
eBook - ePub
Citizen Development
The Handbook for Creators and Change Makers
This is a test
Share book
- 253 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
Citizen Development
The Handbook for Creators and Change Makers
Book details
Book preview
Table of contents
Citations
About This Book
Citizen development allows anyone to build applications without software expertise, significantly faster, and at a fraction of the cost. Unlock the value within your organization. Learn the tools and techniques needed to introduce and scale citizen development. This book brings together the latest thinking on citizen development from industry thought leaders, no-code/low-code vendors, transformation experts, and executives who oversee large technology investments. It guides organizations to deliver citizen development projects, design better apps, scale the operating model, align key stakeholders, and nurture and grow citizen development.
Frequently asked questions
How do I cancel my subscription?
Can/how do I download books?
At the moment all of our mobile-responsive ePub books are available to download via the app. Most of our PDFs are also available to download and we're working on making the final remaining ones downloadable now. Learn more here.
What is the difference between the pricing plans?
Both plans give you full access to the library and all of Perlego’s features. The only differences are the price and subscription period: With the annual plan you’ll save around 30% compared to 12 months on the monthly plan.
What is Perlego?
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 1000+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn more here.
Do you support text-to-speech?
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more here.
Is Citizen Development an online PDF/ePUB?
Yes, you can access Citizen Development by in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Business & Project Management. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.
Information

Power to the People
We are in the age of disruption and transformation. Every sector and industry is being disrupted by the digital revolution. Almost US$1 trillion of economic value (Alturi, Sanhi, & Rao, 2018) is either being created or destroyed as organizations struggle to meet customer needs and remain competitive in a world dominated by digital applications and data.
Advances in artificial intelligence (AI) are rapidly disconnecting end users from the complexity of the technology they use. The result is a world where we can do many things without having to understand how it all works. A good example is Apple's intelligent assistant, Siri, which allows any user to ask complicated questions using natural language input and receive answers immediately, all without having to spend time on complex research. In the world of application development, a similar revolution is emerging. Software engines are now sophisticated enough to write code from a few visual diagrams put together by a business user. Traditionally, called “no code” or “low code,” these new software applications are becoming more and more practical, creating a US$20 billion market (Rymer, Mines, Hammond, Vizgaitis, & Reese, 2017) as organizations try to leverage this new technology to gain a competitive advantage. This new capability, “citizen development,” democratizes the skills required to develop applications such that every citizen can do it. This term has found new life in other industries experiencing similar developments, including citizen data scientists, citizen doctors, and so on.
 | DID YOU KNOW? |
Back in 2012, Gartner analysts declared, “We're all developers now”—a reference to the nascent citizen developer movement (Ramel, 2015).
We call the enabling technology for enterprise applications citizen development application platforms (CDAPs). These platforms are intuitive and quick to use and give citizen developers the tools they need to be creative and solve problems. One of the key benefits is the sophistication of an AI engine that can effectively write code given a set of specifications. Advances in AI will effectively disaggregate the technical knowledge required from the business knowledge, enabling citizen developers to create disruptive technologies without the prerequisite technical knowledge. In addition, many business leaders now recognize the value of delegating decision making to the person or team within their organization that has the knowledge and experience to make the most informed decision. Hierarchical and centralized decision making is being replaced by a new paradigm: The Project Economy. The Project Economy is one in which people have the skills and capabilities they need to turn ideas into reality. It is where organizations deliver value to stakeholders through the successful completion of projects and delivery of products.
The Project Economy will fundamentally redesign how work gets done and is creating a distinct shift away from functional specializations toward temporary project structures comprised of cross-functional teams focused on short- and medium-term goals. Citizen developers are bringing two major changes to how organizations work: capacity and speed. They provide capacity to IT teams as citizen developers can take on many of the backlog requirements that ordinarily an IT specialist or department would need to address. Secondly, citizen developers, as domain experts, have the potential to solve some of an organization's challenges quickly and effectively. The speed at which they can take an idea, then design, build, test, and deploy solutions enables organizations to bring products and services to market in unprecedented time frames.
 | LEARN MORE |
To learn more about The Project Economy, visit:
https://www.PMI.org/The-Project-Economy
As organizations look to leverage citizen development in their digital transformation programs, there are many pitfalls to avoid, including the lack of a comprehensive methodology and framework, and adequate training is required to allow citizen developers to succeed. Central to PMI's goal of enabling successful and sustainable change, this book was written to address the key issues organizations must understand to successfully create value when implementing citizen development.
 | DEFINITION |
No code
No-code development platforms allow programmers and nonprogrammers to create application software through graphical user interfaces and configuration instead of traditional computer programming (“No-Code Development Platform,” 2020).
Low code
Low-code development platforms may call for limited amounts of coding, requiring nontechnical users to work together with developers during some or all of the development process (Tobin, 2020).
Who Is This Book For?
At its core, this book is for anyone looking to convert ideas into reality, with larger organizations more likely to benefit most from the transformative potential of citizen development. Specifically, this book is for individuals and managers who see opportunities to change and improve their own work, how teams and departments around them work, and how the organization operates and serves its customers, where speed and time to market are the driving forces.
This book is relevant to all employees within an organization, whether they are process experts, business analysts, operational subject matter experts (SMEs), hired consultants, project and program managers, IT specialists, architects, C-suite executives, or students leaving the world of education for the job market. It is ultimately a book for anyone who is involved in citizen development in a large organizational setting, regardless of whether they are developing the applications themselves or facilitating the development.
There are three main groups that make citizen development possible: practitioners, architects, and strategists. While the content of this book is predominantly aimed toward citizen developer practitioners and architects, it will also prove to be a useful reference guide for strategists. In Table 1, we define these three groups and the typical roles they may fill in an organization.
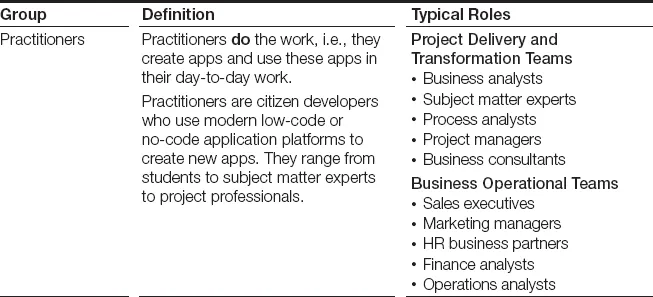
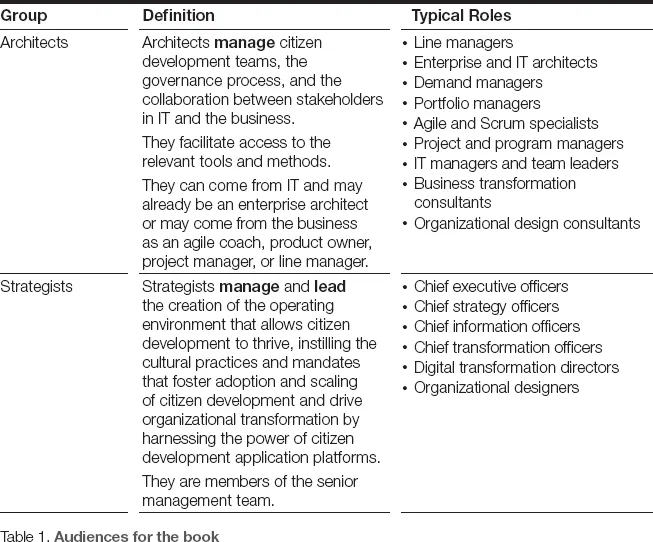
We introduce key concepts and provide a framework and methodology that will guide individuals and managers through a set of steps to successfully introduce citizen development into an organization, build capability to scale, and create a culture of citizen development innovation.
Not only will this book help citizen development projects deliver tangible outcomes, it will also support the business community in safely developing business applications, giving rise to a significant increase in an organization's capacity to transform digitally.
What Is a Citizen Developer?
 | DEFINITION |
Citizen developer
A citizen developer is someone who can build applications without coding knowledge, but usually with the support of IT.
For the purpose of our definition, we use the words citizen developer and citizen developer practitioner interchangeably throughout the book.
Follow the link to see a short synopsis video on what a citizen developer is:
https://www.PMI.org/citizen-developer
Citizen developers tend to be domain experts who have a deep understanding of a business process or a series of tasks performed in the organization. They are therefore very well placed to identify new opportunities that improve operational efficiency or allow the business to better serve its customers.
Citizen developers come from all walks of life. They could be sales executives who feel they can spend much more time with their customers if the administrative tools were easier to use. Or they could be payroll administrators who want to reduce the number of manual steps and interactions with the employees when approving expenses. They could also be externally hired consultants who have been brought in to support the organization in its digital transformation. A key common aspect is that citizen developers are people who are willing to make the change, to create the solutions that they, their team, their department, or their customers need.
Citizen developers have been around for some time. In the past, they were the people who made a difference by building macros in spreadsheets using Visual Basic for Applications (VBA) or who identified ways to improve their work and the work of others. Arguably, from an IT perspective, these people caused all sorts of problems. They introduced risky, unsupported, and often poorly designed applications that lacked any standard or control. In doing so, they created operational risk, key-person dependency, and fueled the creation of what has come to be known as “shadow IT” (an unsupported and unsanctioned IT).
 | DEFINITION |
Shadow IT
The use of information technology systems, devices, software applications, and services without explicit IT department approval. It has grown exponentially in recent years with the adoption of cloud-based applications and services (Forcepoint, n.d.).
In our rapidly changing business and technology landscape, organizations must constantly evolve to maintain relevance. IT departments are tasked with the responsibility of delivering business change; however, with the increasing demand for software and training, IT departments have limited ability to cope with this ever-expanding backlog of wants and needs. Approximately 79% of IT leaders and decision makers agree that they are under a constant source of pressure to manage this (Project Management Institute, 2020), while being able to “keep the lights on” and ensure the existing IT estate continues to function alongside the higher demand. IT also has to deal with limited budgets in addition to increasingly scarce and in-demand skilled technical specialists. One consequence of this inability to deliver is the emergence and growing reliance of shadow IT, which is the result of business owners and stakeholders reaching for other options to address their challenges ...