
- 18 Kinship Verification Using Convolutional Neural Network
- 19 Machine Intelligence-Based Approach for Effective Terrorism Monitoring
- 20 Utilizing Artificial Intelligence to Design Delay and Energy Aware Wireless Sensor Networks
- Index