
- 600 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
Project Management with SAP Project System
About this book
Jumpstart your next project with this comprehensive guide to SAP Project System (PS). From development to invoicing, map out and manage each project phase with PS, which can be customized to a wide range of industry-relevant processes and workflows. This new edition covers mobility enhancements, SAP HANA-based reporting, and details on the new SAP Commercial Project Management tool. Let's get to work!
Highlights:
- Master data maintenance
- Budgeting functions
- Work breakdown structure and network
- Results analysis, cost forecast, overhead rates
- Time scheduling and resource planning
- Milestones, confirmations, material procurement
- Mobile solutions
- SAP Portfolio and Project Management
- SAP HANA-based reporting
- SAP Commercial Project Management
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
In SAP Project System, structuring projects is the basis for all subsequent project management steps. Therefore, selecting the right structures and an efficient structuring process are critical when managing your projects.
1Structures and Master Data
A prerequisite of project management using SAP Project System is the mapping of projects in the SAP system via appropriate structures. These structures form the basis for planning, entering, and analyzing all data that is relevant to a project. For this purpose, SAP Project System provides two structures: work breakdown structures (WBS) and networks. These two structures differ in the way they enable you to structure projects and in the functions provided for them in the SAP system. For example, if you need a hierarchical budget management function for a project, then you would want to use a work breakdown structure. If you also want to perform capacity requirements planning for the same project, then you would have to use networks as well.
We begin this chapter with a description of the basic differences between work breakdown structures and networks and the authorization concept of SAP Project System, which was already enhanced for Enhancement Package (EHP) 3. Then we will discuss the essential master data of the two structures and milestones, documentation options, and Customizing activities that are necessary in a structuring process. Statuses play a major role in controlling projects. We will show you the functions that statuses are responsible for in SAP Project System and how you can define your own statuses. We will also introduce you to the transactions and tools you can use for structuring purposes and for processing master data. You will learn how to use versions of SAP Project System to document the progress of a project and for what-if scenario analyses. Finally, we’ll describe the different steps and necessary prerequisites for archiving and deleting project structures.
1.1Basic Principles
Depending on your specific requirements, you may only be able to map a project via a work breakdown structure, or only by using networks, or a combination of both.
Figure 1.1 illustrates the different structuring options. The symbols used for the different structure objects in the figure correspond to the symbols used in the SAP system to represent those objects. The following sections describe the basic differences between the different structuring options.
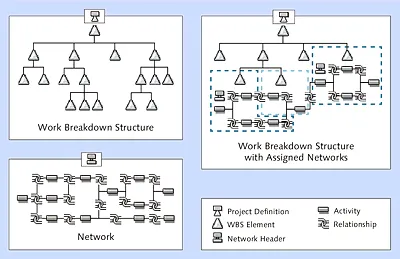
Figure 1.1Usage Options of Work Breakdown Structures (WBS) and Networks to Structure Projects
1.1.1Overview of Project Structures
Work breakdown structures enable you to map the structure of a project in the SAP system. This is done via WBS elements that are located at different levels and that structure the project hierarchically (see Figure 1.2). An advantage of a hierarchical structure is that within the structure, data can be inherited or distributed in the top-down direction, and it can be aggregated or summarized in the bottom-up direction.
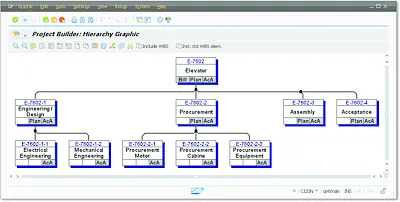
Figure 1.2Hierarchical Structure of a Work Breakdown Structure (Hierarchy Graphic)
You can use WBS elements to structure your projects (for example, based on phases, functions, or organizational aspects) at the individual level. There is no universal recommendation with regard to how you should structure a project using a work breakdown structure. Instead, the selection of appropriate structures depends on many different aspects and should be carefully thought out before a project starts. Section 1.2 has some general tips on how you can structure projects using a work breakdown structure.
The following list provides an overview of important functions of work breakdown structures in the SAP system:
- Planning and entering dates
- Cost planning and account assignment of documents
- Planning and invoicing revenues
- Planning and monitoring payment flows
- Hierarchical budget management
- Material stock management
- Various period-end closing tasks
- Monitoring a project’s progress
- Aggregated data analysis
Because of their functional scope, work breakdown structures that are not assigned to networks are typically used to map projects that focus on controlling aspects and therefore require fewer logistical functions. These kinds of projects usually involve overhead cost or investment projects. Work breakdown structures are also frequently used in real life due to their controlling functions, and actual project management tasks are performed using other project management tools (see Chapter 7). Work breakdown structures are also used, for example, instead of internal orders, because a WBS enables you to carry out hierarchical project controlling activities. For example, you can distribute a budget to individual parts of a project within a work breakdown structure. This is not possible if you use internal orders.
You can use one or several networks to map the flow of a project or of parts of a project in the SAP system. To do this, you need networks that are linked to each other via relationships (see Figure 1.3).
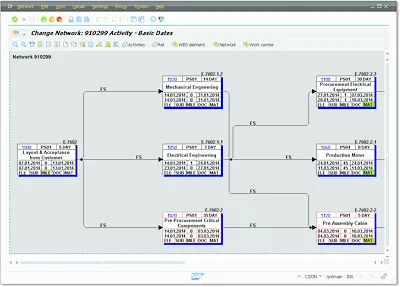
Figure 1.3Flow Structure of a Network (Network Graphic)
The relationship between two activities defines the logical sequence of the activities (predecessor-successor relationship) and their time-based interdependencies. You can also map project flows across different networks by linking activities of different networks to each other. An essential advantage of the network technique is that SAP systems can automatically determine planned dates for each activity and the entire network on the basis of the duration of individual activities and their chronological sequence. In addition, the system can also determine floats and time-critical activities.
The following list provides an overview of important functions of networks in the SAP system:
- Scheduling
- Resource planning
- Confirmation of work
- External procurement of services
- Material requirements planning, procurement, and delivery
- Network costing
- Various period-end closing tasks
- Monitoring a project’s progress
Because of their functionality, networks are predominantly used to map projects in which logistical functions, such as automatic time scheduling, resource planning, or the procurement of materials, are required. You can use networks independently of or in conjunction with a WBS.
To utilize the functions and benefits of work breakdown structures and networks at the same time, you can assign network activities to WBS elements. A WBS element can be assigned several activities (even from different networks, if required); however, an activity can only be assigned to a maximum of one WBS element. Once you have assigned activities to WBS elements, you can exchange data between the work breakdown structure and the activities. For example, activities can inherit statuses from the WBS elements they are assigned to. Conversely, you can total up project activity dates to the WBS elements or check funds allotted to activities against the budget of the WBS elements. In reporting, you can obtain an aggregated analysis of the data of assigned activities at the level of WBS elements.
In general, the structures available in SAP...
Table of contents
- Dear Reader
- Notes on Usage
- Contents
- Introduction
- 1 Structures and Master Data
- 2 Planning Functions
- 3 Budget
- 4 Project Execution Processes
- 5 Period-End Closing
- 6 Reporting
- 7 Integration Scenarios with Other Project Management Tools
- A BAPIs in SAP Project System
- B Query and Reuse Views of SAP Project System in SAP HANA Live
- C Selected Project System Database Tables
- D Transactions and Menu Paths
- E The Author
- Index
- Service Pages
- Legal Notes
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription
No, books cannot be downloaded as external files, such as PDFs, for use outside of Perlego. However, you can download books within the Perlego app for offline reading on mobile or tablet. Learn how to download books offline
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 990+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn about our mission
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more about Read Aloud
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS and Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Yes, you can access Project Management with SAP Project System by Mario Franz in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Computer Science & Computer Science General. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.