
Applied Learning Algorithms for Intelligent IoT
- 356 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Applied Learning Algorithms for Intelligent IoT
About this book
This book vividly illustrates all the promising and potential machine learning (ML) and deep learning (DL) algorithms through a host of real-world and real-time business use cases. Machines and devices can be empowered to self-learn and exhibit intelligent behavior. Also, Big Data combined with real-time and runtime data can lead to personalized, prognostic, predictive, and prescriptive insights. This book examines the following topics:
- Cognitive machines and devices
- Cyber physical systems (CPS)
- The Internet of Things (IoT) and industrial use cases
- Industry 4.0 for smarter manufacturing
- Predictive and prescriptive insights for smarter systems
- Machine vision and intelligence
- Natural interfaces
- K-means clustering algorithm
- Support vector machine (SVM) algorithm
- A priori algorithms
- Linear and logistic regression
Applied Learning Algorithms for Intelligent IoT clearly articulates ML and DL algorithms that can be used to unearth predictive and prescriptive insights out of Big Data. Transforming raw data into information and relevant knowledge is gaining prominence with the availability of data processing and mining, analytics algorithms, platforms, frameworks, and other accelerators discussed in the book. Now, with the emergence of machine learning algorithms, the field of data analytics is bound to reach new heights.
This book will serve as a comprehensive guide for AI researchers, faculty members, and IT professionals. Every chapter will discuss one ML algorithm, its origin, challenges, and benefits, as well as a sample industry use case for explaining the algorithm in detail. The book's detailed and deeper dive into ML and DL algorithms using a practical use case can foster innovative research.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
1
Convolutional Neural Network in Computer Vision
Introduction
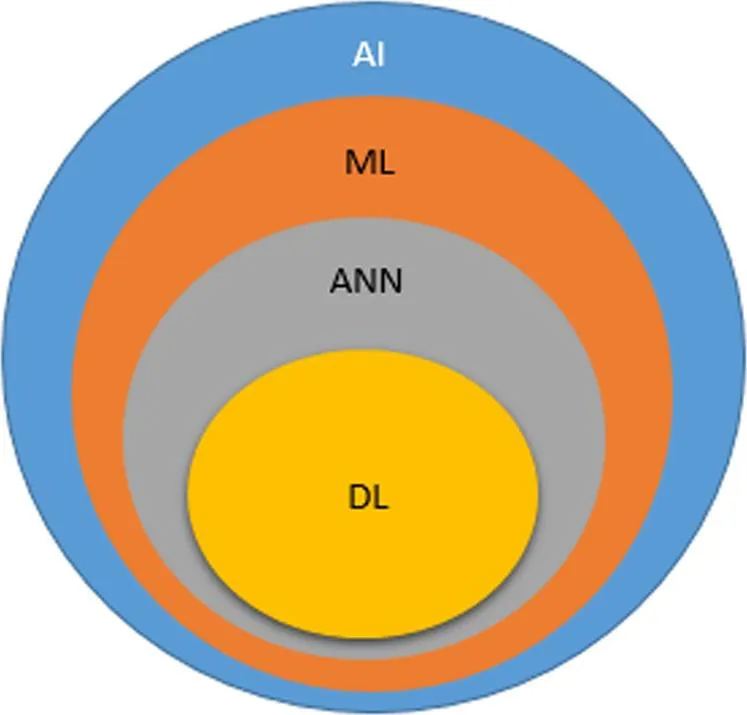
Convolutional Neural Network (CNN)
Table of contents
- Cover
- Half Title
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Contents
- Contributor List
- Chapter 1: Convolutional Neural Network in Computer Vision
- Chapter 2: Trends and Transition in the Machine Learning (ML) Space
- Chapter 3: Next-Generation IoT Use Cases across Industry Verticals Using Machine Learning Algorithms
- Chapter 4: A Panoramic View of Cyber Attack Detection and Prevention Using Machine Learning and Deep Learning Approaches
- Chapter 5: Regression Algorithms in Machine Learning
- Chapter 6: Machine Learning-Based Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) and Its Applications
- Chapter 7: Employee Turnover Prediction Using Single Voting Model
- Chapter 8: A Novel Implementation of Sentiment Analysis Toward Data Science
- Chapter 9: Conspectus of k-Means Clustering Algorithm
- Chapter 10: Systematic Approach to Deal with Internal Fragmentation and Enhancing Memory Space during COVID-19
- Chapter 11: IoT Automated Spy Drone to Detect and Alert Illegal Drug Plants for Law Enforcement
- Chapter 12: Expounding k-Means-Inspired Network Partitioning Algorithm for SDN Controller Placement
- Chapter 13: An Intelligent Deep Learning-Based Wireless Underground Sensor System for IoT-Based Agricultural Application
- Chapter 14: Predicting Effectiveness of Solar Pond Heat Exchanger with LTES Containing CuO Nanoparticle Using Machine Learning
- Index
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app