
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Human-Robot Interaction Control Using Reinforcement Learning
About this book
A comprehensive exploration of the control schemes of human-robot interactions
In Human-Robot Interaction Control Using Reinforcement Learning, an expert team of authors deliversa concise overview of human-robot interaction control schemes and insightful presentations of novel, model-free and reinforcement learning controllers. The book begins with a brief introduction to state-of-the-art human-robot interaction control and reinforcement learning before moving on to describe the typical environment model. The authors also describe some of the most famous identification techniques for parameter estimation.
Human-Robot Interaction Control Using Reinforcement Learning offers rigorous mathematical treatments and demonstrations that facilitate the understanding of control schemes and algorithms.It also describes stability and convergence analysis of human-robot interaction control and reinforcement learning based control.
The authorsalsodiscussadvanced and cutting-edge topics, like inverse and velocity kinematics solutions, H2 neural control, and likely upcoming developments in the field of robotics.
Readers will also enjoy:
- A thorough introduction to model-based human-robot interaction control
- Comprehensive explorations of model-free human-robot interaction control and human-in-the-loop control using Euler angles
- Practical discussions of reinforcement learning for robot position and force control, as well as continuous time reinforcement learning for robot force control
- In-depth examinations of robot control in worst-case uncertainty using reinforcement learning and the control of redundant robots using multi-agent reinforcement learning
Perfect forsenior undergraduate and graduate students, academic researchers, and industrial practitioners studying and working in the fields of robotics, learning control systems, neural networks, and computational intelligence, Human-Robot Interaction Control Using Reinforcement Learning is also an indispensable resource forstudents and professionals studying reinforcement learning.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
Part I
Human‐robot Interaction Control
1
Introduction
1.1 Human‐Robot Interaction Control
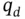
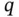
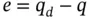
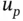
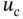
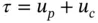
Table of contents
- Cover
- Table of Contents
- Title Page
- Copyright
- Dedication
- Author Biographies
- List of Figures
- List of Tables
- Preface
- Part I: Human‐robot Interaction Control
- Part II: Reinforcement Learning for Robot Interaction Control
- A Robot Kinematics and Dynamics
- B Reinforcement Learning for Control
- Index
- End User License Agreement
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app