![]()
![]()
1. Private Financing for Sustainable and Quality Infrastructure in the Face
of Covid-19
Naoyuki Yoshino, Nella Sri Hendriyetty, Derek Hondo
Infrastructure Needs to Achieve the SDGs
As societies continue to work towards achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), many challenges exist in determining the most effective approaches to support them in doing so. One of the biggest lies the upgrading of current infrastructure, and the development and maintenance of new infrastructure, which is crucially important to promote socioeconomic development. Infrastructure is instrumental in increasing resilience economically, environmentally, and socially. It must be resilient itself so that it can withstand any shocks and stresses that it may encounter. Subsequently, infrastructure will contribute to increased productivity, promotion of financial inclusion, facilitate trade and connectivity, all while stimulating economic growth in a sustainable way if the appropriate planning and policies are implemented. This chapter emphasises the importance in investing in quality infrastructure and how this can support a transition towards more resilient and sustainable societies. It will highlight the spillover effects of infrastructure investments and how they can address many of the SDGs. Lastly, it will explore different innovative financing schemes which policymakers can adopt to alleviate the strain on public budget deficits, especially in the post-Covid-19 era.
Infrastructure can be categorised into two main types: soft infrastructure and hard infrastructure. Soft infrastructure refers to all the essential services that maintain economic, health, cultural, social standards, and the institutions which oversee these services within a society. Conversely, hard infrastructure covers the physical, such as roads, bridges, railways, and other built things. Digital infrastructure is not limited to one or the other and can also support the development of both soft and hard infrastructure. By investing in both types, including digital infrastructure, countries will be able to move closer towards achieving the SDGs.
Sustainable and Quality Infrastructure
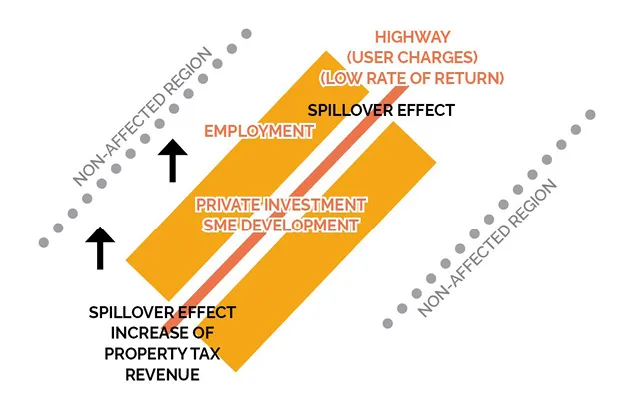
Quality infrastructure can be defined as infrastructure that contributes in a significant way to the development of a region. This can be measured by evaluating the spillover effects of investment in a particular infrastructure project, which increases economic value of the region.
Once the infrastructure and affected areas or regions are identified, two approaches can be taken to determine whether the infrastructure is of high-quality and worthwhile to invest in. The first is to examine the changes in GDP in the area affected by or along the infrastructure, in the case of a road, railway, or water pipeline. The second approach is to observe the changes in tax revenue also in the area or region along the infrastructure. For both approaches, comparisons should be made between the situation with the built infrastructure and the situation without any infrastructure.
Quality infrastructure has a multiplier effect and brings immense benefits to a region. By investing in quality infrastructure, a region will see an increase in economic activities with the creation of new businesses and employment opportunities. Moreover, as businesses open and people move to the area, new residential districts will arise, leading to an increase in the revenue collected from property and corporate taxes (Figure 1.1). To further increase the spillover effects generated by infrastructure investments, local policymakers and private companies need to work collaboratively to maintain the development momentum of a region, expanding beyond the initial infrastructure project.
One challenge that remains in both developing and developed countries is increasing connectivity between rural and urban areas. Both soft and hard infrastructure can play a role in connecting regions physically and digitally. Investing in infrastructure opens up opportunities to boost economic value, achieved through developing railways, roads, and highways. In the case of developing physical infrastructure, the agriculture industry, including farmers, will be able to transport their products to urban centres, increasing market accessibility and expanding trade networks to reach vast regions beyond their local areas. The following section will explore the potential spillover effects that soft and digital infrastructure investments can lead to.
Another important component of infrastructure is ensuring that it is sustainable. This means that policymakers, developers, and investors must establish long-term plans that incorporate the SDGs. Sustainable infrastructure needs to make cities better equipped with public transportation to increase social mobility and equity, increase access to healthcare and education, digital connectivity and technology, while also shifting to a greener, more efficient energy usage.
Fig. 1.1 - Spillover effects created by infrastructure
Role of Digital Infrastructure during Covid-19 and Post-Pandemic Recovery
The Covid-19 pandemic, which has had widespread impacts on social and economic activity across the globe, has shed light on the central role that digital infrastructure and technology can play in society. With lockdowns in place, many businesses and education systems shifted their operations online. In order to do this, accessibility to stable internet connections through quality digital infrastructure became a necessity.
However, more than 4 billion people lack access to the Internet and of this figure, 90% are in developing countries. This struggle with providing digital connectivity hampers the ability for information to be disseminated, which has consequences on business opportunities and education. Furthermore, failure to recognise the impacts that digital infrastructure can have on a region jeopardises not only business activity there but also secondary and university education. According to Yoshino and Abidhadjaev (2016), investment in infrastructure that promotes education adds to the spillover effects (Table 1.1). Providing access to secondary education and training programs will better prepare the workforce with essential skills for entering labour markets. Higher education will enhance t...