
Big Data Analysis for Green Computing
Concepts and Applications
- 174 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Big Data Analysis for Green Computing
Concepts and Applications
About this book
This book focuses on big data in business intelligence, data management, machine learning, cloud computing, and smart cities. It also provides an interdisciplinary platform to present and discuss recent innovations, trends, and concerns in the fields of big data and analytics.
Big Data Analysis for Green Computing: Concepts and Applications presents the latest technologies and covers the major challenges, issues, and advances of big data and data analytics in green computing. It explores basic as well as high-level concepts. It also includes the use of machine learning using big data and discusses advanced system implementation for smart cities.
The book is intended for business and management educators, management researchers, doctoral scholars, university professors, policymakers, and higher academic research organizations.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
1 Multi-Criteria and Fuzzy-Based Decision Making Applications in Environment Pollution Control for Sustainable Development
CONTENTS
- 1.1 Introduction to Fuzzy
- 1.2 Introduction to MCDM
- 1.2.1 MADM
- 1.2.2 MODM
- 1.2.3 Needs of Fuzzy MCDM
- 1.3 Literature Survey
- 1.4 Fuzzy Control System
- 1.4.1 Fuzzy Classification
- 1.4.2 De-Fuzzification
- 1.5 Mathematical Programming Using Fuzzy Models
- 1.5.1 Fuzzy Linear Programming
- 1.5.2 Fuzzy Integer Linear Problems
- 1.5.3 Fuzzy Dynamic Programming
- 1.5.4 Mathematical Programming as a Tool for Fuzzy Rule Learning Process
- 1.6 MCDM with Fuzzy AHP
- 1.6.1 Analytical Hierarchy Process
- 1.6.2 Need for Fuzzy AHP
- 1.6.3 Case Study of Fuzzy AHP
- 1.6.4 Application of Fuzzy AHP: Air Pollution Control
- 1.7 Comparison between AHP and Fuzzy AHP
- 1.8 Conclusion
- References
1.1 Introduction to Fuzzy
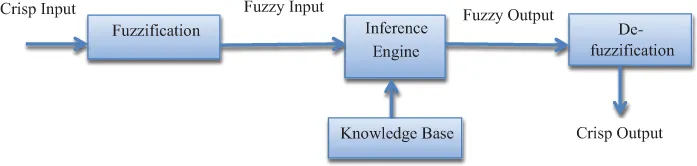
- Fuzzification
- De-fuzzification
- Knowledge base
- Inference engines
1.2 Introduction to MCDM
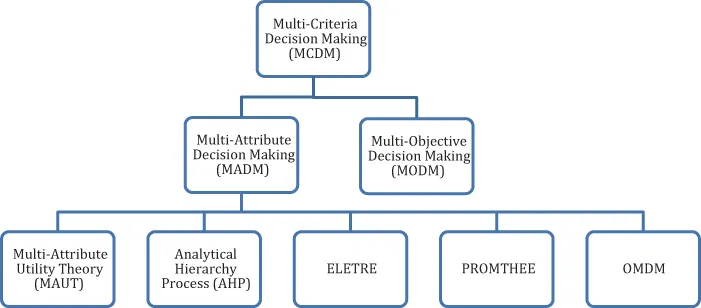
1.2.1 MADM
1.2.2 MODM
1.2.3 Needs of Fuzzy MCDM
1.3 Literature Survey
Table of contents
- Cover
- Half Title Page
- Series Page
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Table of Contents
- Preface
- Editors
- Contributors
- Chapter 1 Multi-Criteria and Fuzzy-Based Decision Making: Applications in Environment Pollution Control for Sustainable Development
- Chapter 2 Security and Privacy Requirements for IoMT-Based Smart Healthcare System: Challenges, Solutions, and Future Scope
- Chapter 3 The Rise of “Big Data” on Cloud Computing
- Chapter 4 Effect of the Measurement on Big Data Analytics: An Evolutive Perspective with Business Intelligence
- Chapter 5 Performance Analysis for Provisioning and Energy Efficiency Distributed in Cloud Computing
- Chapter 6 Using Internet of Things (IoT) for Smart Home Automation and Metering System
- Chapter 7 Big Data Analysis and Machine Learning for Green Computing: Concepts and Applications
- Chapter 8 Fundamental Concepts and Applications of Blockchain Technology
- Chapter 9 Mental Disorder Detection Using Machine Learning
- Chapter 10 Blockchain Technology for Industry 4.0 Applications: Issues, Challenges and Future Research Directions
- Index
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app