
- 663 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
About this book
This book covers different aspects of Inorganic Chemistry in terms of 10 Chapters with in-depth and up-to-date coverage. Starting with the VSEPR theory in the first chapter, the book symmetrically presents delocalized p-bonding in polyatomic molecules; structure, bonding and topology of borane and related compounds; synthesis and reactivity of metal clusters and their bonding; some aspects of stability constants of metal complexes; magnetochemistry; mechanism of inorganic reactions; molecular orbital (MO) approach of bonding in transition metals; bonding in organometallic sandwich compounds based on MO approach. Safe and economical inorganic experiments at UG and PG Levels are also presented in the last chapter. At the end, five relevant topics are included as appendices for updating students and faculty members.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
Chapter I Valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR) theory: principles and applications
1.1 Introduction
1.2 Postulates of VSEPR theory: Sidgwick and Powell
- The unpaired electrons in the valence shell of central atom form bond pairs (bps) with surrounding atoms while paired electrons remain as lone pairs (lps).
- The electron pairs surrounding the central atom repel each other. Consequently, they stay as far apart as possible in space to attain stability.
- The geometry and shape of the molecule depend upon the number of electron pairs (bond pair as well as lone pair) around the central atom.
- The geometrical arrangements of electron pairs with different number of electron pairs around central atom are given in Table 1.1.
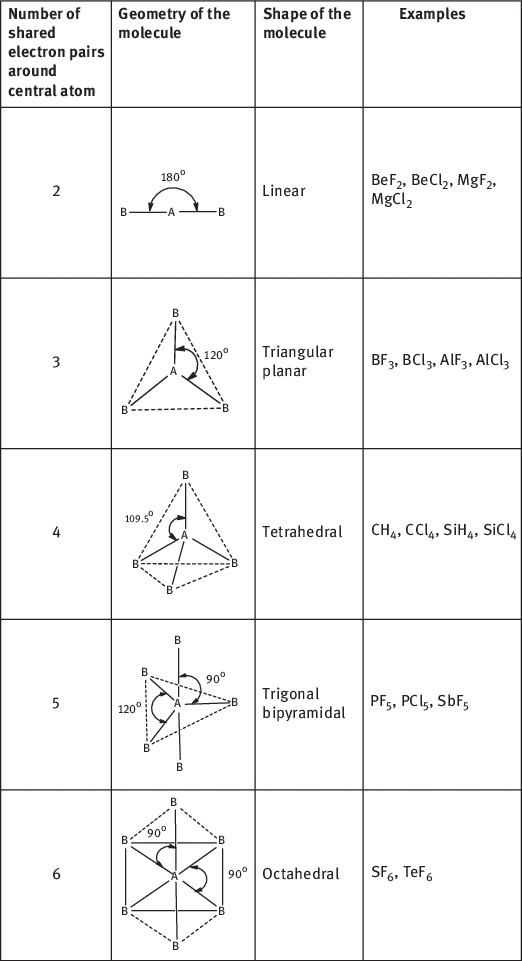 |
1.3 Rules proposed by Gillespie and Nyholm
1.3.1 Rule 1. Spatial arrangement of electron pairs around the central atom of a given molecule/ion
1.3.2 Rule 2. Regular and irregular geometry: presence of hybrid orbitals containing bond pairs and lone pairs
Table of contents
- Title Page
- Copyright
- Contents
- Preface
- Chapter I Valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR) theory: principles and applications
- Chapter II Delocalized π-bonding in polyatomic molecules: molecular orbital approach
- Chapter III Chemistry of borane and related compounds: structure, bonding and topology
- Chapter IV Synthesis and reactivity of metal clusters, and their bonding based on molecular orbital approach
- Chapter V Stability constants of metal complexes: some aspects
- Chapter VI Principles of magnetochemistry and its multiple applications in coordination compounds
- Chapter VII Mechanism of inorganic reactions: a study of metal complexes in solution
- Chapter VIII Bonding in transition metal complexes: molecular orbital theory approach
- Chapter IX Bonding in organometallic sandwich compounds: molecular orbital theory approach
- Chapter X Some aspects of safe and economical inorganic experiments at UG and PG levels
- Appendix III Nomenclature of inorganic compounds: the rules
- Index
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app