
- 1,056 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
Teradata SQL
About this book
This book includes over 1000 examples of all aspects of SQL starting at the most basic level and going to the most advanced level with real examples that work and explain exactly what is going on. The building block approach that continues to take things a step deeper at a time makes this a perfect SQL guide for everyone.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
Chapter 1 - Basic SQL Functions
“A journey of a thousand miles begins with a single step.”
- Lao-tzu
- Lao-tzu
Introduction
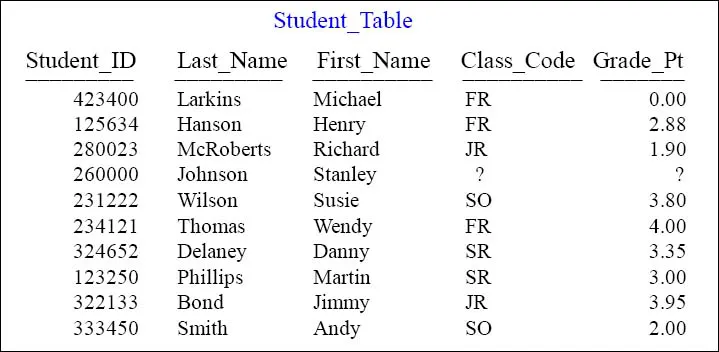
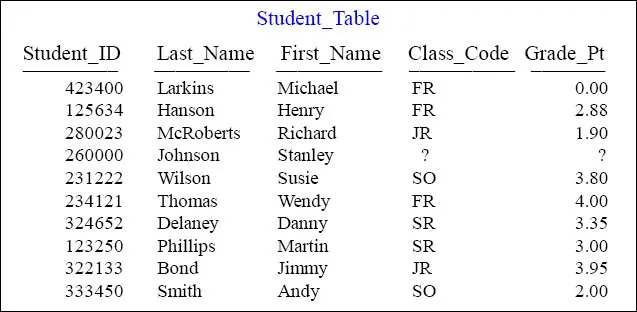
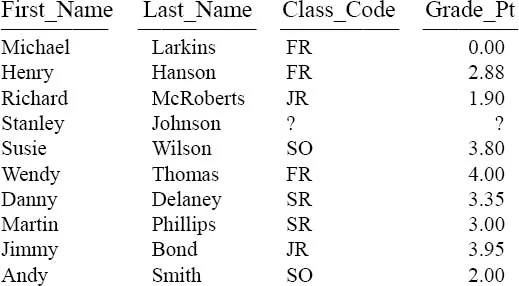
The Student_Table above will be used in our early SQL Examples
This is a pictorial of the Student_Table which we will use to present some basic examples of SQL and get some hands-on experience with querying this table. This book attempts to show you the table, show you the query, and show you the result set.
SELECT * (All Columns) in a Table
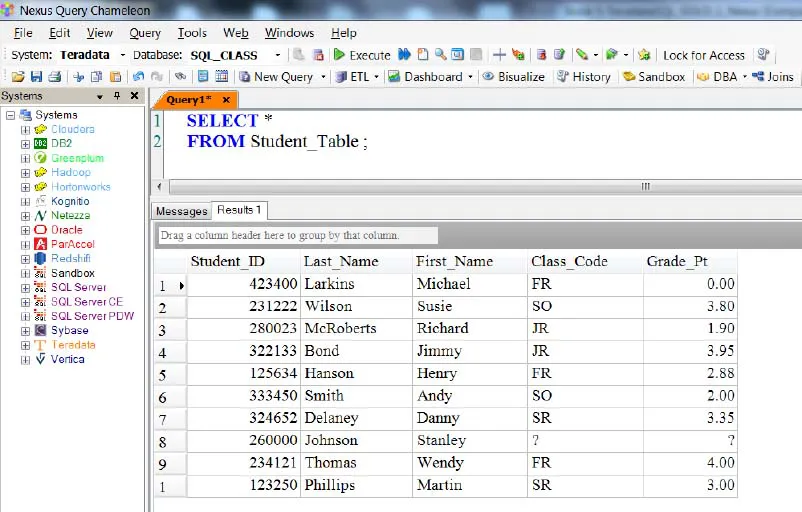
Mostly every SQL statement will consist of a SELECT and a FROM. You SELECT the columns you want to see on your report, and an Asterisk (*) means you want to see all columns in the table on the returning answer set!
SELECT Specific Columns in a Table
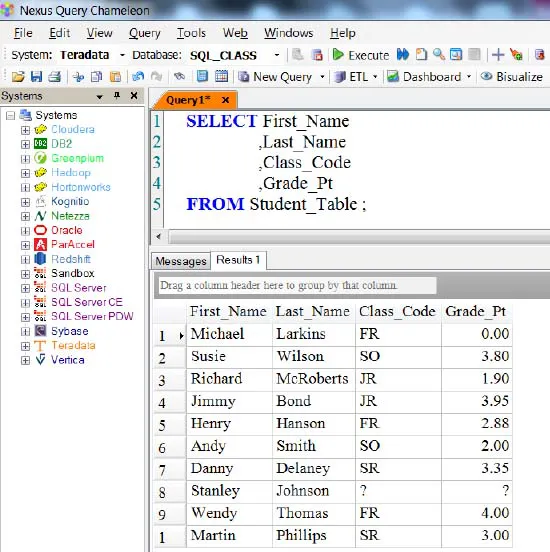
Column names must be separated by commas. Notice that only the columns requested come back on the report, not all columns. Also, notice that the order of the columns in the SQL is the same order on the report.
Using the Best Form for Writing SQL
| SELECT | First_Name, |
| Last_Name, | |
| Class_Code, | |
| Grade_Pt | |
| FROM | Student_Table; |
| SELECT | First_Name, |
| ,Last_Name, | |
| ,Class_Code, | |
| ,Grade_Pt | |
| FROM | Student_Table; |
Can you spot the difference between these two examples?
Why is the example on the right better, even though they are functionally equivalent?
Commas in the Front or in the Back?

| SELECT | First_Name, |
| ,Last_Name, | |
| ,Class_Code, | |
| ,Grade_Pt | |
| FROM | Student_Table; |

| SELECT | First_Name, |
| Last_Name, | |
| Class_Code, | |
| Grade_Pt | |
| FROM | Student_Table; |
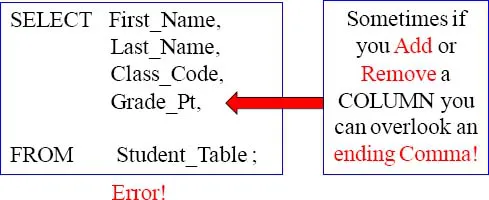
Commas in the front (example 1) is Tera-Tom's recommendation to writing, but the next page is an even better example for a company standard. Both queries will produce the same answer set and have the same performance
Place your Commas in front for better Debugging Capabilities
| SELECT | First_Name |
| ,Last_Name | |
| ,Class_Code | |
| ,Grade_Pt | |
| FROM | Student_Table; |
Successful
Having commas in front to separate column names makes it easier to debug.
Sort the Data with the ORDER BY Keyword
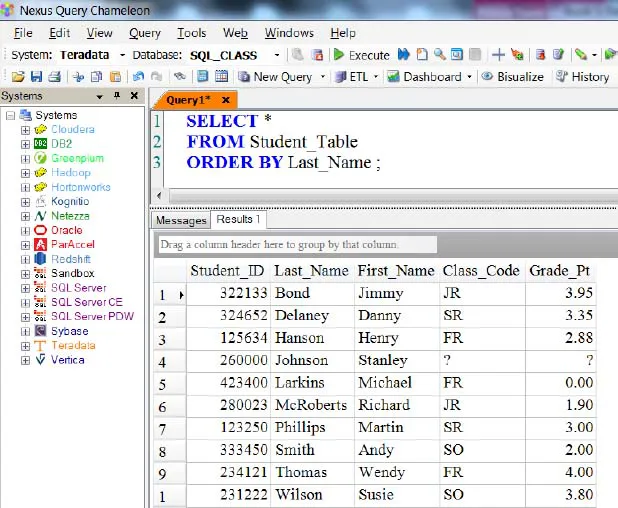
Rows typically come back to the report in random order. To order the result set, you must use an ORDER BY. When you order by a column, it will order in ASCENDING order. This is called the Major Sort!
ORDER BY Defaults to Ascending
SELECT *
FROM Student_Table
ORDER BY Last_Name;
FROM Student_Table
ORDER BY Last_Name;
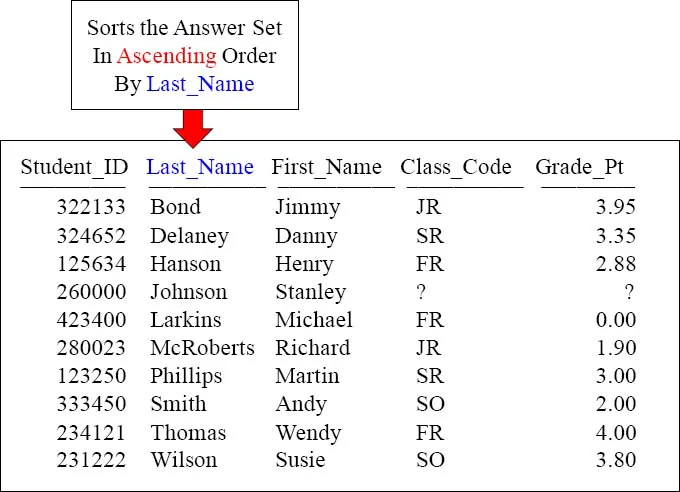
When you use the ORDER BY statement, it will default to ascending order. But you can ...
Table of contents
- Cover Page
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- About Tom Coffing
- About Michael Larkins
- Contents
- Chapter 1 - Basic SQL Functions
- Chapter 2 - The WHERE Clause
- Chapter 3 - Distinct Vs. Group By
- Chapter 4 - The TOP Command
- Chapter 5 – Review
- Chapter 6 - HELP and SHOW
- Chapter 7 - Aggregation Function
- Chapter 8 - Join Functions
- Chapter 9 - Date Functions
- Chapter 10 - Format Functions
- Chapter 11 - OLAP Functions
- Chapter 12 - The Quantile Function
- Chapter 13 - Temporary Tables
- Chapter 14 - Sub-query Functions
- Chapter 15 - Substrings and Positioning Functions
- Chapter 16 - Interrogating the Data
- Chapter 17 - View Functions
- Chapter 18 - Macro Functions
- Chapter 19 - Set Operators Functions
- Chapter 20 – Creating Tables, Secondary Indexes, and Join Indexes
- Chapter 21 - Data Manipulation Language (DML)
- Chapter 22 - Stored Procedure Functions
- Chapter 23 - Trigger Functions
- Chapter 24 - Math Functions
- Chapter 25 - Sample
- Chapter 26 - Statistical Aggregate Functions
- Chapter 27 - Explain
- Chapter 28 - Collect Statistics
- Chapter 29 - Hashing Functions
- Chapter 30 - BTEQ – Batch Teradata Query
- Chapter 31 – Top SQL Commands Cheat Sheet
- Back Cover
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription
No, books cannot be downloaded as external files, such as PDFs, for use outside of Perlego. However, you can download books within the Perlego app for offline reading on mobile or tablet. Learn how to download books offline
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 990+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn about our mission
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more about Read Aloud
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS and Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Yes, you can access Teradata SQL by Tom Coffing,Mike Larkins in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Computer Science & Data Warehousing. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.