
- 750 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
SAP HANA 2.0 Administration
About this book
Novice or expert, this is your one-stop shop for administering SAP HANA 2.0! You'll begin with a deep dive into database and engine architecture. Then explore your key tools: SAP HANA cockpit, SAP HANA Studio, the command-line interface, and more. From there, choose the topics you need. Backup and recovery? High availability? Data tiering? Security? Objects, tables, and transactions? All covered within these pages! From installation to performance tuning, this book has it all. Highlights include: 1) Installation and updates
2) Architecture
3) SAP HANA cockpit
4) SAP HANA Studio
5) Persistency
6) High availability/disaster recovery
7) Scale-out systems
8) Data tiering
9) Objects and tables
10) Security
11) Performance
12) Monitoring
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription.
At the moment all of our mobile-responsive ePub books are available to download via the app. Most of our PDFs are also available to download and we're working on making the final remaining ones downloadable now. Learn more here.
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 1000+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn more here.
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more here.
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS or Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Yes, you can access SAP HANA 2.0 Administration by Mark Mergaerts,Bert Vanstechelman in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Computer Science & Computer Science General. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.
Information
1 SAP HANA Overview
SAP HANA is an in-memory, column-oriented, relational database system capable of handling huge amounts of data. SAP HANA can be used in a variety of scenarios. In this chapter, we give an overview of the SAP HANA capabilities and the different use cases in which SAP HANA brings added value to your business.
SAP HANA is a column-store in-memory database capable of handling huge amounts of memory in real time. SAP HANA allows you to deploy online transaction processing (OLTP) and online analytical processing (OLAP) applications in the same database without the need to duplicate data in aggregates.
SAP HANA is much more than just a database. The software appliance layer includes SAP HANA extended application services, which allows you to develop and run your own applications on top of the database system. There is a full-text processing and search engine capable of handling structured and unstructured data. Some features are delivered as add-ons, such as SAP HANA Predictive Analysis Library (PAL) and SAP HANA Business Function Library (BFL). Data provisioning and data integration are supported using real-time replication tools.
The speed of SAP HANA isn’t only related to its in-memory capabilities. The concept of the column store plays an important role in its performance increase. This a fundamental concept will be discussed in detail in the next section. After the explaining the concept of the column store, we’ll dive into the specific hardware requirements for SAP HANA, after which we continue with the use cases for an in-memory database, data provisioning, advanced analytics, and data integration.
1.1 The Column Store
One specific feature you should certainly be aware of is the distinction between a column store and row store. Combined with the in-memory storage of the database, the column store is a key factor in the tremendous performance that an SAP HANA database is able to deliver.
The traditional concept of a table in a relational database is row-oriented: one row, made up of a series of columns or fields, is followed by the next row, containing these same columns, and so on. This is also the way data is stored in a conventional relational database. While row-based storage is generally a good solution for transactional (OLTP) access, it has a significant drawback in an analytical (OLAP) context, where typically large volumes of data are queried using complex selection criteria. A very simple one-table example will illustrate this: a table contains, among others, the fields CUST (customer), ORDNR (order number), and PURCH_DATE (purchase date). In a row-based table, this looks schematically as shown in Figure 1.1.
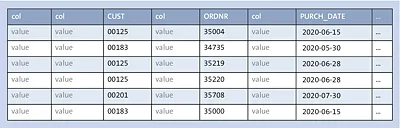
Figure 1.1 Row-Based Table
Suppose that an OLAP query wants to retrieve all orders made by customer 00125 with a purchase date in the second quarter of 2020. The database engine will scan the table for matching column values, but in a row-store table, the average distance between two consecutive values for a given column is the average physical length of an entire table row. If, for example, the average row length is 1,000 bytes and the database has a physical data block size of 8 KB, then only eight sets of column values can be read per data block. As a result, the scanning process may have to traverse a huge number of data blocks, not all of which will be present in the data cache in memory, thus causing an expensive disk read. Conventional databases can mitigate this to some extent by creating indexes, but each additional index imposes extra write overhead, and indexes are therefore best restricted to the columns most often used in queries.
There is a neat architectural solution to this problem: what if the data were stored column by column instead of row by row? All customer values would be tightly packed together, and so would the other columns. Large sets of values could then be scanned at immense speed. Adding indexes to get decent performance would become unnecessary. The idea of column-based data storage is not new, and SAP HANA is not the only database to have it; for example, SAP IQ (formerly Sybase IQ) is also a column-based database, but it uses traditional disk storage, not in-memory storage. In the case of SAP HANA, the combination of in-memory storage and use of a column store makes it possible to obtain query results in seconds instead of hours. (Sorry, that sounds like marketing talk—but it’s the truth.)
Column-based storage in SAP HANA goes several steps further than simply organizing the data in columnar fashion. The amount of data for each column is further reduced by using various methods of data compression. The most important of these is dictionary-based encoding, which replaces actual column values (like character strings) with a simple, compact reference. In the end, the column-store counterpart of our example might look like the tables in Figure 1.2 (again, this is an oversimplification).
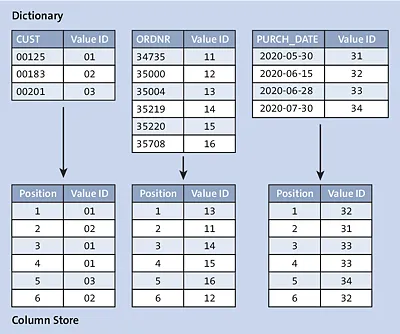
Figure 1.2 Column-Based Table
The top half of the figure shows the dictionaries for the three columns, where each distinct value is assigned a simple and short identifier. The bottom ha...
Table of contents
- Dear Reader
- Notes on Usage
- Table of Contents
- Preface
- 1 SAP HANA Overview
- 2 Architecture of the SAP HANA System
- 3 Administration Tools
- 4 Instance Administration
- 5 Database Administration
- 6 System Replication
- 7 Scale-Out Systems and High Availability
- 8 Data Tiering
- 9 Planning and Setting Up the SAP HANA Landscape
- 10 Installation and Updates
- 11 Database Objects
- 12 Working with Tables
- 13 Security
- 14 Performance Analysis
- 15 Monitoring and Troubleshooting
- A Setting Up Your Trial System
- B References and Further Reading
- C The Authors
- Index
- Service Pages
- Legal Notes