
Antenna and EM Modeling with MATLAB Antenna Toolbox
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Antenna and EM Modeling with MATLAB Antenna Toolbox
About this book
ANTENNA AND EM MODELING WITH MATLAB ANTENNA TOOLBOX™
An essential text to MATLAB Antenna Toolbox™ as accessible and easy-to-use full-wave antenna modeling tool
Antenna and EM Modeling with MATLAB Antenna Toolbox™ is a textbook on antennas intended for a one semester course. The core philosophy is to introduce the key antenna concepts and follow them up with full-wave modeling and optimization in the MATLAB Antenna Toolbox™. Such an approach will enable immediate testing of theoretical concepts by experimenting in software. It also provides the direct path to research work.
The fundamental families of antennas — dipoles, loops, patches, and traveling wave antennas — are discussed in detail, together with the respective antenna arrays. Using antenna parameters such as impedance, reflection coefficient, efficiency, directivity, and gain, the reader is introduced to the different ways of understanding the performance of an antenna.
Written for senior undergraduates, graduates as well as RF/Antenna engineers, Antenna and EM Modeling with Antenna Toolbox™ is a resource that:
- Provides 14 video assisted laboratories on using Antenna Toolbox™
- Includes approximately 50 real-world examples in antenna and array design
- Offers approximately 200 homework problems
- Provides multiple ready-to-use standalone MATLAB ® scripts
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
CHAPTER 1
Antenna Circuit Model. Antenna Matching. Antenna Bandwidth
SECTION 1 LUMPED CIRCUIT MODEL OF AN ANTENNA. ANTENNA INPUT IMPEDANCE
- 1.1 Antenna Circuit Model. Antenna Loss
- 1.2 Maximum Power Transfer to (and from) Antenna
- 1.3 Antenna Efficiency
- 1.4 Antenna Input Impedance and Impedance Matching
- 1.5 Point of Interest: Input Impedance of a Dipole Antenna and Its Dependence on Dipole Length
- 1.6 Beyond the First Resonance
- 1.7 Numerical Modeling
- References
- Problems
1.1 ANTENNA CIRCUIT MODEL. ANTENNA LOSS
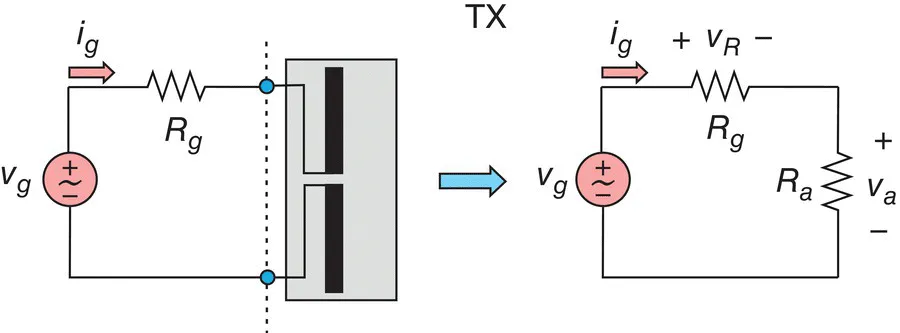
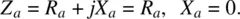
- Radiation resistance of the antenna Rr that describes the circuit power loss due to radiation by the antenna into free space.
- Loss resistance of the antenna RL that describes the circuit power loss in the antenna itself. Case in point: a long thin wire with a significant ohmic resistance or a helical antenna with a ferrite lossy core.
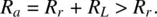
- it is zero for ideal antennas (a metal antenna made of perfect electric conductors);
- it is usually relatively small for metal antennas covering the band 0.3–3 GHz (UHF, L‐band, S‐band) where it may be often ignored;
- it may be very significant for printed antennas on lossy dielectric substrates and in the vicinity of lossy dielectric (such as FR4, ABS, human body, etc.);
- it is vital for very small antennas whose size is much less than the wavelength.
Example 1.1
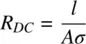
Table of contents
- Cover
- Table of Contents
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Dedication Page
- Preface and Text Organization
- List of Notations
- About the Companion Website
- CHAPTER 1: Antenna Circuit Model. Antenna Matching. Antenna Bandwidth
- CHAPTER 2: Receiving Antenna
- CHAPTER 3: Antenna Radiation
- CHAPTER 4: Antenna Balun. Antenna Reflector. Method of Images
- CHAPTER 5: Dipole Antenna Family: Broadband Antennas that Operate as Dipoles at Low Frequencies
- CHAPTER 6: Loop Antennas
- CHAPTER 7: Small Antennas
- CHAPTER 8: Patch and PIFA Antennas
- CHAPTER 9: Traveling Wave Antennas
- CHAPTER 10: Antenna Designer Including Circularly Polarized Antennas
- CHAPTER 11: Antenna Arrays
- Index
- End User License Agreement