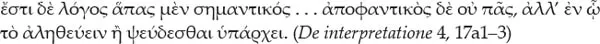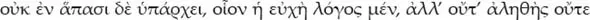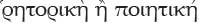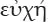![]()
PART I
![]()
The problem of truth in the decisive origins of philosophical logic, and the seedbed of traditional logic (focused on Aristotle)
Prefatory remark
[127] As we now discuss this question with a glance back to some texts of Aristotle, it does not mean that we are trying to give a complete interpretation of those texts. Let’s presuppose such an interpretation as having already been carried out. Then, using our guiding question, let us simply focus on some individual theses of Aristotle. Our investigation aims at an original understanding of the problem of truth and a radical way of solving it, one in which our investigation of the problem up to now will gain its legitimacy, and in which its positive content will come to light.
We begin our concrete investigation of the current determinations of truth by characterizing the truth of propositions. This is hardly accidental or arbitrary. We do so because according to the traditional report, the proposition or judgment is the proper place of truth. What is the connection here?
In §11, we will deal with the place of truth and with the proposition (
). Out of those preliminary discussions will come the need to discuss the basic structure of
and, in connection with that, to clarify the phenomenon of meaning.
1§11. The place of truth, and (proposition)
The thesis that the proper place of truth is the proposition or judgment must be understood as an image insofar as “place” is a spatial term,
whereas
is not extended in space. [128] What the expression means is: the proposition is where truth originally and properly belongs. The proposition is what makes truth possible as such. When this thesis is asserted and taken unquestioningly as the basis of every explanation of truth, it is most often accompanied by a second thesis, one concerned with content—namely, that the thesis about the proposition as the place of truth was first enunciated by Aristotle. And usually this second thesis is connected with a third, namely, that Aristotle was the one who first determined the concept of truth—as the correspondence of thought with things. However (so this thesis usually affirms), since this concept of truth cannot stand up against critical reflection, Aristotle is the originator of this naïve concept of truth.
2To put it another way, we have three theses:
1. The place of truth is the proposition.
2. Truth is the correspondence of thought with beings.
3. These two statements originate with Aristotle.
These three theses, which are widespread today and have been for a long time, are so many prejudices. It is not the case that Aristotle enunciated the first two theses, nor does he directly or indirectly teach what these theses assert. He originates theses (1) and (2) only in the sense that these came into circulation through an appeal to Aristotle that was based on an inadequate interpretation of him; and it continues unabatedly, even today, to determine the conception of the problem.
What does Aristotle say about
truth and its relation to
as proposition?
In the first place, we must keep in mind the basic point: Aristotle never determined “truth” as such by going back to the proposition. Rather, if he ever makes any connection between
(proposition) and truth, he does so in such a way that he determines the proposition through [129] truth, or more precisely, through the ability-to-be-true. But even this way of putting it is inadequate. The propositional statement is determined by Aristotle as speech that can be true or false.
All speech is about something {i.e., in general terms, it means something} . . . but not all speech is indicative {i.e., lets something be seen}, but only speech in which being-true or being-false is present {as the ways of speaking}.3
This makes it clear in principle that being-true is the distinguishing feature of a certain kind of speech, the kind that states or asserts something. The proposition is determined by its reference to truth—not vice versa, as if truth were derived from the proposition. When Aristotle emphasizes that the statement is a special kind of speech because of its reference to truth, we need to understand this correctly. The statement has a reference to the ability to be true or false. Being-true simpliciter and being true or false, are entirely different phenomena.
According to Aristotle this “either/or,” this “either-true-or-false,” is intrinsic to the proposition. Therefore, for him the proposition certainly does not have to be there in order for truth to be what it is; and if a proposition is true, it is true as something that also can be false.
Of course, we have not yet established what this either/or really means or why the proposition can be characterized in terms of it. We have not even shown what it is about the proposition that requires that it be caught in this alternative.
This either/or is what distinguishes speech qua statement and delimits it from other kinds of speech. [130] What other kinds? Aristotle gives a brief indication of those other kinds when he continues the sentence previously cited:
But being-true-and-false is not present in every kind of speech. A request, for example, is a form of speech, but it is neither true nor false.
Here Aristotle envisions (although he does not name) a rich variety of other forms of speech, including wishes, commands, and questions. Aristotle merely mentions in passing that the proper disciplines for studying them are
, rhetoric or poetics.
4 Sentences like “Please pass me the scissors” or “Get off this land!” or “Was there another storm today?” are not statements, because they are neither true nor false. This division that Aristotle makes within the various forms of
speech has not always been maintained. In fact, it has been strongly challenged—by Bolzano, for example,
5 and in a certain sense even by Husserl—to the effect that even sentences expressing wishes, commands, and questions are thought to have the property of statements.
The question is still debated, and yet anyone can see that getting a clear resolution of the question is a basic presupposition [131] for any scientific grammar.6 Here we will not pursue the question as a matter of controversy. Instead, we will try to see whether discussing the phenomenon of truth can lead us to a foundation on which we can at least correctly pose (if not resolve) the much-debated question about the expression of objectivizing and non-objectivizing acts. Let us simply get a bit clearer on the distinction Aristotle established.
What does it mean to say that being-true and being-false are not present in an
, a request? If I say, “Please give me the scissors that are on the table,” when in fact there are no scissors on the table, what I say does not correspond with what is the case. My speech is objectively false. I am deceived, and my utterance expr...