
eBook - ePub
Fundamentals of Materials Engineering - A Basic Guide
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
Fundamentals of Materials Engineering - A Basic Guide
About this book
Fundamentals of Materials Engineering - A Basic Guide is a helpful textbook for readers learning the basics of materials science. This book covers important topics and fundamental concepts of materials engineering including crystal structure, imperfections, mechanical properties of materials, polymers, powder metallurgy, corrosion and composites. The authors have explained the concepts in an effective way and by using simple language for the benefit of a broad range of readers. This book is also beneficial to the students in engineering courses at B.Sc, M.Sc, and M.Tech. levels.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
The Structure Of Materials
R. Shashanka, Orhan Uzun
Abstract
Do you know all the materials are made up of atoms? And there are different types of atoms named as elements? Have you ever wondered why an atom consists of electrons, protons, and neutrons? Do you know the number of electrons in the outer shell depicts the number of atoms present? Can you tell me why metals are ductile compared to hard and brittle ceramics? Why ductile iron becomes harder when we add a small amount of carbon? Why some materials act as conductors of heat and electric current and some are insulators [1]? To understand all these concepts one should learn the atomic structure, chemical bonding, structure of amorphous and crystalline materials. The present chapter describes all these concepts in a very simple way.
Keywords: Amorphous materials, BCC, Covalent bonding, Crystalline materials, FCC, Ionic bonding, Lattice points, Macrostructure, Metallic bonding, Micro-structure, Nanostructure, Radius ratio, Unit cells, Van der Waals bonding.
1. INTRODUCTION
In this chapter, we will discuss how the microstructure, composition, and processing method of the materials control their different properties. The structure of an atom is shown in Fig. (1) [2].
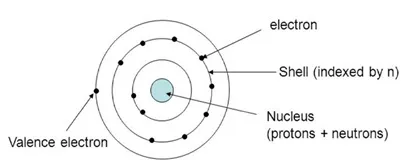
Structure of an atom [2].
The structures of materials are classified mainly based upon their sizes; (i) atomic structure, (ii) microstructure, and (iii) macrostructure as shown in Fig. (2) [2-4].
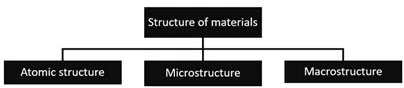
Classification of materials.
The atomic structure consists of those features that cannot be seen through our naked eyes; like bonding between atoms and how the atoms are arranged.
As we know, the atoms are composed of electrons, protons, and neutrons, where, electrons are negatively charged particles and protons are positively charged particles, neutrons have a neutral charge. The magnitude of each charged particle in an atom is 1.6×10-19 Coulombs. Both neutrons and protons have almost the same masses; whereas electrons show negligible mass. The unit of mass is an atomic mass unit (amu) =1.66×10-27 kg and equals 1/12th mass of a carbon atom. The Carbon nucleus has Z=6, and A=6, where 'Z' is the number of protons, and 'A' the number of neutrons. Neutrons and protons have very similar masses, roughly equal to 1 amu each [5-7]. A neutral atom has the same number of electrons and protons, Z.
Microstructure involves the features that can be easily seen by using an optical or electron microscope as shown in Fig. (3) [8]. The word “microstructure” is used to explain the appearance of the materials on the nanometer-centimeter length scale. When we describe the microstructure of the material; it is very important to consider the length scale because different length scales will give different microstructural features [8].
Macrostructure is the one that can be seen with little or no magnification or can be seen with naked eyes. Generally, the macrostructure investigations are performed on flat samples, called templates, and also on the fracture surfaces of the materials. To investigate the topography of the structure, the surface of the template is polished and carefully etched with acid or alkaline solutions. The macrostructure study reveals the discontinuity of the metal surface due to cavities, gas bubbles, porosity, etc.; and it also reveals the distribution of impurities, crystallites, and inclusions in different parts of the material. The macrostructure study plays an important role in determining the initial quality of the materials [9].
The chemical, physical, thermal, electrical, magnetic, and optical properties of all materials mainly depend upon their structure. Nevertheless, micro and macrostructure not only influence mechanical but also other properties. Atomic bonding affects the strength of metals by holding the atoms together by strong bonds. As we know that metals can be formable only when bonds allow atoms to move freely inside the materials. To understand this, we should discuss how the atoms are arranged and bonded in a material.

Microstructure of steel [8].
2. ATOMIC BONDING
To understand the behavior of materials and wide differences in their properties, it is neces...
Table of contents
- Welcome
- Table of Content
- Title
- BENTHAM SCIENCE PUBLISHERS LTD.
- FOREWORD
- PREFACE
- Introduction to Materials Engineering
- The Structure Of Materials
- Imperfections or Defects in Crystals
- Mechanical Properties of Materials
- Polymers
- Powder Metallurgy
- Corrosion
- Composites
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription
No, books cannot be downloaded as external files, such as PDFs, for use outside of Perlego. However, you can download books within the Perlego app for offline reading on mobile or tablet. Learn how to download books offline
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 990+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn about our mission
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more about Read Aloud
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS and Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Yes, you can access Fundamentals of Materials Engineering - A Basic Guide by Shashanka Rajendrachari,Orhan Uzun in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Technology & Engineering & Materials Science. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.