![]()
Chapter 1: The Concept Of Human Resource Management
Chapter one introduces Human Resource Management (HRM) as both a term that defines a management function and an operating department within an organization. The chapter outlines the progressive existence of HRM and recounts various perspectives, theories, and approaches to the concept. The purpose is to ensure the reader’s understanding of the definition, evolutionary progress, opposing viewpoints, basic functions, and challenges of Human Resource Management.
Key learning objectives should include the reader’s understanding of the following:
a) The nature and concerns of HRM
b) How Human Resource Management evolved to what it is today
c) The theories governing the principles of Human Resource Management
d) The various approaches and their effect on the concept of Human Resource Management
e) Why Human Resource Management is necessary but not compulsory
f) Responsibilities and challenges for a human resource manager
Most modern organizations are victims of issues such as regulatory compliance, employee-underperformance, relatively low outputs, and many more. As a result, such organizations either become stagnant or witness a rapid decline in productivity. This decline fosters the purpose for which Human Resource Management (HRM) has either already been or should be established. Human Resource Management is consequently tasked with planning strategies to solve these problems.
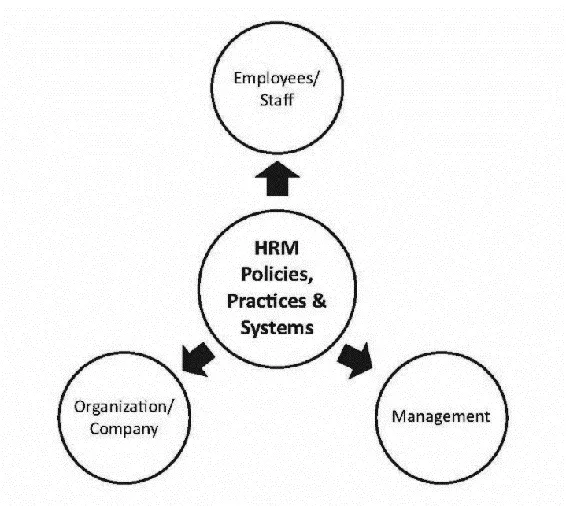
Human Resource Management is a description of formalities and established patterns targeted at creating problem-solving strategies for the progress of an organization. It is a simple scheme that employs policies, practices, and systems to close any unpromising gaps between the company, management, and staff. These impending gaps could be both abstract and concrete. However, the objective of HRM is to identify the gap(s) and implement the strategies that best impede the discord between the primary constituents of its purpose.
HRM policies, practices, and systems are developed and implemented with a focus on three primary components:
a) Company/Organization
b) Management
c) Staff/Employees
Extensively, the company includes commodified resources (i.e., an organizational commodity) for productivity. For many companies, one of the most abundant resources is humans. Thus, human resources become an essential element for productivity and subsequent organizational performance. Organizations that seek to effectively address regulatory compliance issues, employee-underperformance, low outputs, and other pain points, must first safeguard its vital resource—its employees.
Employer-employee relationships can be complicated. Because the relationship introduces both abstract and concrete interaction such as sharing ideas, behavior, emotion, human capital, tangible work products, attitudes, performance, and more, there is a delicate means by which organizations must address protecting the relationships. Human Resource Management attempts to protect the relationship that fuels the human productivity element that contributes to the organization’s success. This protection is best served by developing and implementing appropriate strategies to address issues that compromise the relationship between employees, management, and the company. Many organizations establish an individual business division or department referred to as Human Resource Management to be the developer, keeper, and enforcer of these problem-solving strategies.
Human Resource Management
The Human Resource Management division of an establishment is often tasked with duties pointing towards the general development of employees. This stems from interviews, analysis of an organizational stance – financial and proprietary, imparting excellent and yielding knowledge on employees, work discipline, curbing harassing and intimidating acts among staff in the company, and most importantly, holding and preserving the industrial and progressive relationship of an organization. Later in the text, we will explore commonly adopted and accepted general functions of HRM.
Staggering and various reports suggest the correct or appropriate human resource personnel to employee ratios. Leading consultants, SHRM (Society for Human Resource Management), business bloggers, and others have all shared what they deem to be best practices or the most common and effective strategies for when to employ HR personnel. On average, most reports and information suggest that a human resources professional should be hired when a company has approximately 40 employees. Above all, it is important to know that with the absence of this vital authority in any modern organization, there will be a series of challenges that affect the entire facets of the company. In essence, setbacks such as poor staffing, strained staff relationships, poor employer-employee connection, and various other hindrances would be everyday happenings. The key is to seek a human resource professional early enough in the process to avoid mishaps tied to compliance, law, recruitment, performance, development, retention, and separation.
1.1 Evolution of Human Resource Management
The term Human Resource Management stretches back to the ancient medieval period. However, recent studies suggest that the concept of Human Resource Management dates back to the beginning of time. Although the concept of human resources is as old as time, there is no explicit early acknowledgment of the Human Resource Management term. Further, the degree of an employer-employee relationship was more or less abysmal, which is why the concept is not so connected with the early days.
In the 1920s, new official posts were employed that promoted the growth of Human Resources. One such is the Labor Manager or Employment Manager post, which came on board as a check on the general buildup of an industry with a particular focus on labor and employees. This was mostly applicable in factories with high productivity for ease of production and production check/management. In turn, this triggered an exceptional boost in productivity at the expense of mere encouragement of employees, sometimes for a competitive advantage over other factories.
Human Resource Management moved to a fuller usage in the 1980s. However, it still surfaced in a time that failed to grasp the concept of the employer-employee relationship, which we often find present in modern-day establishments. Furthermore, it is believed to have attained its near-modern head-start from women’s desire for a secure ground for themselves and their children. Beyond this, the focus for the concept was also on the vitality of better outputs in the industries.
A Historical Perspective
Human Resource Management as a term and as a field of study did not just come to be. It passed through several phases and labor divisions to forge its prominence within organizations. Practically, the medieval period saw the rise of Human Resource Management and its procession from an era limited to agriculture to industrialization and on to post-industrialization.
Pre-Industrial Revolution
As the name implies, this revolution encompassed a limited occupation in society. The primary occupation was agriculture, accompanied by handicrafts. The idea of industrialization was lacking, and as such, the use of mostly natural resources in a natural way owned the period.
To make simple the idea, here are the three main categories notable in three aspects – slavery, serfdom, and contracted labor.
a) Human Resource Management and Slavery :
The use of humans as workforce commenced on the mounds of slavery. The source of labor was majorly slaves purchased by masters to work on farms. The masters were often less concerned or not concerned with any aspects of staffing, including wellbeing, health, and working hours. On this ground, masters were unable to filter unproductive workers from the field. Instead, unable slaves were terribly dealt with and compelled to work under difficult and sometimes impossible conditions. However, there stood a closeness between the master and the slave. A loyal slave would often get a reward of some sort or get sold out to the better working ground. Eventually, some workers would depart and establish their own industries while some others remained with their masters.
b) Human Resource Management and Serfdom :
Serfs were bound to the land and owned by feudal lords. Since the era was mainly feudal, the responsibility of serfs started and ended on agricultural grounds. Serfs enjoyed some sorts of treats from the feudal lords who often rewarded them. The reward could be in money or any valuable material thing.
c) Human Resource Management and Contracted Labor :
As time evolved, human resources changed, and this altered the overall conception of labor. The days began to witness indentured or contracted labor who enjoyed most of the liberty over slaves and serfs. Masters tended to respect the laborers during this time, and it was largely due to the contracted nature of the dealing. The masters, on seeing hardworking laborers, intended to keep them for longer periods through extended contracts or for a lifetime. To achieve this, masters introduced several work benefits, incentives, and some positive motivational influence for workers to remain happy and extend contracts.
Industrial Revolution (1750 - 1850)
The industrial revolution marked the end of the shift from agriculture to full-time industrialization. Communication was more prominent during this era than it had been in the past, and this bolstered the continuous growth of human resource acknowledgment. A salaried scale system for labor and a more passionate approach towards the treatment of workers in available industries emerged. The revolution was witnessed worldwide, and this caused unrest among the majority of workers. They needed to find practical ways to conquer the brewing situations that threatened their way of life.
Workers’ hours were complemented with low wages. To address the concern, the institution of labor unions notably sprung up around 1790, and this provided more authoritativeness for industry workers. Personnel management divisions upped their game to a more skillful pattern of handling the situations that concerned public affairs.
Robert Owen is regarded as the father of personnel management. He is noted to have brought about the idea of reforming working hours for employees. I...