
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
About this book
Heat is a branch of thermodynamics that occupies a unique position due to its involvement in the field of practice. Being linked to the management, transport and exchange of energy in thermal form, it impacts all aspects of human life and activity.
Heat transfers are, by nature, classified as conduction, convection (which inserts conduction into fluid mechanics) and radiation. The importance of these three transfer methods has resulted – justifiably – in a separate volume being afforded to each of them. This first volume is dedicated to thermal conduction, and, importantly, assumes an analytical approach to the problems presented, and recalls the fundamentals. Heat Transfer 1 combines a basic approach with a deeper understanding of the discipline and will therefore appeal to a wide audience, from technician to engineer, from doctoral student to teacher-researcher.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
1
The Problem of Thermal Conduction: General Comments
1.1. The fundamental problem of thermal conduction
- a) for all problems, a heat equation is considered, resulting from a local heat balance;
- b) for specific conditions of the problem, the conditions are constituted at the limits that are applied to the heat equation.
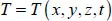
- – stationary conductive heat transfer;
- – non-stationary conductive heat transfer.
- – problems of stationary conduction with a single dimension: T = T(x) or T = T(r)
- – problems of non-stationary conduction with a single dimension: T = T (x,t) or T =T (r,t)
1.2. Definitions
1.2.1. Temperature, isothermal surface and gradient
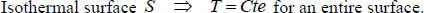
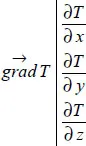
Table of contents
- Cover
- Table of Contents
- Title Page
- Copyright
- Preface
- Introduction
- 1 The Problem of Thermal Conduction: General Comments
- 2 The Physics of Conduction
- 3 Conduction in a Stationary Regime
- 4 Quasi-stationary Model
- 5 Non-stationary Conduction
- 6 Fin Theory: Notions and Examples
- Appendices
- References
- Index
- End User License Agreement
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app