
Building Enterprise Blockchain Solutions on AWS
A Developer's Guide to Build, Deploy, and Managed Apps Using Ethereum, Hyperledger Fabric, and AWS Blockchain (English Edition)
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Building Enterprise Blockchain Solutions on AWS
A Developer's Guide to Build, Deploy, and Managed Apps Using Ethereum, Hyperledger Fabric, and AWS Blockchain (English Edition)
About this book
Define your enterprise blockchain system using the AWS blockchain managed service.
Key Features
? Practical implementation of blockchain applications across Healthcare, Banking, and Finance.
? Covers complete solutions, including writing smart contracts, executing chain codes, and deploying blockchain private networks.
? Best practices to write smart contracts, add authentication, manage security, and create Ethereum wallets.
Description
Building Enterprise Blockchain Solutions on AWS is a step-by-step guide for building, deploying, and managing decentralized applications on the AWS Blockchain. You will learn to build real-world decentralized applications for the Healthcare supply chain, Asset Tracker, and bank auditing applications with Hyperledger Fabric and Ethereum.The first section introduces you to the world of blockchain, AWS Blockchain offerings, and the Quantum Ledger Database. The second section introduces the concepts of Hyperledger Fabric, building the Hyperledger Fabric network with the Amazon Managed Blockchain, running the chaincode for the healthcare supply chain, building the API and UI using the Fabric node.js SDK, and adding members to the Fabric network on AWS. This book will help you to master Ethereum, Hyperledger Fabric, and the AWS Blockchain. You will be able to develop dApps for any domain, build private networks, and run your dApps on the AWS Blockchain. You will be an expert in writing and running smart contracts with Solidity and node.js chaincodes.
What you will learn
? Learn Hyperledger Fabric to build your private blockchain network.
? Write and deploy smart contracts on both Ethereum and Hyperledger Fabric.
? Add security, authentication, and keep monitoring the performance of dApps.
? Practical exposure of blockchain explorer, Truffle, Web3js, Ganache, Etherscan, Metamask, Ethereum wallet, and Remix.
Who this book is for
This book is well-crafted for software developers, system architects, application developers, and aspiring blockchain developers who want to create decentralized applications (dApps) at speed without wasting time in concepts and making complete use of Amazon-managed blockchains. Readers with some understanding of Ethereum and smart contracts would be helpful to speed up the learning of the concepts although it not an essential requirement.
Table of Contents
1. An Introduction to a Blockchain
2. Exploring a Blockchain on AWS
3. Exploring the Amazon Quantum Ledger Database
4. Exploring Hyperledger Fabric
5. The AWS Managed Blockchain to Create a Fabric Network
6. Developing the Chaincode, API, and UI with the Fabric SDK on AWS
7. Adding Members to the Fabric Network on AWS
8. Deep Dive into the Ethereum Blockchain
9. The AWS Blockchain Template to Create a Private Ethereum Network
10. The Solidity Smart Contract Language
11. Creating and Deploying the Asset Tracker Contract on AWS
12. Testing and Interacting with the Asset Tracker on AWS
About the Authors
Murughan Palaniachari is a developer, speaker, blogger, trainer, DevOps, and Blockchain expert. He has 14+ years of software development and operations experience in multiple technology stacks, including C#, Javascript, NodeJS, Java, Python, and Blockchain. He has expertise in Blockchain, Ethereum, Solidity, Hyperledger Fabric, and Cryptocurrency. He is an expert in building Enterprise Blockchain solutions using Ethereum, Hyperledger Fabric, and Stellar. He is an organizer of TAC – Technical Agility Conference, meetup organizer of Blockchain, DevOps, and Cloud.
Blog links: https://elevate-org.com/, https://devopsgames.com
LinkedIn Profile: https://www.linkedin.com/in/murughan/
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
CHAPTER 1
An Introduction to a Blockchain
Structure
- What is a blockchain?
- Why a blockchain?
- Issues with Web2.0 and centralized infrastructure
- Features of a blockchain
- How a blockchain works
- Consensus mechanism algorithms
- Public blockchain
- Private and permissioned blockchain
- Criteria to choose a blockchain
- Blockchain use-cases
Objectives
- Understand the concept of a blockchain
- Understand how a blockchain works
- Discuss the types of blockchain
- Identify blockchain use-cases
Challenges with the traditional centralized infrastructure
- Centralized power: Day-to-day applications we use are central in nature, and the operating company has complete control over the application behavior and data.
- Lack of trust and integrity: The data stored in centralized systems can be tampered anytime by the system owners or hackers, which leaves us to work within a non-trustable environment, spending a lot of money with agreements, and paying for a third party like a bank to manage the trust between the parties.
- Lack of traceability: It is unable to track the province of any asset like high-value goods (Rolex, Diamond, Gold, and so on.), supply chain, healthcare, and government. In the supply chain, when a consumer finds the food is contaminated, we don't have any trusted process to find out the root cause as hundreds of parties are involved in the entire system starting from the producer to the consumer. Each one maintains their own central digital database, or even worse, maintains data in a non-digital format or do not maintain any data at all.
- Lack of visibility: Data is not transparent across the business. For instance, in the transportation and logistics industry, when a consumer sends the parcel, it takes days or weeks to reach the destination. While it's in the transition period, the consumer can't get the right information on the state of their parcel. For example, if the parcel is a perishable item, then is that parcel being maintained at the right temperature and humidity, or when will the end user receive the product. All these pieces of information are not visible to everyone or to relevant parties.
- Fraud and data tampering: Since the data is controlled by the central authority, they can tamper the data. Business legal agreements are managed through paper or something else which is not as much transparent and traceable, which opens the door for fraud.
- High operating cost: We spend a lot of money and time to secure servers and data from hackers. There is a high cost to maintain the authenticity of data as many intermediate, manual work, and paperwork are involved in a business.
- Middlemen: Too many middlemen are involved in the business. In agriculture, for example, the farmer often gets paid only a little percentage of money that the consumer pays. Most of the money goes to the middlemen and there is no peer-to-peer business.
What is a blockchain?
Cryptographically secured

Immutability
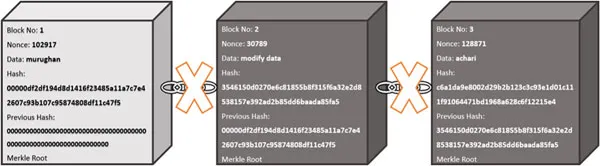
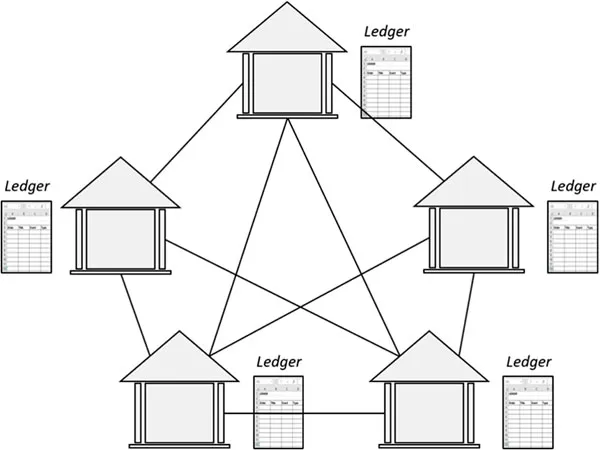
Distributed ledger

Decentralized
Smart contract
How a blockchain works
Table of contents
- Cover Page
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Dedication Page
- About the Author
- About the Reviewer
- Acknowledgement
- Preface
- Errata
- Table of Contents
- 1. An Introduction to a Blockchain
- 2. Exploring a Blockchain on AWS
- 3. Exploring the Amazon Quantum Ledger Database
- 4. Exploring Hyperledger Fabric
- 5. AWS Managed Blockchain to Create Fabric Network
- 6. Developing the Chaincode, API, and UI with the Fabric SDK on AWS
- 7. Adding Members to the Fabric Network on AWS
- 8. Deep Dive into Ethereum Blockchain
- 9. AWS Blockchain Template to Create Private Ethereum
- 10. Solidity Smart Contract Language
- 11. Create and Deploy Asset Tracker Contract on AWS
- 12. Testing and Interacting with Asset Tracker on AWS
- Index