
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
About this book
Microgrid technology is an emerging area, and it has numerous advantages over the conventional power grid. A microgrid is defined as Distributed Energy Resources (DER) and interconnected loads with clearly defined electrical boundaries that act as a single controllable entity concerning the grid. Microgrid technology enables the connection and disconnection of the system from the grid. That is, the microgrid can operate both in grid-connected and islanded modes of operation. Microgrid technologies are an important part of the evolving landscape of energy and power systems.
Many aspects of microgrids are discussed in this volume, including, in the early chapters of the book, the various types of energy storage systems, power and energy management for microgrids, power electronics interface for AC & DC microgrids, battery management systems for microgrid applications, power system analysis for microgrids, and many others.
The middle section of the book presents the power quality problems in microgrid systems and its mitigations, gives an overview of various power quality problems and its solutions, describes the PSO algorithm based UPQC controller for power quality enhancement, describes the power quality enhancement and grid support through a solar energy conversion system, presents the fuzzy logic-based power quality assessments, and covers various power quality indices.
The final chapters in the book present the recent advancements in the microgrids, applications of Internet of Things (IoT) for microgrids, the application of artificial intelligent techniques, modeling of green energy smart meter for microgrids, communication networks for microgrids, and other aspects of microgrid technologies.
Valuable as a learning tool for beginners in this area as well as a daily reference for engineers and scientists working in the area of microgrids, this is a must-have for any library.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
1
A Comprehensive Review on Energy Management in Micro-Grid System
1.1 Introduction
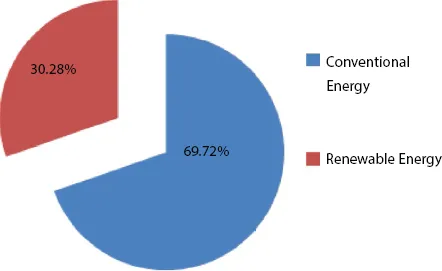
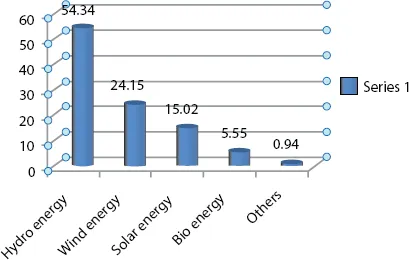
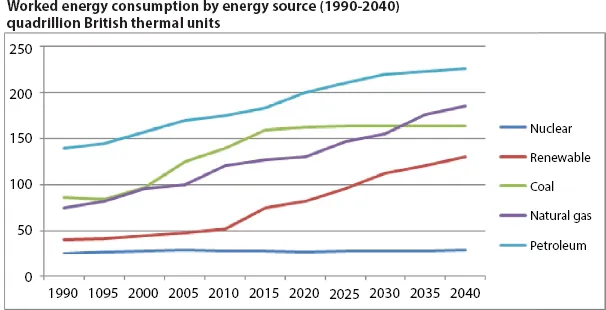
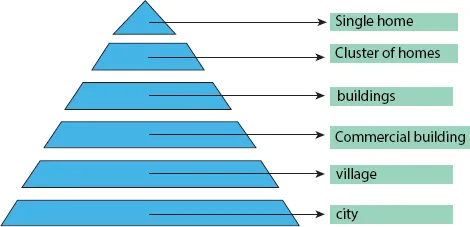
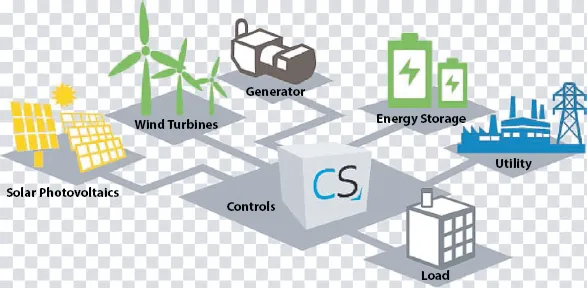
1.2 Generation and Storage System in MicroGrid
1.2.1 Distributed Generation of Electrical Power
Table of contents
- Cover
- Table of Contents
- Title Page
- Copyright
- Foreword
- Acknowledgements
- 1 A Comprehensive Review on Energy Management in Micro-Grid System
- 2 Power and Energy Management in Microgrid
- 3 Review of Energy Storage System for Microgrid
- 4 Single Phase Inverter Fuzzy Logic Phase Locked Loop
- 5 Power Electronics Interfaces in Microgrid Applications
- 6 Reconfigurable Battery Management System for Microgrid Application
- 7 Load Flow Analysis for Micro Grid
- 8 AC Microgrid Protection Coordination
- 9 A Numerical Approach for Estimating Emulated Inertia With Decentralized Frequency Control of Energy Storage Units for Hybrid Renewable Energy Microgrid System
- 10 Power Quality Issues in Microgrid and its Solutions
- 11 Power Quality Improvement in Microgrid System Using PSO-Based UPQC Controller
- 12 Power Quality Enhancement and Grid Support Using Solar Energy Conversion System
- 13 Power Quality Improvement of a 3-Phase-3-Wire Grid-Tied PV-Fuel Cell System by 3-Phase Active Filter Employing Sinusoidal Current Control Strategy
- 14 Application of Fuzzy Logic in Power Quality Assessment of Modern Power Systems
- 15 Applications of Internet of Things for Microgrid
- 16 Application of Artificial Intelligent Techniques in Microgrid
- 17 Mathematical Modeling for Green Energy Smart Meter for Microgrids
- 18 Microgrid Communication
- 19 Placement of Energy Exchange Centers and Bidding Strategies for Smartgrid Environment
- Index
- End User License Agreement
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app