- 632 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
Twining's Textbook of Fetal Abnormalities E-Book
About this book
Access practical guidance on the radiologic detection, interpretation, and diagnosis of fetal anomalies with Twining's Textbook of Fetal Abnormalities. With fetal scanning being increasingly done by obstetricians, this updated medical reference book features a brand-new editorial team of radiologist Anne Marie Coady and fetal medicine specialist Sarah Bower; these authorities, together with contributions from many other experts, provide practical, step-by-step guidance on everything from detection and interpretation to successful management approaches. Twining's Textbook of Fetal Abnormalities is a resource you'll turn to time and again!
- Consult this title on your favorite e-reader, conduct rapid searches, and adjust font sizes for optimal readability.
- Quickly access specific information with a user-friendly format.
- Deliver a rapid, reliable diagnosis thanks to a strong focus on image interpretation, as well as the correlation of radiographic features with pathologic findings wherever possible.
- Clearly visualize a full range of conditions with help from more than 700 images.
- Stay abreast of the latest developments in detecting fetal abnormalities with 4 brand-new chapters: Fetal Growth; Haematological Disorders; Fetal Pathology; and Fetal Tumours.
- Access increased coverage of fetal growth, first trimester anomalies, DDX, and clinical management.
- Understand the major advances in today's hottest imaging technologies, including 3-D Ultrasound, Fetal MRI, and Colour Doppler.
- Effectively interpret the images you encounter with highly organized coordination between figures, tables, and imaging specimens.
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription.
No, books cannot be downloaded as external files, such as PDFs, for use outside of Perlego. However, you can download books within the Perlego app for offline reading on mobile or tablet. Learn more here.
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 1000+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn more here.
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more here.
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS or Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Yes, you can access Twining's Textbook of Fetal Abnormalities E-Book by Anne Marie Coady,Sarah Bower in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Medicine & Radiology, Radiotherapy & Nuclear Medicine. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.
Information
Chapter 1
First-Trimester Detection of Fetal Anomalies
Raffaele Napolitano, Aris T Papageorghiou
Introduction
The first trimester of pregnancy is generally considered to be the first 13 completed weeks. In the past, first-trimester ultrasound has mainly been used to confirm fetal viability, establish pregnancy location, count the number of fetuses and assess gestational age by measurement of fetal crown rump length (CRL). A major breakthrough in screening for fetal abnormalities was the finding that fetal nuchal translucency is increased in cases of chromosomal abnormalities and other fetal anatomical defects, and this forms the basis of screening for chromosomal abnormalities in many countries. With further improvements in ultrasound technology it has become increasingly feasible to examine the fetal anatomy in the first trimester. It is advisable to perform the scan at 11 + 0 to 13 + 6 weeks' gestation as this allows confirmation of viability, accurate assesment of gestational age and number of viable fetuses in addition to evaluation of anatomy and calculation of risk of aneuploidy.1 There are a number of differences and advantages to screening for abnormalities in the first trimester over the second trimester (Table 1-1). The recently published guidelines on the first trimester scan by the International Society of Obstetrics and Gynaecology lists the structures which it should be possible to visualize and assess in the first-trimester routine screening examination.2 (Table 1-2).
TABLE 1-1
Advantages and Disadvantages to Screening for Abnormalities in the First Trimester Over the Second Trimester
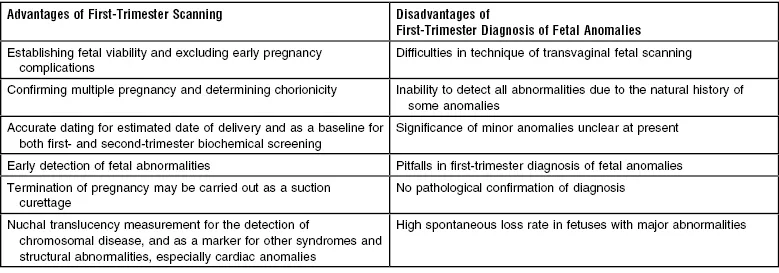
| Advantages of First-Trimester Scanning | Disadvantages of First-Trimester Diagnosis of Fetal Anomalies |
| Establishing fetal viability and excluding early pregnancy complications | Difficulties in technique of transvaginal fetal scanning |
| Confirming multiple pregnancy and determining chorionicity | Inability to detect all abnormalities due to the natural history of some anomalies |
| Accurate dating for estimated date of delivery and as a baseline for both first- and second-trimester biochemical screening | Significance of minor anomalies unclear at present |
| Early detection of fetal abnormalities | Pitfalls in first-trimester diagnosis of fetal anomalies |
| Termination of pregnancy may be carried out as a suction curettage | No pathological confirmation of diagnosis |
| Nuchal translucency measurement for the detection of chromosomal disease, and as a marker for other syndromes and structural abnormalities, especially cardiac anomalies | High spontaneous loss rate in fetuses with major abnormalities |
TABLE 1-2
Suggested Anatomical Assessment at Time of 11 to 13+6-week scan
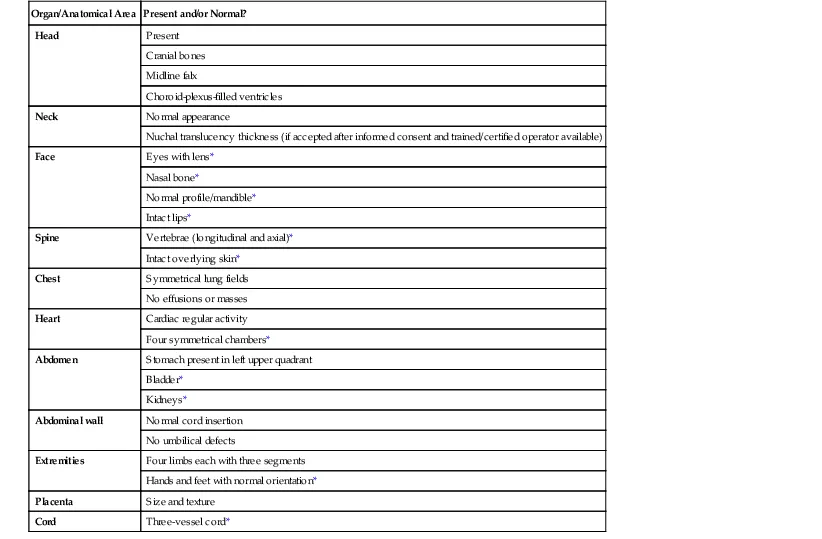
| Organ/Anatomical Area | Present and/or Normal? |
| Head | Present |
| Cranial bones | |
| Midline falx | |
| Choroid-plexus-filled ventricles | |
| Neck | Normal appearance |
| Nuchal translucency thickness (if accepted after informed consent and trained/certified operator available) | |
| Face | Eyes with lens* |
| Nasal bone* | |
| Normal profile/mandible* | |
| Intact lips* | |
| Spine | Vertebrae (longitudinal and axial)* |
| Intact overlying skin* | |
| Chest | Symmetrical lung fields |
| No effusions or masses | |
| Heart | Cardiac regular activity |
| Four symmetrical chambers* | |
| Abdomen | Stomach present in left upper quadrant |
| Bladder* | |
| Kidneys* | |
| Abdominal wall | Normal cord insertion |
| No umbilical defects | |
| Extremities | Four limbs each with three segments |
| Hands and feet with normal orientation* | |
| Placenta | Size and texture |
| Cord | Three-vessel cord* |
* Optional structures.
Viability, Multiple Pregnancy and Gestational Age Assessment
About 2.8% of pregnancies will be non-viable at 10–13 weeks of gestation and chromosomal abnormalities may be present in 45–70% of these.3 First-trimester ultrasound is highly accurate in diagnosis of non-viable pregnancies, but it is important to ensure that missed miscarriage is distinguished from a very early viable pregnancy where the fetal heartbeat is simply not seen. This should be of particular concern within the first 6–8 weeks. Recent studies suggest that a mean sac diameter (MSD) cut-off of over 25 mm and a CRL of over 7 mm minimizes the risk of a false-positive diagnosis of miscarriage4 (Figures 1-1 and 1-2). In cases where these measurements are below the threshold for a one-stop diagnosis a further scan should be arranged in 7 days to assess embryonic or sac growth in that interval.
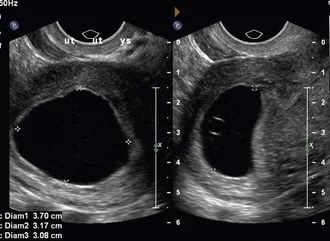
FIGURE 1-1 A large gestation sac MSD >25 mm lacking an embryo which is consistent with early pregnancy failure. (Courtesy of Dr Anne Marie Coady.)
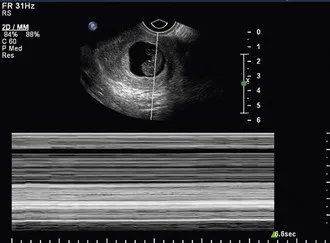
FIGURE 1-2 An embryo of CRL over 7 m...
Table of contents
- Cover image
- Title page
- Table of Contents
- Copyright
- Preface
- List of Contributors
- Dedication
- 1 First-Trimester Detection of Fetal Anomalies
- 2 Fetal Aneuploidies*
- 3 Routine Fetal Anomaly Scan
- 4 Amniotic Fluid
- 5 Disorders of the Placenta
- 6 Prenatal Diagnosis of Fetal Infections
- 7 Fetal Anomalies – The Geneticist's Approach
- 8 Diagnosis of Hydrops and Multiple Malformation Syndromes
- 9 Assessment of Twin Gestation
- 10 Fetal Growth
- 11 Cranial Abnormalities
- 12 Diagnosis of Spina Bifida and Other Dysraphisms in the Fetus
- 13 Abnormalities of the Face and Neck
- 14 Cardiac Abnormalities and Arrhythmias
- 15 Pulmonary Abnormalities
- 16 Skeletal Abnormalities
- 17 Abdominal and Abdominal Wall Abnormalities
- 18 Urinary Tract Abnormalities
- 19 Haematological Disorders
- 20 Fetal Tumours
- 21 Fetal Magnetic Resonance Imaging
- 22 Fetal Pathology
- Index