
Artificial Intelligence and Speech Technology
Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Speech Technology, (AIST2020), 19-20 November, 2020, Delhi, India
- 505 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Artificial Intelligence and Speech Technology
Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Speech Technology, (AIST2020), 19-20 November, 2020, Delhi, India
About this book
The 2nd International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Speech Technology (AIST2020) was organized by Indira Gandhi Delhi Technical University for Women, Delhi, India on November 19–20, 2020. AIST2020 is dedicated to cutting-edge research that addresses the scientific needs of academic researchers and industrial professionals to explore new horizons of knowledge related to Artificial Intelligence and Speech Technologies. AIST2020 includes high-quality paper presentation sessions revealing the latest research findings, and engaging participant discussions. The main focus is on novel contributions which would open new opportunities for providing better and low-cost solutions for the betterment of society. These include the use of new AI-based approaches like Deep Learning, CNN, RNN, GAN, and others in various Speech related issues like speech synthesis, speech recognition, etc.
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
CHAPTER 1
Classification approaches for automatic speech recognition system
Amritpreet Kaura, Rohit Sachdevab, Amitoj Singhc
1.1 Introduction
1.2 Methods
- A leading encoding strategy was used in the mathematical context for HMM. This is an inter-related method, generated by two processes, a Markov chain which is rooted in a limited variety of states, and a particular function of probabilities is correlated with each of these states, to determine the odds of the acoustic properties. State probabilities can be modeled through continuous likelihood function, semi-continuous production of probability, or constant production of probability. Mixture distributions consisting of a linear combination of Gaussian or Laplacian density functions are the typical models for the constant probability distribution.
- ANN is a computer device driven by the arrangement of cell types in the living person’s mind. The most commonly used category of ANN in speech recognition (Masmoudi, Frikha, Chtourou & Hamida 2011) is Multi-Layer Perceptron (MLP). A potential substitute to substitute or assist HMM in classification style was digital NN & and more precisely MLP. Some ANN methods to develop state-of-the-art ASR structures were suggested (Fauziya & Nijhawan, 2014; Renjith & Manju, 2017).
- Deep learning methods are proposed as an advancement of ANN in order to get significant improvement in the performance of the acoustic models. Restricted Boltzmann machine, Deep Belief Networks (DBN) (A.-R. Mohamed, Dahl, & Hinton, 2009; A. R. Mohamed, Dahl, & Hinton, 2012), Deep Neural Networks (DNN) (Hinton et al., 2012; Senior, Heigold, Bacchiani, & Liao, 2014), Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) (Abdel-Hamid et al., 2014; Passricha & Aggarwal, 2019a), Capsule Network are popular variants of deep learning technique that is successfully adopted speech recognition tasks. Evolutionary Techniques search approaches focused on the theory of natural evolution are adaptive methods such as Genetic Algorithms (GAs), Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO), etc. These strategies have the potential to produce a simple community of potential responses and a really strong capacity to identify the best approaches of all those reasonable solutions (Dua, Aggarwal, & Biswas, 2018; Passricha & Aggarwal, 2019b).
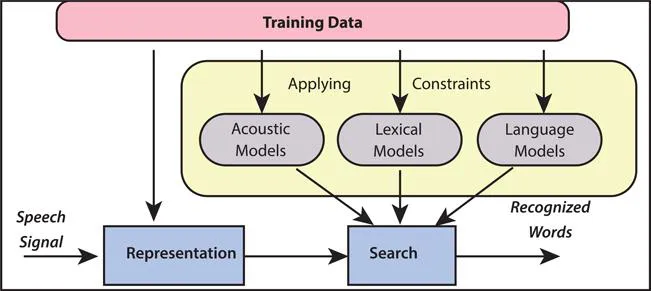
1.3 Architecture of Speech Recognition
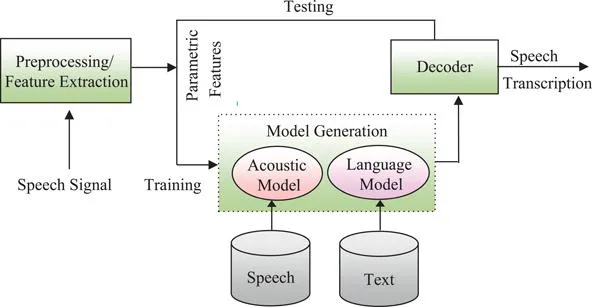
1.3.1 Preprocessing and Feature Extraction
1.4 Models of Speech Recognition
1.5 Comparative Analysis of SR Models
Table of contents
- Cover
- Half Title
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Table of Contents
- Organisation
- Preface
- 1 Classification approaches for automatic speech recognition system
- 2 Early detection of PCOD using machine learning techniques
- 3 Application of real-time object detection techniques for bird detection
- 4 Machine learning algorithms used for detection of prostate cancer
- 5 How training of sigmoidal FFANN affected by weight initialization
- 6 Machine learning for web development: A fusion
- 7 Bot attack detection using various machine learning algorithms
- 8 Present scenario of emotionally intelligent voice-based Conversational Agents in India
- 9 Blockchain-based secured data transmission of IoT sensors using thingspeak
- 10 Impact of energy storage device on the performance of AGC using ALO tuned PID controller
- 11 The instrument to measure happiness at workplace
- 12 IoT based smart cyber sealing system
- 13 A novel approach for summarizing legal judgements using graph
- 14 Deep CNN architectures for learning image classification: A systematic review, taxonomy and open challenges
- 15 The quest for crop improvement in the era of artificial intelligence, machine learning, and other cognitive sciences
- 16 A run-through: Text independent speaker identification using deep learning
- 17 Summarization of video lectures
- 18 Artificial intelligence approach in video summarization
- 19 Extractive summarization of recorded Odia spoken feedback
- 20 Frame change detection in videos – challenges and research directions
- 21 Speech impairment recognition using XGBoost classifier
- 22 Research insight of Indian tonal languages: A review
- 23 Advances in speech vocoding for text-to-speech with continuous parameters
- 24 Applying entity recognition and verb role labelling for information extraction of Tamil biomedicine
- 25 Identification of two tribal languages of India: An experimental study
- 26 Mental illness diagnosis from social network data using effective machine learning technique
- 27 Hybrid classifier for brain tumor detection and classification
- 28 Parametric study of through transmission laser welding with teaching learning based optimization
- 29 Research landscape of artificial intelligence in human resource management: A bibliometric overview
- 30 An efficient Class-F PA with SSL/SIL based matching network for body centric wireless transceiver
- 31 Envisaging the future homes with ‘human-building interaction’
- 32 Comparative analysis of first-order optimization algorithms
- 33 A review on application of artificial intelligence techniques in control of industrial processes
- 34 Crop monitoring system for effective prediction of agricultural analytics in Indian agriculture using WSN
- 35 Trend analysis of meteorological index SPI using statistical and machine learning models over the region of Marathwada
- 36 An insight into reconfigurable antenna design
- 37 Optimized XGBoost algorithm using agglomerative clustering for effective user context identification
- 38 1D CNN based approach for speech emotion recognition using MFCC features
- 39 Review on text detection and recognition in images
- 40 Comparative analysis of machine learning algorithms on gender classification using Hindi speech data
- 41 COVID-19 detection through Mamdani-based fuzzy inference system
- 42 Assistive technology is a boon or bane: A case of persons with disabilities
- 43 Sensor data fusion using machine learning techniques in indoor occupancy detection
- 44 Covid’19 virus life progress span by using machine learning algorithms and time series methods
- 45 Sustainable development through adoption of digitization towards functioning of self help groups
- 46 Security and vulnerability issues in NoSQL
- 47 Artificial intelligence applications and techniques in interactive and adaptive smart learning environments
- 48 SIM-BERT: Speech intelligence model using NLP-BERT with improved accuracy
- 49 A literature review on virtual assistant for visually impaired
- 50 Congestion control mechanisms to avoid congestion in VANET: A comparative review
- 51 Comparative Study of various Stable and Unstable sorting Algorithms
- 52 Prediction analysis of forecasting applications with concept drifting distributions
- 53 A hybrid cardiovascular disease prediction system using machine learning algorithms
- 54 Financial inclusion via Fintech: A conceptual framework for digitalizing the banking landscape of rural India