
Soft Computing Approach for Mathematical Modeling of Engineering Problems
- 296 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Soft Computing Approach for Mathematical Modeling of Engineering Problems
About this book
This book describes different mathematical modeling and soft computing techniques used to solve practical engineering problems. It gives an overview of the current state of soft computing techniques and describes the advantages and disadvantages of soft computing compared to traditional hard computing techniques. Through examples and case studies, the editors demonstrate and describe how problems with inherent uncertainty can be addressed and eventually solved through the aid of numerical models and methods. The chapters address several applications and examples in bioengineering science, drug delivery, solving inventory issues, Industry 4.0, augmented reality and weather forecasting. Other examples include solving fuzzy-shortest-path problems by introducing a new distance and ranking functions. Because, in practice, problems arise with uncertain data and most of them cannot be solved exactly and easily, the main objective is to develop models that deliver solutions with the aid of numerical methods. This is the reason behind investigating soft numerical computing in dynamic systems. Having this in mind, the authors and editors have considered error of approximation and have discussed several common types of errors and their propagations. Moreover, they have explained the numerical methods, along with convergence and consistence properties and characteristics, as the main objectives behind this book involve considering, discussing and proving related theorems within the setting of soft computing. This book examines dynamic models, and how time is fundamental to the structure of the model and data as well as the understanding of how a process unfolds
• Discusses mathematical modeling with soft computing and the implementations of uncertain mathematical models
• Examines how uncertain dynamic systems models include uncertain state, uncertain state space and uncertain state's transition functions
• Assists readers to become familiar with many soft numerical methods to simulate the solution function's behavior
This book is intended for system specialists who are interested in dynamic systems that operate at different time scales. The book can be used by engineering students, researchers and professionals in control and finite element fields as well as all engineering, applied mathematics, economics and computer science interested in dynamic and uncertain systems.
Ali Ahmadian is a Senior Lecturer at the Institute of IR 4.0, The National University of Malaysia.
Soheil Salahshour is an associate professor at Bahcesehir University.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
1 Soft Computing Techniques: An Overview
1.1 Introduction
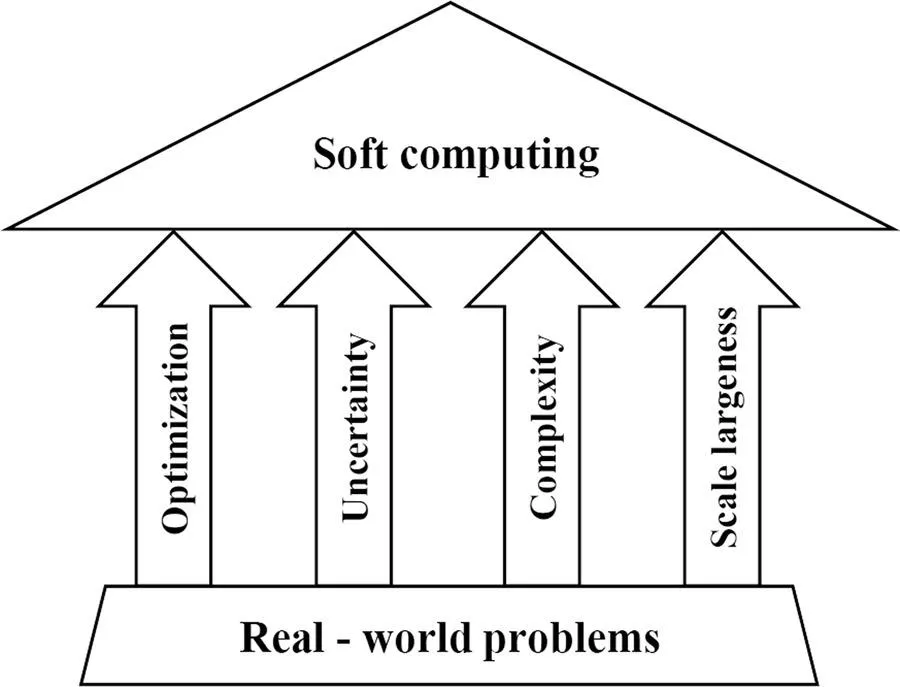
1.2 The Concept of Uncertainty: The Role of Fuzzy Logic


1.3 The Concept of Complexity: The Role of Artificial Neural Networks

Table of contents
- Cover
- Half Title
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Dedication
- Contents
- preface
- Editor Biographies
- Contributors
- Chapter 1 Soft Computing Techniques: An Overview
- Chapter 2 Solution of Linear Difference Equation in Interval Environment and Its Application
- Chapter 3 Industrial Internet of Things and Industry 4.0
- Chapter 4 Industry 4.0 and Its Practice in Terms of Fuzzy Uncertain Environment
- Chapter 5 Consistency of Aggregation Function-Based m-Polar Fuzzy Digraphs in Group Decision Making
- Chapter 6 Path Programming Problems in Fuzzy Environment
- Chapter 7 Weather Forecast and Climate Prediction Using Soft Computing Methods
- Chapter 8 Color Descriptor for Mobile Augmented Reality
- Chapter 9 Cryptosystem for Meshed 3D through Cellular Automata
- Chapter 10 Evolutionary Computing and Swarm Intelligence for Hyper Parameters Optimization Problem in Convolutional Neural Networks
- Chapter 11 New Approach for Efficiently Computing Factors of the RSA Modulus
- Chapter 12 Vision-Based Efficient Collision Avoidance Model Using Distance Measurement
- Index
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app