
Genomic Sequence Analysis for Exon Prediction Using Adaptive Signal Processing Algorithms
- 192 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Genomic Sequence Analysis for Exon Prediction Using Adaptive Signal Processing Algorithms
About this book
This book addresses the issue of improving the accuracy in exon prediction in DNA sequences using various adaptive techniques based on different performance measures that are crucial in disease diagnosis and therapy. First, the authors present an overview of genomics engineering, structure of DNA sequence and its building blocks, genetic information flow in a cell, gene prediction along with its significance, and various types of gene prediction methods, followed by a review of literature starting with the biological background of genomic sequence analysis. Next, they cover various theoretical considerations of adaptive filtering techniques used for DNA analysis, with an introduction to adaptive filtering, properties of adaptive algorithms, and the need for development of adaptive exon predictors (AEPs) and structure of AEP used for DNA analysis. Then, they extend the approach of least mean squares (LMS) algorithm and its sign-based realizations with normalization factor for DNA analysis. They also present the normalized logarithmic-based realizations of least mean logarithmic squares (LMLS) and least logarithmic absolute difference (LLAD) adaptive algorithms that include normalized LMLS (NLMLS) algorithm, normalized LLAD (NLLAD) algorithm, and their signed variants. This book ends with an overview of the goals achieved and highlights the primary achievements using all proposed techniques. This book is intended to provide rigorous use of adaptive signal processing algorithms for genetic engineering, biomedical engineering, and bioinformatics and is useful for undergraduate and postgraduate students. This will also serve as a practical guide for Ph.D. students and researchers and will provide a number of research directions for further work.
Features
- Presents an overview of genomics engineering, structure of DNA sequence and its building blocks, genetic information flow in a cell, gene prediction along with its significance, and various types of gene prediction methods
- Covers various theoretical considerations of adaptive filtering techniques used for DNA analysis, introduction to adaptive filtering, properties of adaptive algorithms, need for development of adaptive exon predictors (AEPs), and structure of AEP used for DNA analysis
- Extends the approach of LMS algorithm and its sign-based realizations with normalization factor for DNA analysis
- Presents the normalized logarithmic-based realizations of LMLS and LLAD adaptive algorithms that include normalized LMLS (NLMLS) algorithm, normalized LLAD (NLLAD) algorithm, and their signed variants
- Provides an overview of the goals achieved and highlights the primary achievements using all proposed techniques
Dr. Md. Zia Ur Rahman is a professor in the Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering at Koneru Lakshmaiah Educational Foundation (K. L. University), Guntur, India. His current research interests include adaptive signal processing, biomedical signal processing, genetic engineering, medical imaging, array signal processing, medical telemetry, and nanophotonics.
Dr. Srinivasareddy Putluri is currently a Software Engineer at Tata Consultancy Services Ltd., Hyderabad. He received his Ph.D. degree (Genomic Signal Processing using Adaptive Signal Processing algorithms) from the Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering at Koneru Lakshmaiah Educational Foundation (K. L. University), Guntur, India. His research interests include genomic signal processing and adaptive signal processing. He has published 15 research papers in various journals and proceedings. He is currently a reviewer of publishers like the IEEE Access and IGI.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
1 Introduction
1.1 Genomics Engineering
1.2 DNA Sequence Structure
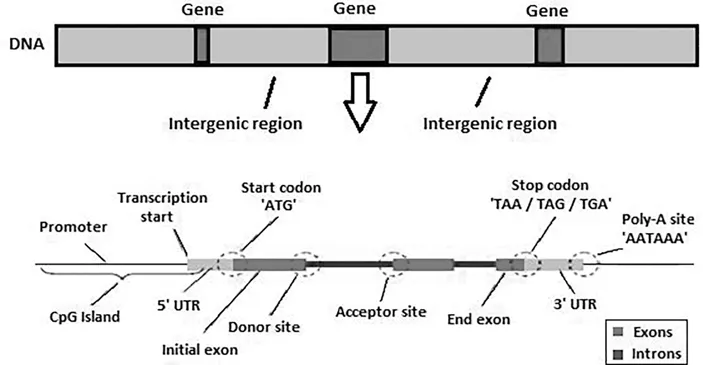
1.3 Motivation for the Work
Table of contents
- Cover
- Half Title
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Table of Contents
- Authors
- Chapter 1 Introduction
- Chapter 2 Literature Review
- Chapter 3 Sign LMS Based Realization of Adaptive Filtering Techniques for Exon Prediction
- Chapter 4 Normalization-Based Realization of Adaptive Filtering Techniques for Exon Prediction
- Chapter 5 Logarithmic-Based Realization of Adaptive Filtering Techniques for Exon Prediction
- Chapter 6 Conclusion and Future Perspective
- References
- Index
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app