
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Comprehensive Practical Hepatology
About this book
Acute and chronic liver disease is a global endemic healthcare concern. More than 500 million people around the world are infected with the hepatitis B or C virus. Approximately 500, 000 patients die of hepatocellular carcinoma every year, implying that trained healthcare professionals and facilities for liver disease patients is a critical issue. Although promising therapies have been developed for viral hepatitis infections, management of liver cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma yet many patients suffer due to lack of adequate healthcare by professional hepatologists. This means that primary care physicians should be informed about diagnosing liver disease and the early management of viral hepatitis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Comprehensive Practical Hepatology provides readers current standard primary care guidelines for treatment and early stage management of patients with liver function abnormalities. This book provides a practical approach for physicians to apply on patients with apparent liver function abnormalities. The guidelines also cover: Acute and chronic liver injury, Information about the liver in systemic diseases, Drug usage in liver diseases, Surgical risk in liver disease patients, and, Recommendations for pregnant as well as elderly patients. Comprehensive Practical Hepatology thus provides complete practical advice on the management of liver diseases to non-hepatologists and general physicians.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
Approach to Patients with Chronic Liver Injury
KEY POINTS
- History taking and physical examination are important in the differential diagnosis of chronic liver injury, with history of alcohol or drug taking essential in diagnosing liver disease caused by these materials.
- Type of liver injury should be classified as hepatocellular, cholestatic or mixed, because classification can help narrow the causes of liver injuries and suggest additional and effective history taking or physical examination.
- Symptoms in patients with chronic liver diseases are nonspecific, with the most common being fatigue. Although patients with advanced liver cirrhosis often complain of pruritus, anorexia, leg edema and/or abdominal distension due to ascites retention, most patients with chronic hepatitis and early stage cirrhosis are asymptomatic.
- Differential diagnosis can be a step-by-step process in the absence of severe or advanced liver injury. Elevated T-Bil (>2.0 mg/dl) or elongation of prothrombin time (PT) may suggest severe injury. Although marked elevation of serum aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and/or alanine aminotransferase (ALT) is also an indicator of severe liver injury, there is no clear threshold.
- Frequency of etiologies of chronic liver injury may differ geographically or ethnically, with the order of blood tests based on the prevalence of each disease in that area.
- Primary care providers should be aware of the diagnostic criteria for common chronic liver diseases. These providers should also be familiar with methods used to initially assess liver injury, as well as when to refer patients to specialists.
- Liver biopsy is useful not only to identify etiology, but to determine the grading and staging of liver disease and to assess the likelihood of progression to cirrhosis or liver failure.
- Cirrhosis is often diagnosed by a combination of laboratory data and patient signs and symptoms. In particular, AST/ALT>1, hypergammaglobulinemia and low platelet count (<100,000/μL) support a diagnosis of cirrhosis. Imaging modalities are also helpful diagnostically, and the presence of portal hypertension (suggested by splenomegaly, enlarged portal vein or esophageal varices) strongly supports a diagnosis of cirrhosis.
- Patients with advanced chronic liver diseases are at high risk for the development of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), and should be assessed by imaging modalities such as ultrasound (US), CT, and MRI, or by measuring serum concentrations of tumor markers, such as alpha-fetoprotein and des-γ-carboxy prothrombin at regular intervals.
INTRODUCTION
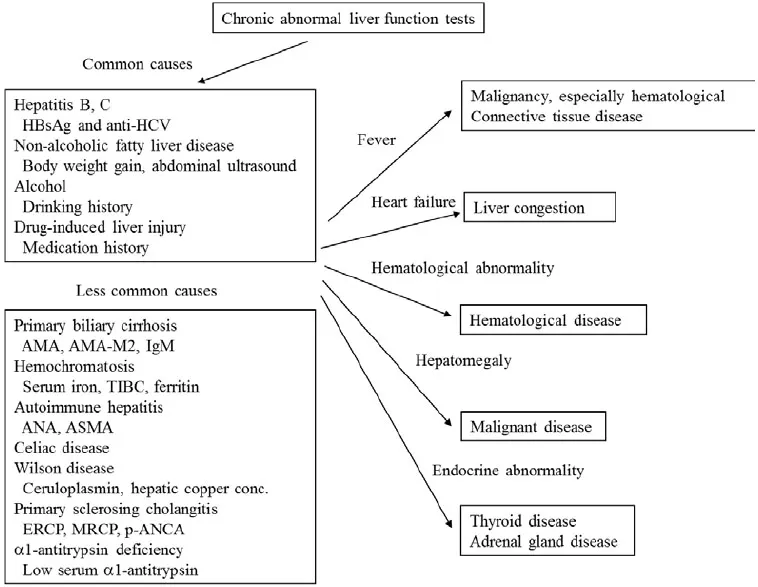
HISTORY TAKING
- Use or exposure to medications or chemicals.
- Family history of liver disease.
- History of hepatitis.
- Alcohol consumption.
- History of blood transfusion.
- History of abdominal operation.
PHYSICAL EXAMINATION
- Jaundice may suggest advanced liver disease or cholestasis.
- Brown skin color may suggest hemochromatosis.
- Skin eruption may suggest drug allergy or cholestasis.
- Xanthelasmata or xanthomata may suggest chronic cholestasis, usually in patients with primary biliary cirrhosis.
- Struma may suggest complicating thyroiditis in patients with autoimmune liver diseases.
- Spider nevi, palmar erythema, gynecomastia, caput medusae, testicular atrophy or muscle wasting may suggest liver cirrhosis.
- Jugular vein dilatation may suggest right-sided heart failure, which could lead to liver congestion.
- Dilated superficial veins of the abdominal wall may represent portal hypertension.
- Hepatomegaly
- Splenomegaly
Table of contents
- Welcome
- Table of Contents
- Title
- BENTHAM SCIENCE PUBLISHERS LTD.
- FOREWORD
- PREFACE
- Symptoms and Signs Suggestive of Liver Disease
- Diagnostic Strategies for Patients with Abnormal Liver Function Tests
- Approach to Patients with Acute Liver Injury
- Approach to Patients with Chronic Liver Injury
- Diagnostic Strategies and Treatment of Liver Tumors
- Liver Function Abnormalities in Systemic Disease
- Sytemic Abnormalities in Liver Disease
- Infection and Liver
- Approach to Liver Injury Caused by Drugs and Toxins
- Risk of Surgery and Drug Therapy in Patients with Liver Disease
- Approach to Children with Abnormal Liver Function Tests Results
- Practical Management of Elderly Patients with Liver Injury
- Practical Management of Pregnant Women with Liver Injury
- Lifestyle Recommendation for Patients with Liver Diseases
- Medical Management of Patients Following Liver Transplantation
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app