
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Handbook of Oral Pathology and Oral Medicine
About this book
Discover a concise overview of the most common oral diseases in a reader-friendly book
Handbook of Oral Pathology and Oral Medicine delivers a succinct overview of a range of oral diseases. The book contains up-to-date evidence-based information organized by clinical topic and supported by over 300 clinical, radiological, and microscopic images. Each chapter includes topics following universally respected curricula of oral pathology and oral medicine.
Divided into seven parts, it covers core topics such as pathology of teeth, pulp, and supporting structures, pathology of jawbones, pathology of the oral mucosa, pathology of the salivary glands, clinical presentation of mucosal disease, orofacial pain, and miscellaneous topics of clinical relevance.
Written for undergraduate dental students, dental hygienists and oral health therapists, Handbook of Oral Pathology and Oral Medicine is an ideal quick reference and is also useful to dental educators and practitioners.
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
Part I
Pathology of Teeth and Supporting Structures
1
Disorders of Tooth Development and Eruption
CHAPTER MENU
- 1.1 Anodontia, Hypodontia and Oligodontia
- 1.2 Hyperdontia (Supernumerary Teeth)
- 1.3 Microdontia and Macrodontia
- 1.4 Gemination, Fusion and Concrescence
- 1.5 Taurodontism and Dilaceration
- 1.6 Amelogenesis Imperfecta
- 1.7 Dentinogenesis Imperfecta
- 1.8 Dentinal Dysplasia (Dentin Dysplasia)
- 1.9 Regional Odontodysplasia (Ghost Teeth)
- 1.10 Delayed Tooth Eruption
- 1.11 Tooth Impaction (Impacted Teeth)
- 1.12 Dens Invaginatus and Dens Evaginatus
- 1.13 Fluorosis (Mottled Enamel)
- 1.14 Tetracycline‐Induced Discolouration of Teeth: Key Features
- 1.15 Enamel Pearl: Key Features
- 1.16 Talon Cusp: Key Features
- 1.17 Hutchinson's Incisors and Mulberry Molars: Key Features
- 1.18 Tooth Ankylosis: Key Features
- 1.19 Supernumerary Roots: Key Features
1.1 Anodontia, Hypodontia and Oligodontia
1.1.1 Definition/Description
- Anodontia: All teeth are developmentally (congenitally) missing
- Hypodontia: one to six developmentally (congenitally) missing teeth except the third molars
- Oligodontia: more than six developmentally (congenitally) missing teeth
1.1.2 Frequency
- Anodontia: extremely rare
- Hypodontia: incidence: 4.4–13.4%. The most common developmental anomaly
- Oligodontia: incidence: 0.25%
- Hypodontia of the deciduous teeth affects less than 1% of children
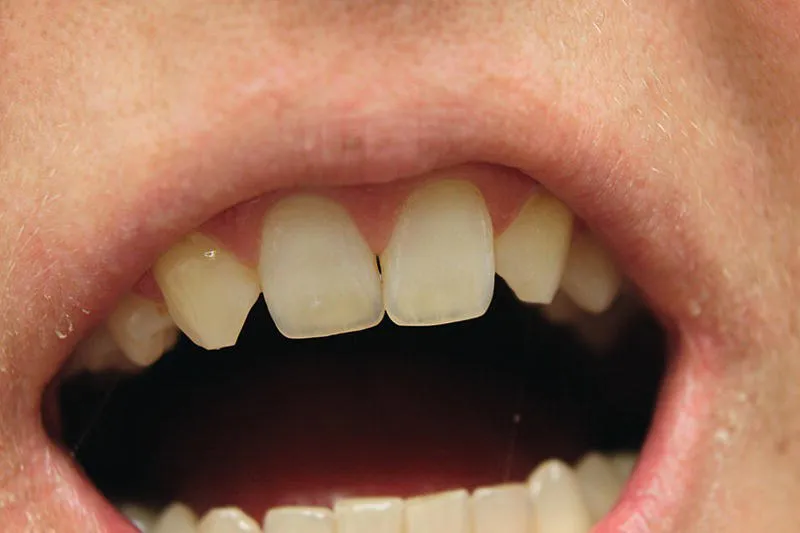 Figure 1.1 Hypodontia: clinical photograph of missing maxillary lateral incisors(source: Bin im Garten, https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Hypodontie_der_zweiten_oberen_Schneidz%C3%A4hne_IMG_1726.webp. Licensed under CC BY‐SA 3.0).
Figure 1.1 Hypodontia: clinical photograph of missing maxillary lateral incisors(source: Bin im Garten, https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Hypodontie_der_zweiten_oberen_Schneidz%C3%A4hne_IMG_1726.webp. Licensed under CC BY‐SA 3.0).
1.1.3 Aetiology/Risk Factors
- Anodontia: mutations in EDA, EDAR and EDARADD genes
- Hypodontia: mutations in MSX1, PAX9, IRF6, GREM2, AXIN2, LRP6, SMOC2, LTBP3, PITX2 and WNT10B. WNT10A genes
- Oligodontia: mutations in MSX1, PAX9, IRF6, GREM2, AXIN2, LRP6, SMOC2, LTBP3, PITX2 and WNT10B. WNT10A genes
- Environmental factors: hypodontia can result from trauma to the developing dental tissues such as chemotherapy or radiotherapy
1.1.4 Clinical Features
- The most common missing multiple teeth (other than third molars) are:
- Maxillary lateral incisors (Figure 1.1). This is followed by the mandibular second premolars and maxillary second premolars
- Skin/nails/hair/sweat glands may be affected in some cases of hypodontia
- Morphology of teeth may be defective (micr...
Table of contents
- Cover
- Table of Contents
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Dedication Page
- Foreword
- Preface
- Acknowledgements
- About the Companion Website
- Nomenclature Used in The Study of Human Disease
- Standard Abbreviations for Prescribers
- Part I: Pathology of Teeth and Supporting Structures
- Part II: Pathology of Jaw Bones
- Part III: Pathology of the Oral Mucosa
- Part IV: Pathology of the Salivary Glands
- Part V: Clinical Presentation of Mucosal Disease
- Part VI: Orofacial Pain
- Part VII: Miscellaneous Topics of Clinical Relevance
- Index
- End User License Agreement