1 Introduction The Challenge of Cybersecurity
Protecting organizational assets from cybersecurity attacks is a cost of doing business today. Such assets include customer and product information, business processes, company websites, social media accounts and content, business plans, trademarks, patents, proprietary hardware, and software.1 In addition to profiteering and gaining competitive advantage, cyberattacks are also motivated by national, social, political, and ideological agendas.2 As attacks continue to become more sophisticated and innovative, firms are being compelled to pay attention and to formulate and implement appropriate information security strategies. Although some organizations are thorough and deliberate in their approach, others seem willing to take chances and stumble and fumble in their actions and reactions to cyberattacks.3
Because there is no guaranteed immunity from such threats and attacks, senior leadership is often at crossroads when it comes to making cyber investments. During a top management meeting at a major healthcare organization, the chief executive officer (CEO) encouraged the leadership team to focus on the mission of providing quality care and not waste time, money, and effort to try and bulletproof the organization from potential attacks. Another senior leader argued that it was beneficial for the company to be attacked, as that is how they would learn about the organization’s vulnerabilities.
With heavy fines being imposed on negligent organizations and the existence of laws, such as the Sarbanes-Oxley (SOX) Act of 2002, that could send executives to jail, turning a blind eye to cyber threats and preparedness is a high-risk strategy. It was a landmark moment and decision when, in 2019, British Airways was found in violation of the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and fined a record amount of $228 million. The reputed airlines suffered a breach that exposed personal data of 500,000 customers.4 Equifax, one of the largest credit-reporting agencies, met a similar fate and settled to pay a penalty of $700 million for a breach that compromised 148 million customer records.5
These massive breach incidents should get the leadership thinking
whether they are content to live with the jeopardy of data protection fines running into the potential nine-figure bracket, or whether it’s more prudent to invest a fraction of that total on better cybersecurity procedures and technologies.6
Cybersecurity governance challenges are numerous and daunting and there are no easy fixes. The book attempts to provide an easy-to-comprehend framework to help readers get their arms around cybersecurity readiness. It recognizes that the battle or war against current and future cyber threats must be fought holistically and comprehensively by adopting people-, process-, and technology-driven measures. Technology alone will not mitigate information security risks. There are several pieces to the complex puzzle of cybersecurity management and technology is only one of them. Committed leadership, robust governance procedures, and informed and motivated personnel are other success factors. The book presents a set of seventeen success factors associated with three high-performance information security culture traits: commitment, preparedness, and discipline.
Chapter 2 begins with a discussion of the global epidemic of cyberattacks enabled by ever expanding attack surfaces and constantly evolving hacking methods and techniques. The consequences and impacts of data breaches are also presented. In Chapter 3, specific breach incidents are reviewed to understand the causes, adverse impacts, and organizational shortcomings. Each case review concludes with a set of summary takeaways and lessons learned. Chapter 4 draws upon the organizational culture and high-reliability organization literature to identify the three cornerstones of a high-performing security culture—commitment, preparedness, and discipline. How each of these cultural traits relates to cybersecurity readiness success factors and best practices is the focus of discussion in Chapters 5, 6, and 7. Key takeaways and actionable recommendations are presented in Chapter 8. Included in the appendix section are six useful resources: a) Information Security Monitoring Controls, b) Cybersecurity Performance Measures, c) Cybersecurity Readiness Scorecards, d) Cybersecurity and Privacy Laws and Regulations, e) Physical, Technical, and Administrative Controls: A Representative List, and f) Case Studies.
Notes to Chapter 1
1. Griffin, T. (2019, December 23). How to Protect Your Company’s Digital Assets. Forbes. https://www.forbes.com/sites/forbestechcouncil/2019/12/23/how-to-protect-yourcompanys-digital-assets/#5f66e6a06c5f
2. Sutherland, L. (2016, March 31). Know Your Enemy: Understanding the Motivation behind Cyberattacks. Security Intelligence. https://securityintelligence.com/know-yourenemy-understanding-the-motivation-behind-cyberattacks/
3. Abraham, C., Chatterjee, D., & Sims, R. (2019). Muddling through Cybersecurity: Insights from the U.S. Healthcare Industry. Business Horizons, 62(4), pp. 539–548.
4. Rogan, M. (2019, September 12). GDPR’s Big Moment Has Just Arrived—With a $228 Million Data Breach Fine. CPO Magazine. https://www.cpomagazine.com/data-protection/gdprs-big-moment-has-just-arrived-with-a-228-million-data-breach-fine/
5. Electronic Privacy Information Center. Equifax Data Breach. Retrieved September 15, 2019 from https://epic.org/privacy/data-breach/equifax/
6. Rogan, M. (2019, September 12). GDPR’s Big Moment Has Just Arrived—With a $228 Million Data Breach Fine. CPO Magazine. https://www.cpomagazine.com/data-protection/gdprs-big-moment-has-just-arrived-with-a-228-million-data-breach-fine/
2 The Cyberattack Epidemic
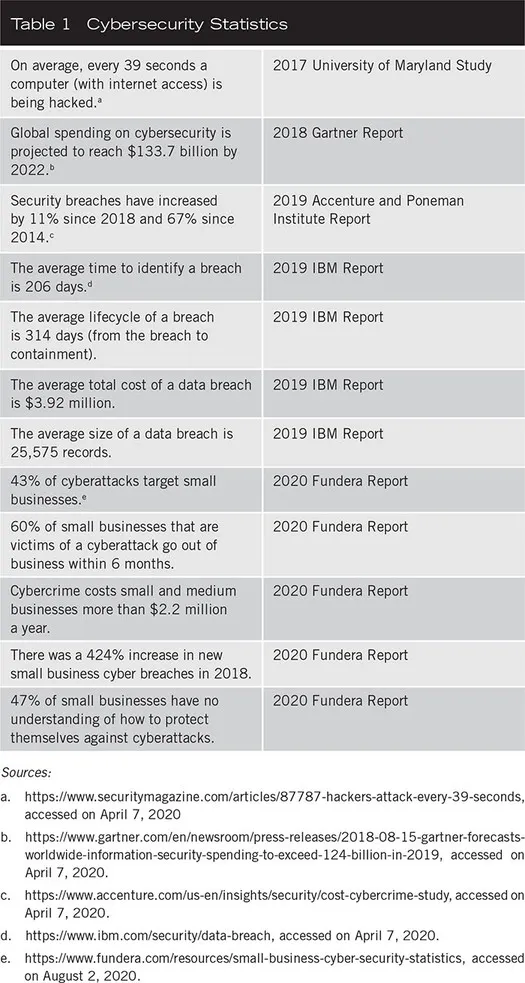
Research and survey reports reveal a continual rise in the frequency and severity of cyberattacks. No country and no industry is being spared; small and large organizations are being targeted; both public and private infrastructures are under attack (Table 1). The United States has been experiencing, on average, 130 large-scale targeted breaches per year and the number is growing by 27% every year. In 2017, the average number of breaches per country was reported to be 24,089. It is predicted that “cybercrimes will cost the world $6 trillion annually by 2021, up from $3 trillion in 2015.”1 The forces fueling the cyberattack epidemic and the nature and extent of its impact are discussed in the following sections.
Table 1 Sources:
a. https://www.securitymagazine.com/articles/87787-hackers-attack-every-39-seconds, accessed on April 7, 2020
b. https://www.gartner.com/en/newsroom/press-releases/2018-08-15-gartner-forecasts-worldwide-information-security-spending-to-exceed-124-billion-in-2019, accessed on April 7, 2020.
c. https://www.accenture.com/us-en/insights/security/cost-cybercrime-study, accessed on April 7, 2020.
d. https://www.ibm.com/security/data-breach, accessed on April 7, 2020.
e. https://www.fundera.com/resources/small-business-cyber-security-statistics, accessed on August 2, 2020.
2.1 Expanding Hardware and Software Attack Surfaces
The more networked the business environment, the greater the opportunities for hackers to break into one system and then find their way into many others.2 The Target retail chain experienced an external intrusion when hackers stole a HVAC vendor’s access credentials to gain access to the retail giant’s network and systems. Once they were inside Target’s network, the perpetrators were able to infect 40,000 of the 60,000 point-of-sale payment card readers with malware.3
Increasing dependency on cloud-based services is also adding to organizations’ vulnerability points. Capital One, for example, experienced a major breach of customer records when a perpetrator was able to gain access to an Amazon Web Services server (that stored Capital One data) by exploiting a misconfigured web application firewall.4
The growing use of Internet of Things (IoT) devices is also increasing the attack surface. Although these smart devices offer many benefits and capabilities, they are known to have weaker security protections and are not easily patchable or updatable.5 Hackers were able to steal customer data of a casino by exploiting a security vulnerability in the smart sensor used to remotely monitor the casino’s aquarium.6 In the healthcare industry, there is a heavy use of IoT devices for a variety of purposes such as tracking hospital bed occupancy, remotely monitoring patients, providing device malfunction alerts, and timely administration of medication.7 A recent research report finds that a majority (82%) of healthcare organizations experienced IoT-focused attacks within a one-year period. The breach consequences ranged from stolen health records to disruption of service, compromised end-user safety, and reputational damage.8
Today’s mobile devices, such as smart phones, are another attractive target for cybercriminals. With organizations allowing employees to use their personal device for work, breaking into such devices will net not only personally identifiable information (PII) but also confidential business data. Such devices are extremely vulnerable and provide a pathway for malware to reach an organization’s cloud or on-premise networks. According to a recent cybersecurity report that polled IT professionals, 59% did not use a mobile threat defense solution to protect employee devices. No wonder hackers are able to successfully compromise these devices in different ways, such as launching phishing and man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks and installing rogue applications. Lost or stolen devices that have not been appropriately configured for security and remote wipe-outs are prime sources of data breach.9
Thus, with increasing digitization and transformation of business processes and models, a highly mobile work environment, greater dependency on cloud-based services, infusion of wearable and IoT devices, and a high level of interorganizational connectivity, hardware and software attack surfaces are growing exponentially. The coronavirus pandemic that began early in 2020 is further fueling the explosion of attack surfaces by compelling remote work. In t...