
Math for Programmers
3D graphics, machine learning, and simulations with Python
- 688 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
About this book
"A gentle introduction to some of the most useful mathematical concepts that should be in your developer toolbox." - Christopher Haupt, New Relic Explore important mathematical concepts through hands-on coding.
Purchase of the print book includes a free eBook in PDF, Kindle, and ePub formats from Manning Publications. Filled with graphics and more than 300 exercises and mini-projects, this book unlocks the door to interesting–and lucrative!–careers in some of today's hottest fields. As you tackle the basics of linear algebra, calculus, and machine learning, you'll master the key Python libraries used to turn them into real-world software applications. Summary
To score a job in data science, machine learning, computer graphics, and cryptography, you need to bring strong math skills to the party. Math for Programmers teaches the math you need for these hot careers, concentrating on what you need to know as a developer. Filled with lots of helpful graphics and more than 200 exercises and mini-projects, this book unlocks the door to interesting–and lucrative!–careers in some of today's hottest programming fields. About the technology
Skip the mathematical jargon: This one-of-a-kind book uses Python to teach the math you need to build games, simulations, 3D graphics, and machine learning algorithms. Discover how algebra and calculus come alive when you see them in code! What's inside Vector geometry for computer graphics
Matrices and linear transformations
Core concepts from calculus
Simulation and optimization
Image and audio processing
Machine learning algorithms for regression and classification About the reader
For programmers with basic skills in algebra. About the author
Paul Orland is a programmer, software entrepreneur, and math enthusiast. He is co-founder of Tachyus, a start-up building predictive analytics software for the energy industry. You can find him online at www.paulor.land. Table of Contents 1 Learning math with code PART I - VECTORS AND GRAPHICS 2 Drawing with 2D vectors 3 Ascending to the 3D world 4 Transforming vectors and graphics 5 Computing transformations with matrices 6 Generalizing to higher dimensions 7 Solving systems of linear equations PART 2 - CALCULUS AND PHYSICAL SIMULATION 8 Understanding rates of change 9 Simulating moving objects 10 Working with symbolic expressions 11 Simulating force fields 12 Optimizing a physical system 13 Analyzing sound waves with a Fourier series PART 3 - MACHINE LEARNING APPLICATIONS 14 Fitting functions to data 15 Classifying data with logistic regression 16 Training neural networks
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
1 Learning math with code
- Solving lucrative problems with math and software
- Avoiding common pitfalls in learning math
- Building on intuition from programming to understand math
- Using Python as a powerful and extensible calculator
1.1 Solving lucrative problems with math and software
1.1.1 Predicting financial market movements
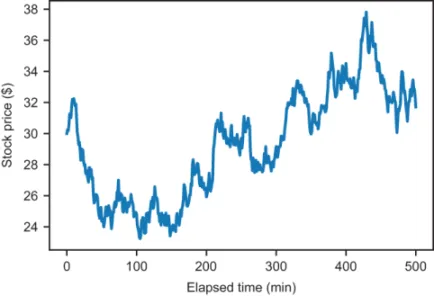
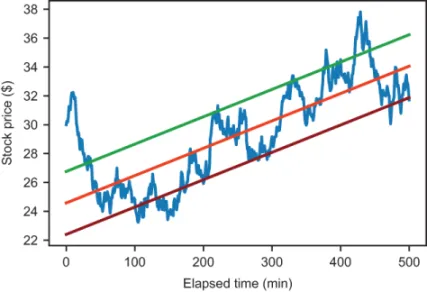
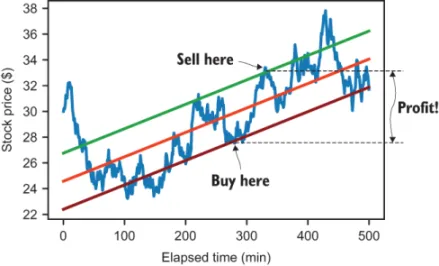
1.1.2 Finding a good deal
Table of contents
- Math for Programmers
- Copyright
- dedication
- contents
- front matter
- 1 Learning math with code
- Part 1. Vectors and graphics
- 2 Drawing with 2D vectors
- 3 Ascending to the 3D world
- 4 Transforming vectors and graphics
- 5 Computing transformations with matrices
- 6 Generalizing to higher dimensions
- 7 Solving systems of linear equations
- Part 2. Calculus and physical simulation
- 8 Understanding rates of change
- 9 Simulating moving objects
- 10 Working with symbolic expressions
- 11 Simulating force fields
- 12 Optimizing a physical system
- 13 Analyzing sound waves with a Fourier series
- Part 3. Machine learning applications
- 14 Fitting functions to data
- 15 Classifying data with logistic regression
- 16 Training neural networks
- Appendix A. Getting set up with Python
- Appendix B. Python tips and tricks
- Appendix C. Loading and rendering 3D Models with OpenGL and PyGame
- index
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app