
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
About this book
Heat transfers are, by nature, classified as conduction, convection (which inserts conduction into fluid mechanics) and radiation. The importance of these three transfer methods has resulted – justifiably – in a separate volume being afforded to each of them. This second volume is dedicated to radiation. After recalling photometry, the calculation of luminance is addressed using the theory of the black body and associated laws: Stefan, Wien. The reciprocal radiation of two surfaces in total influence is discussed extensively, and the case of finished surfaces is also considered.
Heat Transfer 2 combines a basic approach with a deeper understanding of the discipline and will therefore appeal to a wide audience, from technician to engineer, from doctoral student to teacher-researcher.
Trusted by 375,005 students
Access to over 1 million titles for a fair monthly price.
Study more efficiently using our study tools.
Information
1
General Remarks
1.1. Introduction
1.2. Propagation of a sinusoidal electromagnetic wave
1.2.1. Frequencies and wavelengths
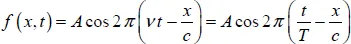
Table of contents
- Cover
- Table of Contents
- Title Page
- Copyright
- Preface
- Introduction
- 1 General Remarks
- 2 Calculating Luminances
- 3 Emission and Absorption
- 4 Radiation Exchanges Between Surfaces
- 5 Analytic Applications
- 6 Modeling and Simulations under ANSYS
- Appendix: G0−λT Function Table
- References
- Index
- End User License Agreement
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app