
- 352 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
About this book
This textbook introduces the reader to quantum theory and quantum chemistry. The textbook is meant for 2 nd – 3 rd year bachelor students of chemistry or physics, but also for students of related disciplines like materials science, pharmacy, and bioinformatics.
At first, quantum theory is introduced, starting with experimental results that made it inevitable to go beyond classical physics. Subsequently, the Schrödinger equation is discussed in some detail. Some few examples for which the Schrödinger equation can be solved exactly are treated with special emphasis on relating the results to real systems and interpreting the mathematical results in terms of experimental observations.
Ultimately, approximate methods are presented that are used when applying quantum theory in the field of quantum chemistry for the study of real systems like atoms, molecules, and crystals. Both the foundations for the different methods and a broader range of examples of their applications are presented.
The textbook assumes no prior knowledge in quantum theory. Moreover, special emphasis is put on interpreting the mathematical results and less on an exact mathematical derivations of those. Finally, each chapter closes with a number of questions and exercises that help in focusing on the main results of the chapter. Many of the exercises include answers.
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
1 What is quantum theory?
1.1 Classical physics
- Position and momentum coordinates are independent of each other and can have arbitrary values.
- If one knows the position and momentum of an object at a certain point in time, as well as all forces acting on the object, the position and momentum coordinates at any later time, in principle, can be computed with any precision.
- The energy of an object can take any value.
- A part of physics deals with bodies, while another part deals with waves. The two parts have little to do with each other.
1.2 Black-body radiation
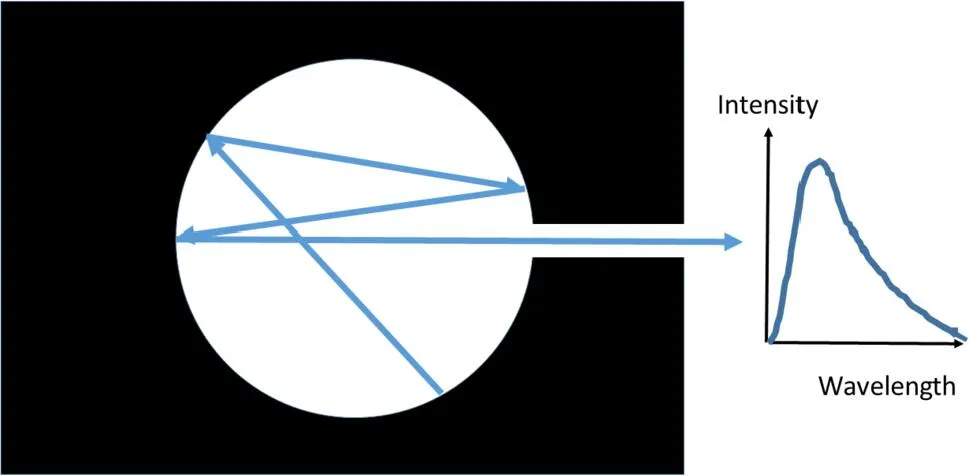
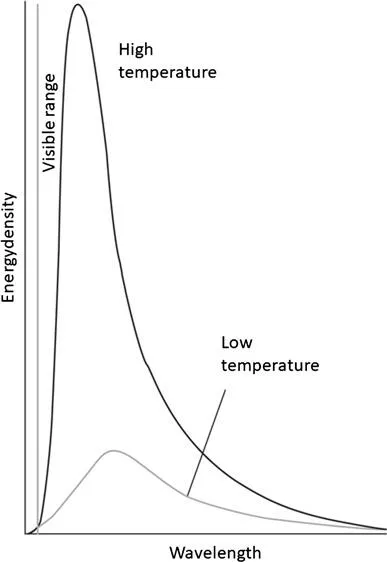
Table of contents
- Title Page
- Copyright
- Contents
- 1 What is quantum theory?
- 2 Basics of quantum theory
- 3 Operators and quantum theory
- 4 Particle in a box
- 5 More or less free particles
- 6 Vibrations
- 7 Rotations
- 8 The hydrogen atom
- 9 Foundations of the approximate methods
- 10 The orbital model
- 11 Atoms
- 12 The smallest molecules
- 13 Other diatomic molecules
- 14 Larger systems: methods
- 15 Larger systems: applications
- 16 Supporting information
- 17 Mathematical formulas
- Subject Index