
eBook - ePub
Investment Management with SAP ERP
The Comprehensive Guide
- 358 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
About this book
Looking for a complete guide to Investment Management? With this e-book, you'll begin by configuring master data for investment programs and appropriation requests in SAP ERP. Then set up internal orders and work breakdown structures (WBS) as investment measures. You'll learn to create an investment program and to position and budget for internal orders and projects. Use standard reports for commitments, plans, and budgets or build custom reports! Highlights Include: 1) Investment programs
2) Program positions
3) Measures
4) Appropriation requests
5) Investment profiles
6) Master data
7) Work breakdown structure (WBS)
8) Reporting
9) Controlling
10) Project System
11) Information System
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription.
No, books cannot be downloaded as external files, such as PDFs, for use outside of Perlego. However, you can download books within the Perlego app for offline reading on mobile or tablet. Learn more here.
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 1000+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn more here.
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more here.
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS or Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Yes, you can access Investment Management with SAP ERP by Pankaj Bhalerao,Shraddha Temgire in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Computer Science & Computer Science General. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.
Information
1 Overview
This chapter will discuss the basic concepts and terminology used in investment management. We’ll also cover the flow of the various activities involved in investment management and their significance from both a business perspective and an SAP system perspective.
Investments of any kind have always been a crucial aspect in every walk of life, right from our personal everyday routines to the highly influential investment decisions taken by the corporate giants of the world. Therefore, understanding what exactly investment management is, especially when big money is involved in large corporate projects, is vitally important. Before jumping directly onto SAP ERP Investment Management (IM), let’s begin by getting a high-level understanding of the term investment management.
In the first three sections of this chapter, we’ll focus on a domain-level understanding of investment management, which will include understanding the general process of how investment decisions are made and implemented by any organization. We’ll also introduce IM as a module of SAP by covering its functionalities, including its integration with other modules. Lastly, we’ll offer some insights into a few important terms used in IM.
1.1 Investment Management from a Business Perspective
When any company is born, the first thing it must do to commence business is to find a suitable project to invest in. The company will first compute the costs and benefits of each project and then come to a final decision about where it wants to invest, if expected to be sufficiently profitable for the company.
These investments are generally referred to as capital expenditures in the financial world. Decisions involving capital expenditures are some of the most important decisions undertaken by management.
Several factors make these decisions difficult, including the time period involved, uncertainty due to volatile and unpredictable market conditions in the future, the inability to revert such huge investments, and, most importantly, the incredible amount of funds involved (i.e., capital costs). Also, getting a perfect measure of the proposed investment in terms of its costs, expected revenues, and outlays can be quite a cumbersome and difficult task considering the unknown future.
If an incorrect decision is made, the company can lose a great deal because reversing huge investment decisions generally comes with a loss. For example, consider an organization that decides to buy high-end equipment for a manufacturing plant that it is planning to set up. The company may acquire a particular machine and then realize that another machine would be needed in its place due to some technical reasons, basically inferring that the investment decision has to be reversed. In such a case, the first machine will have to be sold, but owing to the unfavorable markets for used equipment, this sale will not be an easy task. Moreover, if the machine has been customized for a particular requirement of that organization, then finding a market would be even more difficult. Finally, the machine may have to be scrapped, incurring a loss to the company. This example shows the significance of a thoughtful investment decision as these decisions can have serious repercussions on the financial health of an organization.
In the following section, we’ll touch on a few important features in investment management. First, we’ll look at different kinds of investments based on various criteria, followed by an in-depth look at the process of capital budgeting, and finally, we’ll learn about different techniques to evaluate the profitability of a particular investment.
1.1.1 Types of Investments
Capital investments can be classified in a number of ways. Let’s look at the various ways in which investments can be categorized.
The first way of classifying investments is as tangible investments, monetary investments, and intangible investments. Figure 1.1 shows this classification structure with a few examples for each category.
The second way of classifying investments is as strategic investments and tactical investments, as shown in Figure 1.2.
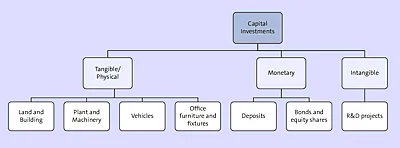
Figure 1.1 Classification 1 of Capital Investments
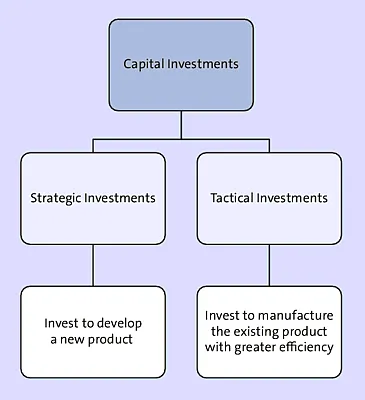
Figure 1.2 Classification 2 of Capital Investments
An example of strategic investment would be if Volkswagen started producing hybrid or lightweight cars. On the other hand, a process redesign project to manufacture existing vehicles in a more efficient manner would be an example of a tactical investment.
Capital investments can also be classified into the following six categories in yet another way, as shown in Figure 1.3:
- Mandatory investments include investing to cater to any requirements that are statutory, like firefighting equipment, medical facilities, cafeteria facilities, etc.
- Replacement investments include spending on the replacement of any old or worn out equipment to help optimize costs and enhance yields.
- Expansion investments are investments required to increase the capacity of production, say, of a steel manufacturing plant.
- Diversification investments allow an organization to expand its scope by introducing new products.
- R&D investments, as the name suggests, include expenditures on all kinds of research projects.
- Miscellaneous investments cover all the remaining kinds of capital expenditures like decorating office interiors, furniture, landscaping, entertainment facilities, etc.
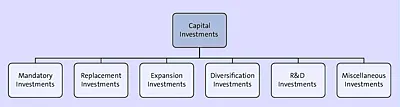
Figure 1.3 Classification 3 of Capital Investments
1.1.2 Capital Budgeting
The main objective of any business organization is to maximize the value of the firm in the market. Every firm aims to meet the expectations of its shareholders as well as of their employees, customers, and vendors. Shareholders’ expectations basically revolve around increasing the value of the company’s shares, which eventually traces back to how well the firm manages its capital. For this reason, proper budgeting of capital is truly important for an organization’s growth and success.
Capital budgeting is a sequential process. The first stage is ...
Table of contents
- Dear Reader
- Notes on Usage
- Table of Contents
- Preface
- Acknowledgments
- 1 Overview
- 2 Investment Programs
- 3 Appropriation Requests
- 4 Internal Orders as Investment Measures
- 5 Projects as Investment Measures
- 6 Process Flow in the Investment Management Lifecycle
- 7 Information Systems in Investment Management
- A The Authors
- Index
- Service Pages
- Legal Notes