
Cost Engineering for Pollution Prevention and Control
- 458 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Cost Engineering for Pollution Prevention and Control
About this book
Environmental engineers work to increase the level of health and happiness in the world by designing, building, and operating processes and systems for water treatment, water pollution control, air pollution control, and solid waste management. These projects compete for resources with projects in medicine, transportation, education, and other fields that have a similar objective. The challenge is to make the investments efficient – to get the best project outputs with a minimum of inputs. Cost Engineering for Pollution Prevention and Control examines how to identify the best solution by judging alternatives with respect to some measure of system performance, such as total capital cost, annual cost, annual net profit, return on investment, cost-benefit ratio, net present worth, minimum production time, maximum production rate, minimum energy utilization, and so on.
Key Features:
- Explains how to estimate preliminary costs, how to compare the life cycle costs of alternative projects, how to find the optimal balance between capital costs and operating costs.
- Emphasis is placed on formulating the problem rather than on the mathematical details of how the calculations are done.
- Provides numerous practical examples and case studies.
- Includes end-of-chapter exercises dealing with water, wastewater, air pollution, solid wastes, and remediation projects.
The important concepts presented in this book can be understood by those students who have taken an introductory course in environmental engineering. Advanced knowledge of process design is not required. The material can also be utilized by engineers, managers, and others who would benefit from a better understanding of how engineers look at problems.
Trusted by 375,005 students
Access to over 1 million titles for a fair monthly price.
Study more efficiently using our study tools.
Information
1 An Introduction to Cost Engineering
1.1 Health and Happiness
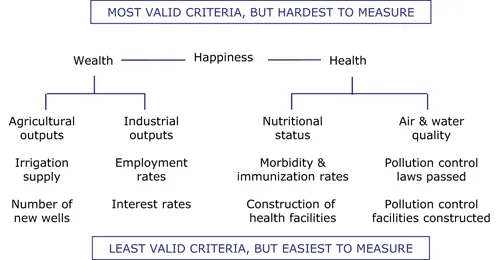
1.2 The Cost of Action and No Action
Impacts on | Examples of Impacts |
Health | Increased burden of disease due to reduced drinking water quality |
Increased burden of disease due to reduced bathing water quality | |
Increased burden of disease due to unsafe food (contaminated vegetables, fish, and other farm products) | |
Increased risk of disease when working or playing in wastewater irrigated areas | |
Increased financial burden on health care | |
Environment | Diminished recreational opportunities |
Decreased biodiversity | |
Degraded ecosystems (e.g., eutrophication and dead zones) | |
Increased greenhouse gas emissions | |
Increased odors and unsightly conditions | |
Production | Reduced industrial productivity |
Reduced agricultural productivity | |
Reduced market value of harvested crops due to unsafe irrigation | |
Reduced tourism and the willingness to pay for recreational activities | |
Reduced fish and shellfish catches, or reduced market value of fish and shellfish |
1.3 About This Book
Table of contents
- Cover
- Half-Title
- Title
- Copyright
- Contents
- Preface
- Author Bios
- Chapter 1 An Introduction to Cost Engineering
- Chapter 2 Defining the Engineering Problem
- Chapter 3 Planning for the Future
- Chapter 4 Capital Cost Estimates
- Chapter 5 Operating Costs
- Chapter 6 Cost Indexes
- Chapter 7 Economy of Scale
- Chapter 8 The Time Value of Money
- Chapter 9 Depreciation and Asset Valuation
- Chapter 10 Financing Capital Costs
- Chapter 11 Financial Management for Operations
- Chapter 12 Utility Service Revenues and Rate Making
- Chapter 13 Financial Management for Engineering Projects
- Chapter 14 Optimization of Linear Models
- Chapter 15 Optimization of Nonlinear Problems
- Chapter 16 Building and Fitting Statistical Models
- Chapter 17 Experimental Methods for Engineering Optimization
- Chapter 18 Designing under Uncertainty
- Chapter 19 Monte Carlo Simulation
- Chapter 20 Designing for Safety and Reliability
- Chapter 21 References and Recommended Reading
- Chapter 22 Appendix AStaged Construction for Linear Growth
- Chapter 23 Appendix BEconomy of Scale Factors
- Chapter 24 Appendix CFactors for Economic Calculations
- Chapter 25 Appendix DInterpreting the LINGO Solution Report
- Chapter 26 Appendix EGenerating Random Numbers in Excel
- Index
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app