Recovery and Purification of (Bio)Pharmaceuticals Using (Nano)Materials
Ana P. M. Tavares, Márcia C. Neves, Tito Trindade, Mara G. Freire CICECO - Aveiro Institute of Materials, Department of Chemistry, University of Aveiro, 3810-193 Aveiro, Portugal
Abstract
Biopharmaceuticals main classes comprise recombinant proteins, antibodies, and nucleic-acid-derived products, while synthetic pharmaceuticals include a wide variety of organic compounds. The purification of (bio)pharmaceuticals, as part of downstream processing, is mainly carried out by chromatographic processes, which are responsible for the therapeutics high cost. Therefore, there is a crucial need on the development of novel and more efficient separation/purification processes or on the improvement of the current chromatographic-based ones, aiming at producing pharmaceuticals of high quality and at a lower cost. Amongst alternative techniques, it has been demonstrated that inorganic or organic (nano)particles, used in solid-phase extraction approaches, may be promising for the purification of (bio)pharmaceuticals. This chapter provides an overview on solid-liquid separation/purification processes used to obtain high purity and high quality pharmaceuticals. The main purification processes are described and summarized. The areas where there has been a sustainable progress, combined with improved therapeutic characteristics, are highlighted. Materials based on silica (nano)particles, carbon-based (nano)particles (carbon nanotubes, graphene and activated carbon) and magnetic (nano)particles are overviewed. Based on the reported results, nanotechnology may play a key role in future pharmaceutical developments and manufacturing, where the design of suitable functionalized (nano)particles is a crucial factor to enhance the selectivity and to obtain high purification and recovery yields of (bio)pharmaceuticals.
Keywords: (Bio)pharmaceuticals, Carbon-based (Nano)particles, Downstream Processing, Magnetic (Nano)particles, Nanotechnology, Pharmaceuticals Manufacturing, Purification Techniques, Silica (Nano)particles, Solid-liquid Extraction, Solid-phase Extraction.
* Corresponding author Mara G. Freire: CICECO - Aveiro Institute of Materials, Department of Chemistry, University of Aveiro, 3810-193 Aveiro, Portugal; E-mail: [email protected] INTRODUCTION
Pharmaceutical industries are indispensable for all public and private health care
systems, and are responsible for the development, production and marketing of pharma products. Increasing market competition has prompted this sector to the search of new manufacturing processes, for which the pharmaceutical industry and academia have contributed to new production/recovery technologies for drugs [1].
The main pharmaceutical companies, known as Big Pharma, consist however, on a small number of big multinational industries, such as Roche, Novartis, Astra- Zeneca, GlaxoSmithKline (GSK), Eli Lilly, Sanofi, Johnson & Johnson, Merck, and Pfizer [1, 2].
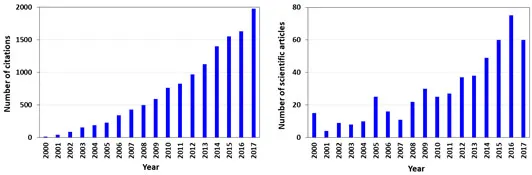
Advances in the discovery of novel pharmaceuticals, with improved therapeutic efficacy and reduced side effects, contributed for the fast development of pharmaceutical industries [3]. Significant progresses in pharmaceuticals have been achieved by the optimization of both the upstream (production) and downstream (purification and recovery of the target product from complex media) processing, which include the search on new technologies and adaptation of the existing unit operations to increase efficiency, without the increase of the final product cost [4, 5]. In pharmaceutical industries, the lack of efficient downstream processes can seriously affect the success of a new product and even results in its failure. Thus, the search on alternative, more efficient and less costly downstream processing technologies is of crucial importance for the manufacturing of pharmaceuticals. In the past years, more than 60 scientific manuscripts addressing ‘pharmaceuticals’ and ‘downstream processing’ were published. Fig. (1) under- lines the scientific publications trend in this field since 2000.
Fig. (1)) Number of scientific articles and total citations referring to “pharmaceuticals and downstream processing”, from 2000 to 2017 (search on the ISI Web of Knowledge, May 2018).
In this book chapter, an overview on pharmaceutical industry processes, on existing methods for process optimization and integration, and on innovative approaches, is provided. In particular, downstream processing technologies based on the use of (nano)particles for the purification of (bio)pharmaceuticals are presented and discussed in detail.
SEPARATION AND PURIFICATION OF PHARMACEUTICALS
Classical pharmaceuticals are low molecular weight organic compounds, known as medicines or drugs, used as main active compounds in today’s therapeutic approaches. These compounds comprise more than 90% of the currently available drugs [6]. On the other hand, biological compounds with therapeutic activity, known as biopharmaceuticals, biotechnology medicines or biologics, are pharma- ceuticals derived from living organisms, such as bacteria, yeast, animal or human cells, viruses, and transgenic animals or plants [7]. The designation of ‘bio- pharmaceutical’ was first adopted in the 80’s [8], and then used to define a class of therapeutic proteins produced by genetic engineering or by hybridoma technology [8]. Currently, biopharmaceuticals represent one of the most promising frontiers in medicine [6]. Biopharmaceutical products include vaccines, cell or gene therapies, plant extracts, recombinant therapeutic proteins, cytokines and tissue growth factors, blood components or derivatives, among others [9, 10]. The first manufactured biopharmaceutical, approved in 1982 by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), was the recombinant DNA human insulin produced by Escherichia coli [11, 12]. Currently, up to 650 protein-based biopharma- ceuticals have been approved worldwide [13]. Biopharmaceuticals can be applied not only in the treatment of diverse diseases, but also in clinical diagnosis and prevention strategies [8, 14]. It is however required that such products are safe, effective, of good quality, and prescribed and used rationally.
Biopharmaceuticals are distinct from chemical drugs. Synthetic drugs are small organic molecules, typically obtained through chemical synthesis. On the other hand, almost all biologic-derived pharmaceuticals are composed of more structural complex molecules with high molecular weight. As a result, the full characterization of biopharmaceuticals is more difficult to achieve [15, 16]. Fig. (2) illustrates the chemical structure of a traditional small synthetic molec...