
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Calculus: The Logical Extension of Arithmetic
About this book
Calculus: The Logical Extension of Arithmetic re-examines the calculus paradigm by expanding the set of 'indeterminate forms' espoused by l'Hôpital 320 years ago. Starting from the 54 possible binary combinations of the foundational numbers (zero, one and infinity), a replacement for the function theory formulated earlier by Newton and Leibniz, is presented. A logical extension of the three concepts of differentiation, integration and the Naperian base number e follows this introduction, which is interpreted as 'zero divided by zero', 'infinity times zero' and 'one raised to the infinite power', respectively. The concept that a number postulated as representing 'nothing' is reinforced a useful connection to calculus theory. This treatise proposes a 'similar' number to denote and quantify 'all', in order to understand the concept of infinity. Other topics covered in this text include analytical geometry, infinite sequences and infinite series.
Calculus: The Logical Extension of Arithmetic is a useful reference on advanced calculus theory for mathematics students and researchers.
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
Zero Divided by Zero − and the Concept of Differentiation
Abstract
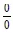
Table of contents
- Welcome
- Table of Contents
- Title
- BENTHAM SCIENCE PUBLISHERS LTD.
- Calculus as the Logical Extension of Arithmetic, rather than as a Whole New Subset of Mathematics
- Re-Examination of Basic Algebra and Trigonometry
- Zero Divided by Zero − and the Concept of Differentiation
- Infinity Times Zero and the Concept of Integration
- Analytic Geometry
- One Raised to the Infinite Power, the Concept of Natural Logarithms, and Hyperbolic Trigonometry
- Infinite Sequences and Series