
- 244 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Data Driven Energy Centered Maintenance
About this book
Over recent years, many new technologies have been introduced to drive the digital transformation in the building maintenance industry. The current trend in digital evolution involves data-driven decision making which opens new opportunities for an energy centered maintenance model. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning are helping the maintenance team to get to the next level of maintenance intelligence to provide real-time early warning of abnormal equipment performance.
This edition follows the same methodology as the First. It provides detailed descriptions of the latest technologies associated with Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning which enable data-driven decision-making processes about the equipment's operation and maintenance.
Technical topics discussed in the book include:
- Different Maintenance Types and The Need for Energy Centered Maintenance
- The Centered Maintenance Model
- Energy Centered Maintenance Process
- Measures of Equipment and Maintenance Efficiency and Effectiveness
- Data-Driven Energy Centered Maintenance Model:
-
- Digitally Enabled Energy Centered Maintenance Tasks
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Energy Centered Maintenance
- Model Capabilities and Analytics Rules
- Building Management System Schematics
The book contains a detailed description of the digital transformation process of most of the maintenance inspection tasks as they move away from being manually triggered. The book is aimed at building operators as well as those building automation companies who are working continuously to digitalize building operation and maintenance procedures. The benefits are reductions in the equipment failure rate, improvements in equipment reliability, increases in equipment efficiency and extended equipment lifespan.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
1
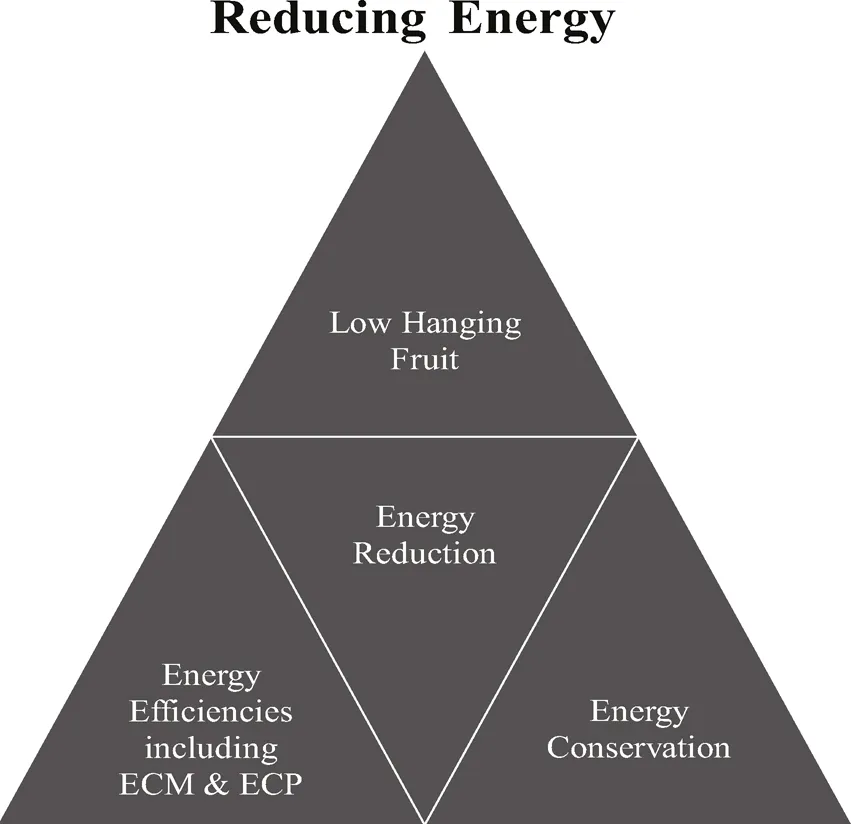
Energy Reduction
1.1 Energy Cost
- Implement the low hanging fruit and address identified energy waste.
- Implement energy conservation program in our organization.
- Implement energy efficiency measures which include energy efficiency projects and energy centered maintenance.
1.2 Implementing Low Hanging Fruit
- Not already implemented.
- Easy to implement.
- For my organization, low cost or no cost.
- Can sell to my management.
- Will reduce energy consumption.
- Establish a compelling energy policy.
- Implement an energy star procurement policy.
- Turn off lights and communicate energy conservation plan to all personnel.
- Unplug appliances and electronics when not in use.
- Use power chords that turn off when not in use.
- Verify equipment operational hours and time schedule.
- Checking illumination levels and switching off excess lighting.
- Ensure doors and windows are closed as much as possible to prevent heat loss or infiltration.
- Check door or windows sealant and insulation performance.
- Conduct an energy awareness campaign that educates the staff, residents, and tenants about their impact on energy use.
1.3 Identifying Energy Waste Brainstorming Sessions:
1.3.1 Management/Employee Brainstorming Sessions
- Specify clearly the main objective of the meeting, which is related to identifying the potential energy waste in your workplace, for example: “What Energy Waste is Experienced or Evident in your work Area?”
- Perform “Silent Generation” by having each person identify three energy waste items in their job areas. For example, computer monitors and CPU are not turning off after being idle, the brightness of computers has not been reduced, not using duplex printing, and curtains are over windows not letting light into the room thereby reducing the lumens in the work area.
- Go “Round Robin” by having the energy rep go around the room and have each participant offer one of their three suggestions and have it written on white board or pad by the scribe. Continue until all possible ideas have been written.
- Discuss each idea, eliminating duplicates, altering some by consolidation, etc., until a final list is obtained.
- Normally the ideas are prioritized, and selections are made. However, in this situation, the list is given to the energy team to do the selecting.
1.3.2 Walkthroughs or Energy Audits
- Projections of savings.
- Energy efficiency measures.
- Comparisons with baseline data.
- Tariff rates.
- All anticipated costs for energy efficiency measure with its return on investment.
- A precise time bounded plan for implementation of actions.
Who? Facilities, engineers, technicians, energy team leader, and others who can contribute.
What? Kick-off meeting, walk around the building and record anything that uses energy, what it is the amount of energy used (if pos-sible), whether it can reach a state of excessive energy consumption, what preventative maintenance is being performed now, and other pertinent information.
- Occupancy Sensors: Observe infrequently visited areas and determine whether an occupancy sensor will save energy. Look at restrooms, break rooms, copying or printing areas, mechanical areas, hallways, and other areas.
- Lights in Administrative Areas: Note types such as T-12s, T-8s, and T-5s. Look for areas daylighting can be used and skylights would help. Look at light bulbs and see if they are dirty with film covering them.
- Building Envelope: Search for leaks in doors and windows. Determine if windows should be glazed, caulked, or replaced. Weatherstrip the doors where needed or replace them.
- Walls and Roof Insulation: Check the insulation level and determine if more would help.
- Motors and Other Equipment Except for HVAC: Note each and check the switches and sensors associated with each. Check time schedule of each equipment and whether it runs according to it or continuously running.
- Data Centers: Look for hot and cold aisles and whether hot air is kept from commingling with the cold air on its return to the computer (CRAC).
- Security Lights: Check to see if they are adequate and energy friendly.
- HVAC: Note brand, capacity, date installed, the motors, and switches associated with the system, and check roof vents and other parts for adequacy and maintenance.
- Building Automation System (BAS) and Metering: See if BAS is outdated. Note where additional metering can help identify potential problem areas.
- Computers, monitors, imaging equipment, fax machines, and other office equipment.
Table of contents
- Cover
- Half Title
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Table of Contents
- Dedication
- Preface
- Glossary
- List of Tables
- List of Figures
- 1 Energy Reduction
- 2 Different Maintenance Types and the Need for Energy Centered Maintenance
- 3 Energy Centered Maintenance Origin and Model
- 4 ECM Process – Equipment Identification
- 5 ECM Process – Data Collection
- 6 ECM Process — ECM Inspections
- 7 ECM Process — Measuring Equipment Current Performance
- 8 ECM Process — Identifying Corrective/Preventive Action and Cost Effectiveness
- 9 ECM Process — Updating Preventative Maintenance Plans
- 10 Energy Centered Maintenance to avoid Low Delta T Syndrome in Chilled Water Systems
- 11 Energy Centered Maintenance in Data Centers
- 12 Measures of Equipment and Maintenance Efficiency and Effectiveness
- 13 Energy Savings Verification
- 14 Building Energy Centered Behavior Leading to an Energy Centered Culture
- 15 Data Driven Energy Centered Maintenance Model
- 16 Conclusion
- ECM References
- List of Acronyms
- Index
- About the Authors
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app