
Quick Guideline for Computational Drug Design (Revised Edition)
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Quick Guideline for Computational Drug Design (Revised Edition)
About this book
Bioinformatics allows researchers to answer biological questions with advanced computational methods which involves the application of statistics and mathematical modeling. Structural bioinformatics enables the prediction and analysis of 3D structures of macromolecules while Computer Aided Drug Designing (CADD) assists scientists to design effective active molecules against diseases. However, the concepts in structural bioinformatics and CADD can be complex to understand for students and educated laymen. This quick guideline is intended as a basic manual for beginner students and instructors involved in bioinformatics and computational chemistry courses. Readers will learn the basics of structural bioinformatics, primary and secondary analysis and prediction, structural visualization, structural analysis and molecular docking. Therefore, the book is a useful handbook for aspiring scholars who wish to learn the basic concepts in computational analysis of biomolecules.
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
3D Structure Prediction
SA Sehgal, RA Tahir, M Waqas
Abstract
MOTIVATION
STRUCTURE PREDICTION TOOLS
PHYRE2
Introduction
Brief Instructions
- Open the web browser
- Go to Phyre2 homepage ( http://www.sbg.bio.ic.ac.uk/phyre2/html/page.cgi?id= index). An interface will open where the amino acid sequence of the respective protein will be uploaded, e.g., PSEN2
- Provide the institutional e-mail ID ([email protected])
- Results will be sent through e-mail depending upon the sequence (query) length and number of protein sequences in queues
Requirements
Input
Sequence Submission
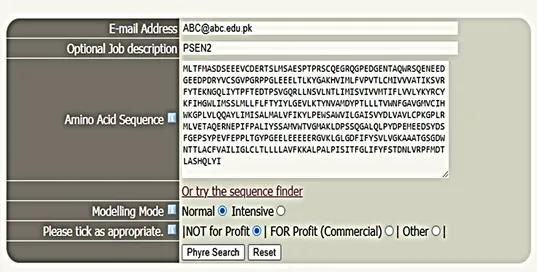
Phyre2 submission page.
Results Interpretation (Results Screen)
Secondary Structure and Disorder Prediction
Table of contents
- Welcome
- Table of Content
- Title
- BENTHAM SCIENCE PUBLISHERS LTD.
- FOREWORD
- PREFACE
- DEDICATION
- Introduction to Structural Bioinformatics
- Protein Primary Sequence Analysis
- Secondary Structure Analyses
- 3D Structure Prediction
- Protein 3D Structure Assessment, Evaluation, and Validation
- Ligand-Based Computational Molecular Docking Analysis
- Protein-Ligand Interactions