
eBook - ePub
Artificial Intelligence for Medicine
People, Society, Pharmaceuticals, and Medical Materials
- 520 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
Artificial Intelligence for Medicine
People, Society, Pharmaceuticals, and Medical Materials
About this book
The use of artificial intelligence (AI) in various fields is of major importance to improve the use of resourses and time. This book provides an analysis of how AI is used in both the medical field and beyond. Topics that will be covered are bioinformatics, biostatistics, dentistry, diagnosis and prognosis, smart materials, and drug discovery as they intersect with AI. Also, an outlook of the future of an AI-assisted society will be explored.
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription.
No, books cannot be downloaded as external files, such as PDFs, for use outside of Perlego. However, you can download books within the Perlego app for offline reading on mobile or tablet. Learn more here.
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 1000+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn more here.
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more here.
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS or Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Yes, you can access Artificial Intelligence for Medicine by Yoshiki Oshida in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Technology & Engineering & Artificial Intelligence (AI) & Semantics. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.
Information
Edition
1Chapter 1 AI in general
1.1 Undefined definition
Air conditioner, cleaner, laundry machine, or many other home appliances are nowadays in market under advertisement of “AI-installed xxx.” Unfortunately, technologies involved in these devices and equipment are not artificial intelligence (AI), rather system engineering or control engineering which has a longer technological history than AI. At the same time, AI is well known to be used in various places such as automatic driving to avoid obstacles, smartphone speech recognition by smartphone, Internet image search, web page search, robot control, or image processing in the industrial field. Besides the term “AI-installed,” there are other terms such as “AI-assisted,” “AI-involved,” “AI-enriched,” or “AI-powered.” Although it can be said that a simple and fundamental concept commonly found in these terms is a mimicking slice(s) of human intelligence and/or behavior. If the definition of AI is asked, it would not be surprised to find that the term “artificial intelligence” is not clearly defined. It refers to a very large category, depending on the position. Being similar to variable definitions of the phenomenological term “engineering fatigue” [1], the definition of intelligence is not clear, so the term “artificial intelligence” cannot be clearly defined and should differ, depending on an area of expertise and position. There is a variety of definitions as follows [2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]: AI is comprehended as a mechanism or system, a computer or computer program, or others. When AI is considered as a mechanism or system, it can be defined as (i) an artificially created human intelligence, (ii) a mechanism with intelligence or a mechanism with a heart, (iii) a system that simulates human brain activity to the limit, (iv) an artificially created intelligent behavior (or system), (iv) a compositional system for imitating, supporting, and transcending human intellectual behavior, (v) a system that can artificially create emotional, (vi) a system that simulates human brain activity to the limit, (vii) concepts and techniques for artificially mimicking human intelligence, or (viii) an artificial system centered on computers that enables highly intelligent tasks and judgments that only humans can do. When AI is considered as a computer or computer program, it can be defined as (i) basically advanced computer programs which can think, learn and decide like humans while considering all the scenarios of a given situation, these programs are then used in all the places like smartphones, robots and all, (ii) natural intelligence (NI) reproduced on a computer, (iii) a computer with human-like intelligence, (iv) the science and technology of making intelligent machines, especially intelligent computer programs, (v) the concept of “computing” and “a branch of computer science” that studies “intelligence” using a tool called “computer,” (vi) research on the design and realization of intelligent information processing systems using computers, or (vii) a broad area of computer science that makes machines seem like they have human intelligence. It can be also defined as (i) an artificially made intelligence but imagines that the level of intelligence is beyond human beings, or (ii) an engineering-made intelligence that imagines that the level of intelligence is beyond human beings [2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]. In my opinion, as far as current AI technology is concerned, AI is an extension of “my world” and can only be handled in principle within the expected range; hence, it is the AI to ignore the thing coming from the other side which is not perceived.
1.2 History of AI development and future
Since the word AI was introduced, there were three booms and two winter seasons in-between, and currently we are entering the third boom, as illustrated in Figure 1.1 [10, 11].
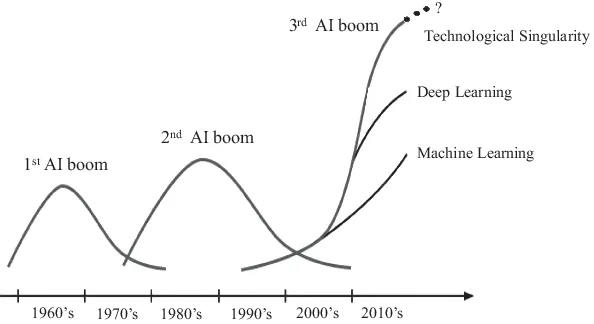
Figure 1.1: Brief history of AI development [10, 11].
The first boom (or generation) of AI can be characterized by reasoning and heuristic search. It was a time when the word “Artificial Intelligence” was born and people’s expectations for computers increased. During this period, research was under way to make computers reason and explore with the aim of complementing and extending people’s functions. AI, at that time, was just a program, it worked only in restricted areas, and it could only be set by the developer. There was the second boom, typified by knowledge expression. In the 1980s, a system called “Expert System (ES)” was proposed to complement the knowledge of people. An ES is a way to accumulate expert knowledge so that anyone can gain the same knowledge as an expert. In order to run the ES successfully, it was necessary to clearly define common-sense expressions that can be understood by human beings and teach them to the system. However, there should be immeasurable numbers of common-sense expressions. In addition, there are differences depending on the context and background, so if these are included, it would be needed to define a huge amount of knowledge. Accordingly, it would be a big cost and the effort to classify the collected data correctly and make it usable in the system was also very large. As a result, the ES with high expectations shrunk [10, 11].
A period since 2012 (the third boom of AI development) started with ML (machine learning) and further characterized by DL (deep learning). The problem with the second AI boom was that humans collected data to be input to the system and judged whether or not humans were lying. It was not realistic to prepare all the necessary data in advance and make a correct decision on success or failure. To solve this problem, there were ML, ICT (information and communication technology) and IoT (Internet of things). ML is a way to get machines to learn, and it learns automatically just by giving data to AI. In addition, the Internet makes it easier to obtain huge amounts...
Table of contents
- Title Page
- Copyright
- Contents
- Preface
- List of abbreviations
- About the Author
- Chapter 1 AI in general
- Chapter 2 AI in information
- Chapter 3 AI in society
- Chapter 4 AI in concern
- Chapter 5 AI in life: from cradle to grave
- Chapter 6 AI in QOL (quality of living), QOS (quality of sleeping), and QOD (quality of dying)
- Chapter 7 AI in food industry
- Coffee break: information diabetes
- Chapter 8 AI in practice of medicine
- Chapter 9 AI in practice of dentistry
- Chapter 10 AI in drug development
- Chapter 11 AI in materials science and development
- Chapter 12 AI in COVID-19 era, infodemic, and post-COVID-19 era
- Chapter 13 AI in future
- Closing remarks
- Index