
Thinking Like a Mathematician
Lessons That Develop Habits of Mind and Thinking Skills for Young Mathematicians in Grade 3
- 152 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Thinking Like a Mathematician
Lessons That Develop Habits of Mind and Thinking Skills for Young Mathematicians in Grade 3
About this book
Thinking Like a Mathematician focuses on high-interest, career-related topics in the elementary curriculum related to mathematics. Students will explore interdisciplinary content, foster creativity, and develop higher order thinking skills with activities aligned to relevant content area standards. Students will engage in exploration activities, complete mathematical challenges, and then apply what they have learned by making real-world connections. Thinking Like a Mathematician reflects key emphases of curricula from the Center for Gifted Education at William & Mary, including the development of process skills in various content areas and the enhancement of discipline-specific thinking and habits of mind through hands-on activities.
Grade 3
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
UNIT 1 SYSTEMS OF COUNTING
RATIONALE
PLAN
LESSON 1.1 EXPLORE DIFFERENT COUNTING SYSTEMS
RESOURCES AND MATERIALS
- Lesson 1.1 Base-4 Counting
- Three stackable cups with the numerals 0, 1,2, and 3 written around each cup lip (per group; see Figure 1 for reference)
- Student math notebooks
ESTIMATED TIME
OBJECTIVES
- discover a pattern from a base-4 numbering system,
- understand the differences between numbering systems, and
- compare and contrast the base-10 numbering system with a base-4 numbering system.
PRIOR KNOWLEDGE
INSTRUCTIONAL SEQUENCE
- Divide students into groups of 2-3. Each group should receive three cups. Distribute Lesson 1.1 Base-4 Counting.
- Have students stack the cups and turn them sideways so the numerals are showing (see Figure 1). Students should start with the number 000. Explain that (moving from left to right) cup 1 represents the hundreds digit, cup 2 represents the tens digit, and cup 3 represents the ones digit. Students will be turning the cups to find a pattern and recording their numbers on Lesson 1.1 Base-4 Counting.
- Have students turn the ones digit (cup 3) to 1 and record the number shown: 001. They should then turn the ones digit again, and write the corresponding numbers until they reach the number 003.
- Once students reach the number 003, have them turn the ones digit back to 0,and then turn the tens digit (cup 2) to 1. They should write down the number: 010.
- Students should continue the pattern until they have reached 333.
- Explain that this number system is called a base-4 number system (consisting of four numerals: 0,1,2,3).
- Lead a whole-group discussion about patterns of numbers.

EXTENSION ACTIVITY
- 110 + 011
- 223 + 121
- 323 - 122
- 301 -223
ASSESSMENT OBSERVATIONS
- Students should discuss patterns in the base-4 numbering system.
- Students should be using the correct counting process with their cups: After students reach 003, they should reset cup 3 to the digit 0 and turn cup 2 to the digit 1.
- Students should discuss place value similarities and numeral differences.
LESSON 1.1
Base-4 Counting
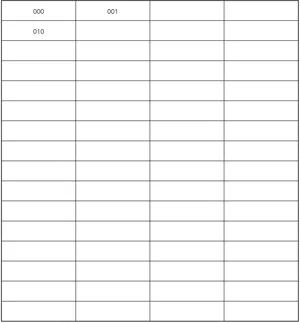
- Write the patterns you see in the new number system.
- How is this counting system similarto the way we count numbers? Explain.
- How is this counting system different from the way we count numbers? Explain.
- What happens when you get to the highest possible ones digit?
- What happens when you get to the highest possible tens digit?
LESSON 1.2 APPLY BINARY COUNTING
RESOURCES AND MATERIALS
- Lesson 1.2 Robot Maze
- Lesson 1.2 Writing in Binary Code
- Student math notebooks
- Coins (one per student)
ESTIMATED TIME
OBJECTIVES
- create a written block code to guide a robot through a maze,
- learn how binary code is formed, and
- crea...
Table of contents
- Cover Page
- Half Title Page
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Table of Contents Page
- Introduction
- Introductory Lesson: What Is a Mathematician?
- Unit 1: Systems of Counting
- Unit 2: Order of Operations
- Unit 3: Patterns
- Unit 4: Time and Measurement
- Unit 5: Graphing, Data, and Charts in Algebra
- Unit 6: Geometry
- Unit 7: Data Analysis and Statistics
- Final Project: Designing a Garden
- Answer Key
- About the Authors